Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Kidney disease refers to a long-term condition affecting the kidneys, while kidney damage generally refers to an injury or impairment of the kidneys, which may be reversible. Kidney disease often leads to permanent damage, affecting the organ’s function over time, whereas kidney damage may be caused by various factors, such as infections or certain medications.
The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, regulating blood pressure, and producing hormones. When these functions are compromised, it can lead to various complications. Understanding the key differences between kidney disease and kidney damage is important for early detection, proper management, and the prevention of further progression.
Being aware of the symptoms and risk factors associated with these conditions can help individuals take proactive steps in maintaining their kidney health.

Credit: www.nature.com
Long-term, uncontrolled high blood pressure and diabetes are the leading causes of kidney disease.
Various factors can lead to kidney damage, including:
Symptoms of kidney disease and kidney damage can be subtle, often manifesting in different ways. It’s important to understand the distinguishing signs to seek timely medical intervention.
The symptoms of kidney disease include:
The signs of kidney damage may include:
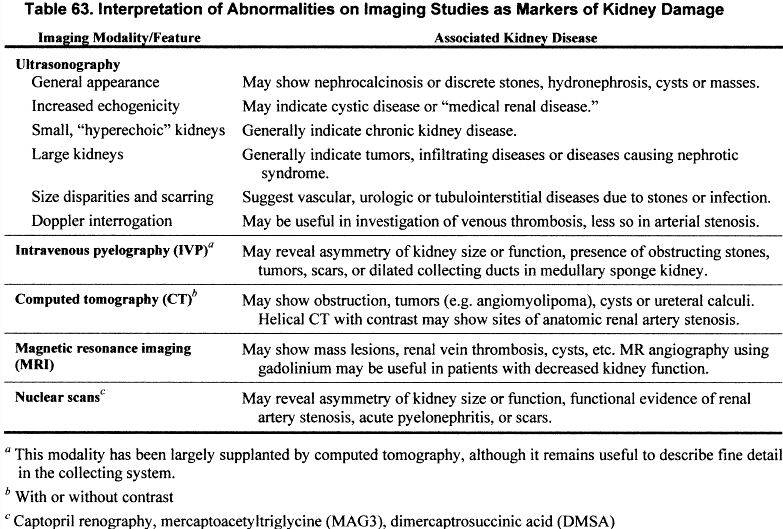
Diagnosing kidney disease and kidney damage involves specific testing and diagnostic methods.
Testing for kidney disease focuses on assessing the function of the kidneys through different methods.
Determining kidney damage often involves specific diagnostic approaches.
When it comes to managing kidney disease and kidney damage, the treatment options can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Approaches for managing kidney disease focus on slowing down the progression of the disease, while therapies for kidney damage aim to restore normal kidney function.
When dealing with kidney disease, there are several approaches that can be taken to help manage the condition:
When kidney damage occurs, there are various therapies available to help restore normal kidney function:
In conclusion, while managing kidney disease focuses on slowing down its progression, therapies for kidney damage aim to restore normal kidney function. Whether it involves dietary changes, medication, or more advanced therapies such as dialysis or transplant, early diagnosis and intervention are vital in enhancing the quality of life for individuals with kidney disease and kidney damage.
Kidney disease and kidney damage are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. Kidney disease refers to a long-term condition, while kidney damage may be acute or chronic. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Kidney disease, also known as renal disease, refers to a condition where the kidneys are not functioning properly. When left untreated or poorly managed, it can lead to various complications that can significantly impact one’s health and quality of life.
One potential complication of kidney disease is fluid retention. The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating fluid balance in the body. When the kidneys are damaged, they may not be able to remove excess fluid, leading to edema or swelling in the legs, ankles, and other parts of the body.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is another common complication of kidney disease. The kidneys help regulate blood pressure by controlling the amount of fluid and minerals in the body. When the kidneys are damaged, this regulation becomes impaired, leading to elevated blood pressure levels.
In addition, kidney disease can also result in anemia. The kidneys produce a hormone called erythropoietin, which stimulates the production of red blood cells. When the kidneys are not functioning properly, erythropoietin production decreases, leading to decreased red blood cell production and anemia.
Another potential complication is bone disease. The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining bone health by regulating minerals such as calcium and phosphorus. When the kidneys are damaged, there can be an imbalance in these minerals, leading to bone loss and an increased risk of fractures.
Kidney damage, also known as renal damage, refers to physical injury or harm to the kidneys. There are several factors that can contribute to kidney damage, and understanding these risks is essential to prevent or manage the condition effectively.
One of the primary risks associated with kidney damage is chronic usage of certain medications. Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and certain antibiotics can cause kidney damage, especially when taken in high doses or over an extended period.
Another risk factor for kidney damage is uncontrolled diabetes. Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease globally, and high blood glucose levels can directly damage the kidneys over time. Monitoring blood sugar levels and managing diabetes effectively is crucial to prevent kidney damage.
High blood pressure is also a significant risk factor for kidney damage. Persistently elevated blood pressure can strain the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to damage over time. Regular blood pressure monitoring and appropriate management are essential to protect kidney health.
Additionally, chronic urinary tract infections (UTIs) can increase the risk of kidney damage. Frequent or untreated UTIs can lead to kidney infections, which can cause inflammation and damage to the kidneys. Prompt treatment of UTIs is vital to prevent complications.
Obesity is another risk factor for kidney damage. Excess weight puts additional pressure on the kidneys and can contribute to the development of kidney disease. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce the risk of kidney damage.
In conclusion, both kidney disease and kidney damage can lead to various complications that significantly impact an individual’s health and well-being. Understanding these potential complications and associated risks is crucial for early detection, prevention, and effective management of kidney-related conditions. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, monitoring blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and seeking timely medical care, individuals can reduce the risk of kidney complications and maintain optimal kidney health.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Kidney disease refers to a chronic condition with the kidney’s reduced function, while kidney damage denotes an acute injury that impacts kidney function. Understanding the difference crucially affects treatment and management strategies to prevent further deterioration. Regular check-ups and lifestyle adjustments are essential for maintaining kidney health.
Kidney disease can often be prevented through lifestyle changes such as eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise.
To prevent kidney damage, it is crucial to monitor blood sugar levels and maintain healthy blood pressure.
Kidney disease and kidney damage can be avoided by following a healthy lifestyle and undergoing regular medical check-ups.
Kidney disease refers to a condition where the kidneys are unable to properly filter waste and excess fluid from the blood. On the other hand, kidney damage refers to any injury or harm caused to the kidneys due to various factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, or certain medications.
Both conditions can lead to kidney failure if left untreated.
Understanding the disparities between kidney disease and kidney damage is crucial for early detection. Proper knowledge empowers individuals to take necessary steps for their kidney health. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can help prevent complications and maintain kidney function.
Stay informed and prioritize your well-being.