Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Groin strain is typically caused by sudden movements or overexertion and can be treated with rest, ice, compression, and elevation, along with physical therapy. To prevent groin strain, it’s important to warm up properly before exercising and to maintain flexibility in the groin area.
Additionally, strengthening the muscles around the groin can help reduce the risk of strain. Understanding the common causes, effective treatment options, and preventive measures for groin strain is essential for promoting overall muscle health and preventing future injuries. This article provides comprehensive information on groin strain, empowering readers to take proactive steps in managing and preventing this common injury.
Groin strain can occur due to sudden movements or overuse. Treatment includes rest, ice, and physical therapy. To prevent groin strain, warm up properly before physical activity and strengthen muscles in the area.
Understanding Groin Strain Groin strain, also known as a groin pull, is a common injury that occurs when the muscles in the groin are overstretched or torn. It is a painful condition that can interfere with daily activities and physical performance. This type of injury most commonly occurs in athletes who participate in sports that involve sprinting, jumping, and sudden changes in direction. However, it can also affect non-athletes who engage in activities that put stress on the groin muscles. Definition of Groin Strain A groin strain is a muscular injury that affects the adductor muscles located on the inside of the thigh. This injury can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, depending on the extent of the strain. It can also lead to swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the affected leg. Groin strains are categorized into three grades based on their severity, with grade 1 being mild and grade 3 being severe. Common Causes 1. Overexertion: Engaging in activities that require sudden explosive movements or excessive force can strain the groin muscles. 2. Lack of Warm-Up: Failing to properly warm up before physical activity can increase the risk of groin strain. 3. Muscle Imbalance: Weakness or imbalance between the adductor and abductor muscles in the inner and outer thigh can contribute to groin strain. 4. Previous Injury: A history of groin or hip injuries can make an individual more susceptible to experiencing a groin strain. 5. Poor Technique: Performing movements with improper form and technique can strain the groin muscles. When dealing with groin strain, timely treatment and preventive measures are crucial for a full recovery and reducing the risk of recurring injuries. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive strategies associated with groin strain, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves from this common injury.
Credit: www.hingehealth.com
For effective treatment options for a groin strain, a combination of rest, ice, compression, and elevation can help reduce pain and swelling. Additionally, physical therapy and exercises to strengthen the muscles can aid in recovery and prevention of future injuries.
Proper warm-up and stretching before physical activity are essential to avoid future groin strains.
Effective treatment options for groin strain aim to reduce pain, inflammation, and promote healing to restore full function. The RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), physical therapy exercises, and other interventions can significantly aid in the recovery process.Preventing groin strain involves proper warm-up, stretching, and strengthening exercises. Adequate rest and gradual increase in physical activity can also help. Avoiding sudden movements and using appropriate protective gear during sports activities are essential preventive measures.
Proper warm-up and stretching are crucial before any physical activity.Discover effective medical interventions for groin strain: learn about causes, treatments, and preventive measures to ensure optimal recovery. Professional care can expedite healing and aid in preventing future strain occurrences. Prioritize your health with expert guidance on managing groin strain effectively.
When it comes to managing groin strains, professional medical interventions play a crucial role in ensuring a proper diagnosis, effective treatment, and successful recovery. Consulting a physician should be the first step in addressing this injury. Depending on the severity of the strain and the individual’s specific circumstances, there are various treatment options available, ranging from conservative approaches to surgical interventions.Recovery and Rehabilitation play a crucial role in effectively managing groin strain injuries. While treatment methods provide immediate relief, the recovery and rehabilitation process focuses on regaining strength, flexibility, and functionality. It is essential to follow a well-structured rehabilitation timeline and take necessary precautions during the recovery phase to ensure a safe and speedy recovery.
The rehabilitation timeline for groin strain injuries varies depending on the severity. However, a general guideline can be followed to aid in the recovery process:
During the recovery period, it is important to take certain precautions to prevent further injury and aid in the healing process:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diagnosing-and-treating-groin-pulls-exercises-and-tips-4142070-01-53b64345955f4afc8c1dcc087714dfcc.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
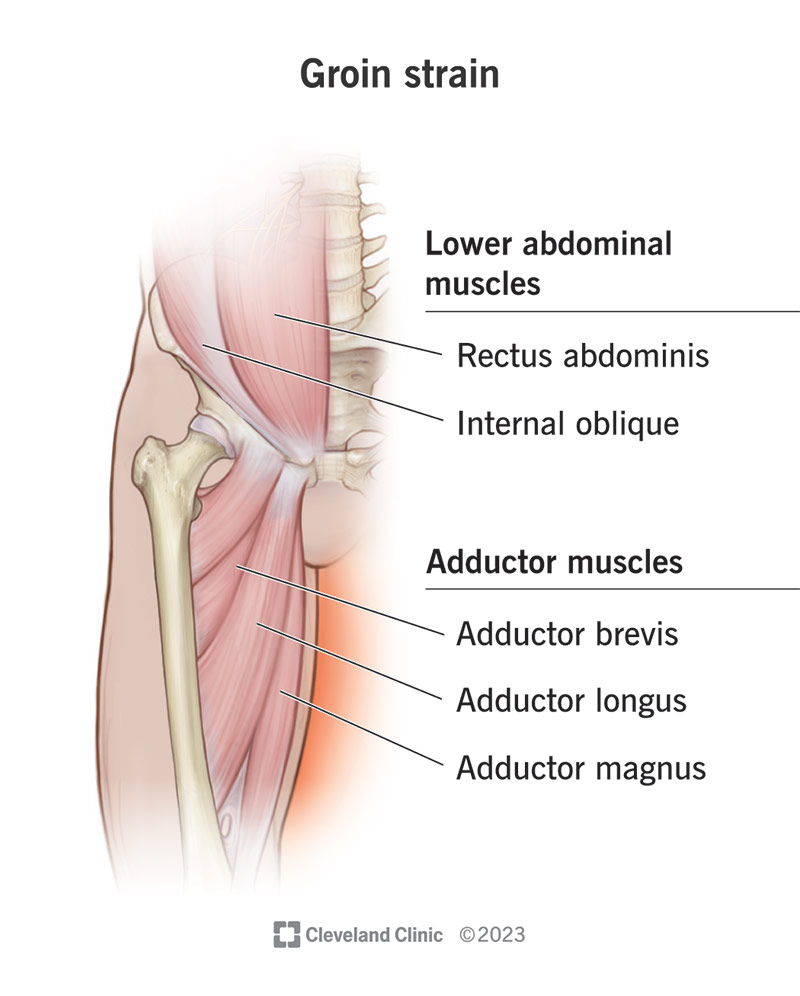
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
The most common cause of groin strain is overuse or excessive stress on the muscles and tendons in the groin area. This can happen during activities that involve repetitive movements, sudden twisting, or high-impact sports.
The fastest way to heal a pulled groin is to rest, apply ice for 20 minutes every hour, compress the area with a wrap, and elevate the leg. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may also help. Gradually stretch and strengthen the muscles once pain subsides.
Seek medical attention if symptoms worsen.
Overuse, sudden movements, lack of warm-up, and poor flexibility can aggravate a groin strain. It’s important to rest and seek proper treatment when experiencing discomfort.
Hip flexor strain or sports hernia can be mistaken for a pulled groin. Symptoms and location of the pain are similar. A thorough physical examination and possibly imaging tests may be needed for an accurate diagnosis.
Being diligent in preventing groin strains is crucial for physical well-being. Always warm up before exercise, stretch, and utilize proper techniques. Early treatment with rest and ice can speed up recovery. Listen to your body and seek professional help if needed.
Overall, proactive care is key to minimizing groin strain risk.

