Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Symptoms of low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, include dizziness, sweating, and confusion. Treatment typically involves consuming 15-20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates.
Experiencing low blood sugar can be unsettling and dangerous if not promptly addressed. It strikes when your blood glucose dips below normal levels, triggering an array of symptoms that your body uses to signal distress. Recognizing these signs is crucial; they serve as a warning to take immediate action to restore balance.
For those managing conditions like diabetes, understanding hypoglycemia is essential, as the risk of occurrence can be higher. The first line of defense against this drop in sugar levels is to consume quick-absorbing sugars, such as fruit juice or glucose tablets, followed by a longer-acting carbohydrate to stabilize your glucose. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and carrying emergency snacks can be life-saving practices for those susceptible to hypoglycemia.
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Recognizing the signs of low blood sugar is crucial for timely management. Symptoms such as dizziness, sweating, and confusion demand immediate treatment, ranging from consuming quick-absorbing glucose to medical intervention. Addressing hypoglycemia promptly restores balance and prevents complications.
Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is crucial to your overall health and well-being. Sudden dips can lead to hypoglycemia—a condition that’s as concerning as it is common. Whether you’re managing diabetes or simply curious about the quirks of your body’s internal chemistry, understanding the nuances of low blood sugar is vital.
Characterized by a plunge in blood glucose levels, hypoglycemia can be more than just a temporary inconvenience—it can disrupt your daily life. Your body thrives on a steady supply of sugar to fuel your cells, especially the brain. When levels fall too low, your body signals distress, with symptoms that can range from mild to severe.
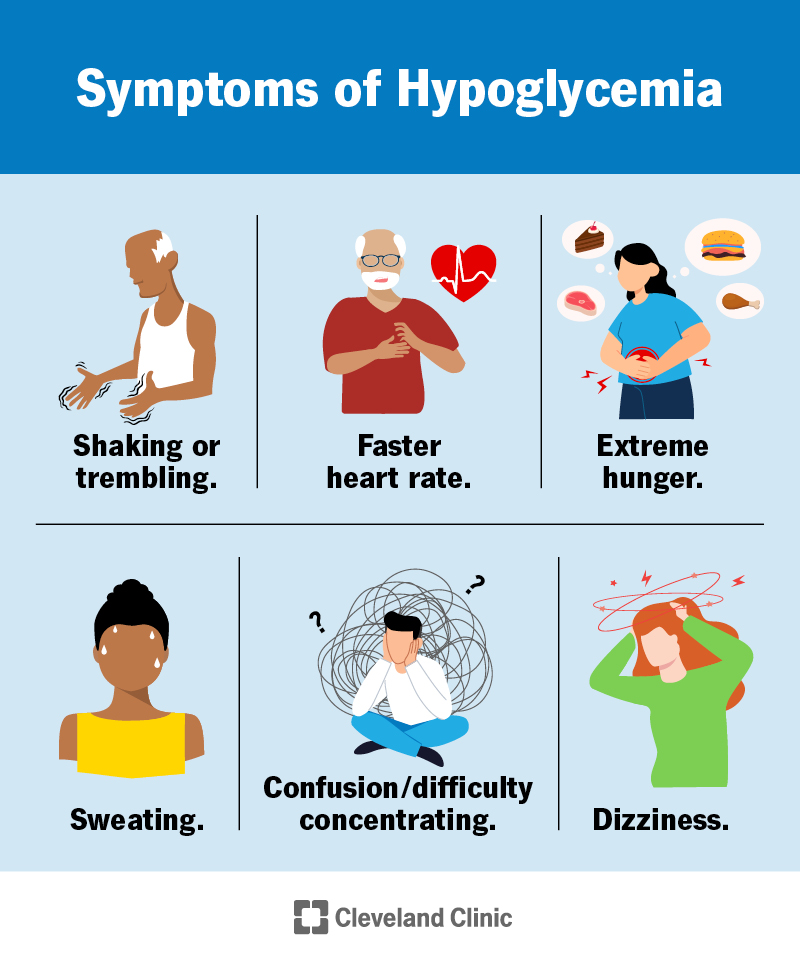
Let’s get down to the specifics of spotting hypoglycemia. Bear in mind, that each body is a universe of its own, and symptoms can vary widely. Here are common indicators:
Each symptom is your body’s way of sounding the alarm. Staying vigilant to these signs is the first line of defense.
Not every sugar slump requires a doctor’s visit, but there are red flags that should prompt immediate medical attention. Here’s when making that call is non-negotiable:
When it comes to hypoglycemia, erring on the side of caution is always the best approach.
Addressing mild cases of hypoglycemia often involves quick dietary fixes. Let’s look at how to nudge those sugar levels back to normal:
The goal is not just immediate recovery but preventing future episodes by knowing what to do and when to do it.
While treatment is important, prevention is key to minimizing hypoglycemic events. Follow these guidelines to reduce risk:
By integrating smart lifestyle choices with a thorough understanding of your health needs, you can keep hypoglycemia at bay.
Navigating the intricacies of low blood sugar is essential not only for those with diabetes but for anyone interested in supporting their health. With knowledge as your ally and prevention as your strategy, hypoglycemia can be managed effectively, allowing you to lead a healthy, energetic life.
Experiencing dizziness, sweating, and a sudden onset of fatigue may signal low blood sugar levels. Promptly treating these symptoms with quick-acting glucose can help restore balance, as part of a comprehensive management strategy for hypoglycemia.
Experiencing a sudden drop in blood sugar levels can be a disconcerting experience, often catching individuals off guard. Low blood sugar, medically known as hypoglycemia, can manifest through various symptoms that shouldn’t be ignored. Recognizing these signs can be the first crucial step toward managing and treating the condition effectively.
Engaging with these symptoms promptly and understanding their implications can make all the difference. It’s crucial to not only recognize the signs but also to know how to react when they occur.
When blood sugar dips too low, it’s essential to address the issue swiftly to avoid complications. The primary goal in treating hypoglycemia is to raise the blood glucose to a normal range. Below are some of the immediate steps and longer-term strategies one can employ to mitigate the risks associated with low blood sugar:
It’s standard practice to initially consume 15-20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or high-sugar foods, to quickly elevate blood sugar levels. Following up with a meal or snack that includes proteins and more complex carbohydrates ensures a steady blood glucose level.
For persistent hypoglycemia or cases that do not respond to dietary changes, medical professionals might recommend medications or alterations to existing treatment plans for those with underlying conditions such as diabetes.
Diligent monitoring of blood sugar levels is critical for those at risk, as it allows for timely adjustments to diet, activity levels, and medication. Education on how to manage blood sugar effectively, including planning meals and understanding how different activities influence glucose levels, is also an essential aspect of treatment.
In certain situations, a doctor may advise wearing a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to keep constant tabs on glucose fluctuations.
By taking proactive measures and seeking medical advice when necessary, individuals can manage low blood sugar symptoms and maintain a better quality of life.
Experiencing symptoms such as dizziness, sweating, and sudden fatigue can signal low blood sugar, a condition requiring prompt attention. Effective treatment includes consuming quick-absorbing sugars, followed by a balanced meal to stabilize glucose levels and safeguard physical health.
Experiencing symptoms of low blood sugar, medically termed hypoglycemia, strikes without warning, and understanding its impact is crucial for prompt intervention. Hypoglycemia affects daily activities and can cause serious health concerns if left untreated.
When blood sugar levels drop below normal, the body signals distress. Recognize these immediate effects:
These symptoms demand swift attention to prevent further decline.
Sustained low blood sugar situations might culminate in severe health problems. Maintaining sugar levels is not only critical short-term but a vital component of your long-term well-being. Persistent hypoglycemia can be a harbinger of worse conditions, such as neurological damage or cardiovascular disease.
To combat low blood sugar, a measured approach to treatment is indispensable:
Following these steps can improve management and reduce the occurrence of hypoglycemia.
Awareness and education are your armor against the risks associated with hypoglycemia. Not only is it key for the individual, but it also equips loved ones to act effectively during an episode. Knowledge about symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies is potent in managing this condition.
Share, learn, and engage about hypoglycemia to foster a supportive environment for those affected.
Cognitive symptoms of hypoglycemia, a critical feature of low blood sugar, often manifest as confusion and difficulty concentrating. Immediate treatment with fast-acting glucose can alleviate these disconcerting signs.
Hypoglycemia, commonly known as low blood sugar, can manifest in various ways, but its cognitive symptoms can be particularly worrying. These symptoms directly affect mental processes and can disrupt everyday activities. Recognizing them early is essential for prompt treatment.
One notable sign of hypoglycemia is a marked decrease in concentration. This can encompass:
Individuals experiencing low blood sugar might find their memory isn’t as sharp as usual:
Here’s what to watch out for concerning confusion:
Mood changes can be a red flag for hypoglycemia. This includes:
Hypoglycemia can throw people off balance:
Understanding the cognitive symptoms of hypoglycemia is key to managing the condition and preventing more severe health issues. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, please consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment plan. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for cognitive health and general well-being.
Understanding the factors that lead to low blood sugar is crucial for prevention and management. Recognizable low blood sugar symptoms necessitate timely treatment to avoid health complications.
Understanding what triggers low blood sugar and recognizing the risk factors associated with it can help you manage the condition better. Whether you’re living with diabetes or concerned about your health, being informed is essential.
Several factors can cause a dip in blood sugar levels. Identifying these triggers can help you avoid unnecessary episodes:
Low blood sugar doesn’t occur in a vacuum; particular individuals may be more susceptible than others. We’ll explore key risk factors that might increase your chance of experiencing hypoglycemia:
Being aware of these triggers and risk factors is crucial. So frequent monitoring and consultation with healthcare professionals are highly recommended for those at risk of hypoglycemia. Maintain a well-balanced diet, adhere to your medication regimen, and be proactive in managing your health to keep blood sugar levels in check.
Understanding low blood sugar symptoms—such as dizziness, sweating, and confusion—is key to prompt treatment. Adopting prevention strategies, like regular meals and monitoring glucose levels, helps manage risks and maintain optimal health.
Maintaining a stable blood sugar level is critical for health and well-being. Here are practical strategies to prevent episodes of low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia.
Careful meal planning plays a pivotal role in staving off hypoglycemia. Here’s how to keep your blood sugar levels balanced:
Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity but requires smart management to avoid low blood sugar levels.
Being physically active is beneficial, but it’s important to align your exercise regimen with your blood sugar management:
Prescription medications can significantly affect blood sugar levels. It is essential to understand their impact:
Medicines, especially those designed to control diabetes, need careful coordination with diet and exercise to prevent low blood sugar episodes:
Knowledge is power, especially when dealing with conditions like hypoglycemia:
Educating yourself about the signs of low blood sugar and how to manage them can make a big difference:
Preventing low blood sugar is about creating a lifestyle that supports balance and awareness. By implementing these proactive strategies, individuals can minimize the risk of hypoglycemia and maintain optimal health.
Recognizing low blood sugar symptoms early, such as dizziness and sweating, is crucial for prompt treatment. Quick-acting glucose sources like fruit juice or glucose tablets effectively counter hypoglycemic episodes, ensuring swift recovery and stabilization.
A sharp drop in blood sugar levels can quickly escalate into a hypoglycemic crisis, a condition that requires immediate attention. Symptoms such as confusion, seizures, or loss of consciousness signal that the body is in urgent need of glucose.
If the individual is conscious and able to swallow, provide a fast-acting source of sugar without delay. This could include:
Sometimes, despite initial efforts, symptoms can persist or worsen. It’s critical to understand:
For instances where sugar intake isn’t feasible due to unconsciousness, an emergency glucagon injection might be the lifesaver. Here are the key points to keep in mind:
Post-crisis, it’s essential to stabilize the individual’s blood sugar to prevent recurrence. This entails:
Technological advancements have introduced CGM devices that track glucose levels round the clock. Their significance includes:
Experiencing shaky hands, dizziness, or fatigue could signal low blood sugar levels. Explore effective treatments ranging from dietary adjustments to medical interventions tailored to manage and alleviate symptoms promptly and safely.
Recognizing the signs of low blood sugar can be a significant first step toward maintaining consistent glucose levels. Addressing hypoglycemia promptly is essential to prevent serious health complications. Now, let’s take a closer look at the treatment options available for managing this condition.
In cases where blood sugar levels drop quickly, the priority is to return them to normal as soon as possible. Standard first-aid treatment for low blood sugar involves:
Steady control of blood glucose levels is crucial for minimizing the risks of hypoglycemia. This strategy often combines lifestyle modifications with regular medical check-ups, including:
By implementing a tailored treatment plan that involves both immediate and long-term strategies, individuals with low blood sugar can lead a healthy and active life. Constant monitoring and adjustments ensure the best defense against the disruptions of hypoglycemia.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices offer real-time insights for managing low blood sugar symptoms. They alert users to potential hypoglycemia, facilitating prompt and effective treatment.
Hypoglycemia, commonly referred to as low blood sugar, is a condition that can prompt an array of symptoms. These symptoms, often ranging from mild to severe, necessitate prompt recognition and treatment. Recognizing the signs early is crucial to manage and prevent the potentially serious consequences that can arise if the condition is left untreated.
Hypoglycemia can manifest through a variety of indicators, each signaling the need for immediate attention:
Continuous glucose monitoring is a revolutionary step towards managing blood sugar levels proactively. By providing real-time blood sugar readings, it empowers individuals to maintain better control over their glucose levels.
When it comes to treating low blood sugar, timing and appropriate action are critical. A methodical approach can quickly restore normal glucose levels:
Optimizing long-term blood sugar control means incorporating healthy routines and understanding one’s body:
Understanding low blood sugar symptoms is crucial for timely treatment and prevention. Effective management often involves lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, to maintain healthy glucose levels.
Understanding the symptoms of low blood sugar is just the beginning. It’s essential to delve into effective strategies for managing hypoglycemia in the long term. Making lifestyle modifications can significantly lower the chances of future episodes and contribute to overall well-being.
Staying vigilant about your blood sugar is a crucial step in preventing hypoglycemic incidents:
What you eat plays a pivotal role in controlling blood sugar:
Exercise impacts blood sugar, and managing it requires a thoughtful approach:
Medications can prevent fluctuations in blood sugar levels when managed correctly:
Stress can affect blood sugar, making it important to find ways to relax:
By integrating these management practices into everyday life, individuals with a tendency for low blood sugar can create a stable and healthy routine. Remember, everyone’s body is unique, so work with healthcare professionals to tailor these suggestions to your personal needs.

Credit: www.ucsfhealth.org
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, often triggers symptoms like dizziness, sweating, shakiness, and confusion. Prompt recognition of these signs is critical to manage the condition effectively.
Treating hypoglycemia involves consuming fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets, candy, or juice. It’s essential to recheck blood sugar levels after 15 minutes and eat a snack if it remains low.
Yes, hypoglycemia can occur during sleep. Symptoms may include night sweats, nightmares, or waking up feeling tired and disoriented. It’s important to maintain a regular bedtime snack routine if advised by a healthcare professional.
Preventive measures for hypoglycemia include regular blood sugar monitoring, consuming balanced meals, and adjusting medication or insulin doses as directed by a healthcare provider. Consistency is the key to prevention.
Recognizing the signs of low blood sugar is crucial for prompt action. Through balanced meals, regular monitoring, and medical guidance, managing hypoglycemia becomes manageable. Stay informed, be prepared, and consult your healthcare provider to tailor a treatment plan that’s right for you.
Your well-being hinges on proactive blood sugar management.

