Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 is a chronic condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin. This leads to high blood sugar levels.
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 is a prevalent metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance in the body. It results in elevated blood glucose levels, causing various health complications. This condition often develops in adulthood, affecting the body’s ability to regulate sugar properly.
Lifestyle factors like diet and exercise play a crucial role in managing Type 2 diabetes. Proper treatment and monitoring are essential to prevent complications such as cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, and kidney problems. Understanding and managing this condition effectively can lead to a better quality of life for individuals with Type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 is a condition in which the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin or the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin. Let’s delve into some essential aspects of Type 2 Diabetes.

Credit: www.obesityaction.org
Type 2 diabetes mellitus refers to a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). Recognizing the symptoms and obtaining a timely diagnosis is crucial for effective management of the condition. Below we discuss the Common Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes and the Methods for Diagnosis:
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes involves a series of tests to measure blood sugar levels and assess overall health. Some common methods for diagnosis include:
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Understanding the risk factors that contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes, as well as the potential complications associated with the condition, is crucial for effective management and prevention. By being aware of these factors and complications, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their risk and maintain their overall health.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. These include obesity, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet, family history of the condition, age, ethnicity, and gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
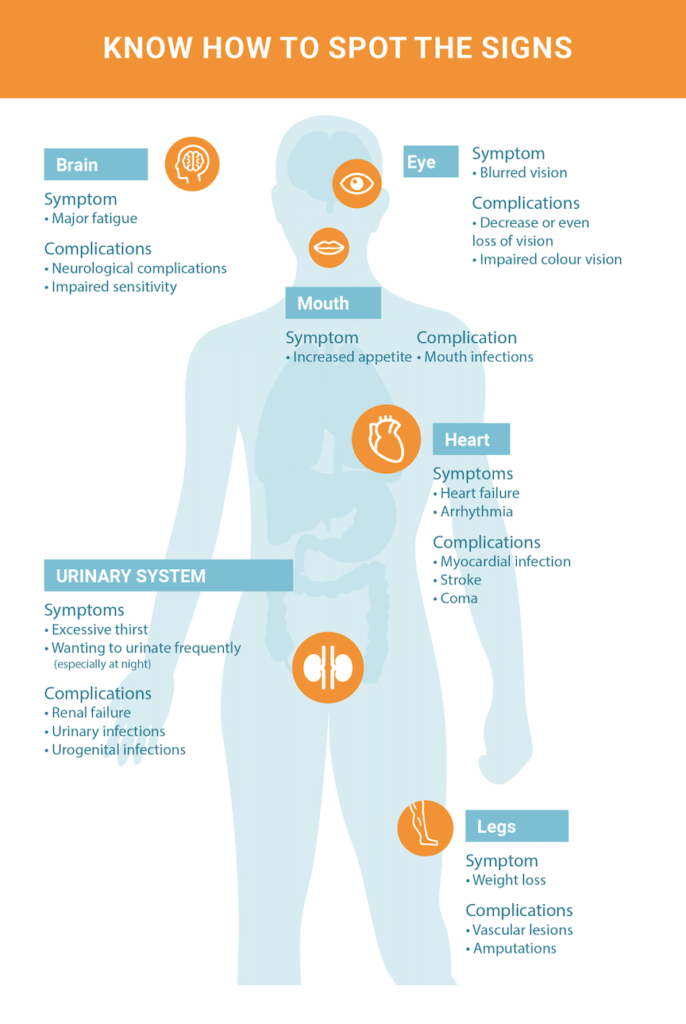
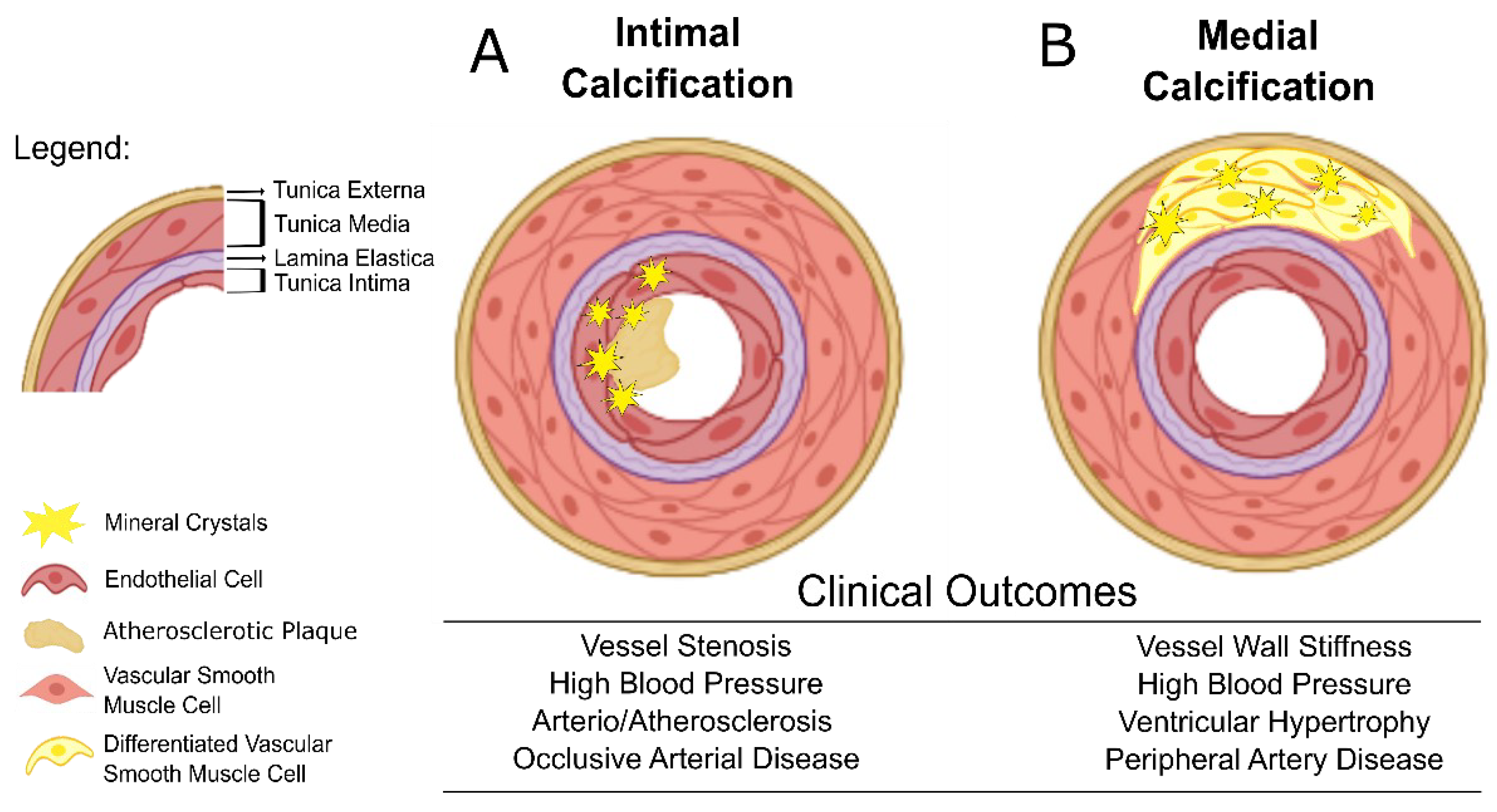
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 can lead to a range of complications that affect various parts of the body. These include cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, eye damage, foot damage, hearing impairment, skin conditions, and a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Credit: servier.com
When it comes to managing diabetes mellitus type 2, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role. Making key changes to your everyday habits can significantly impact your health and help control your blood sugar levels. Two key aspects that contribute to effective lifestyle modifications are diet and nutrition, as well as regular exercise. Let’s delve deeper into the importance of these factors:
Your diet and nutrition are fundamental when it comes to managing diabetes mellitus type 2. By making smart food choices, you can ensure that your body receives the nutrients it needs while keeping your blood sugar levels in check. A balanced diet that is rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps maintain stable blood glucose levels, reduces the risk of heart disease, and aids in weight management. Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
Exercise is not only beneficial for general health, but it also plays a significant role in managing diabetes mellitus type 2. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, helps lower blood sugar levels, and aids in maintaining a healthy weight. Here are some key points to consider when incorporating exercise into your routine:
By making lifestyle modifications, particularly focusing on diet and nutrition, as well as incorporating regular exercise, you can effectively manage diabetes mellitus type 2 and improve your overall well-being. Remember, small changes can make a big difference in your health!
When it comes to managing diabetes mellitus type 2, medical intervention plays a crucial role. Medical management focuses on controlling blood sugar levels and minimizing the complications associated with this chronic condition. Two primary methods of medical management include the use of oral medications and insulin therapy.
Oral medications are often prescribed as the first line of treatment for individuals with type 2 diabetes. These medications work by helping the body use insulin more effectively or by stimulating the pancreas to produce more insulin.
When it comes to oral medications for type 2 diabetes, there are several options available. Some common examples include:
It is important to note that each individual may respond differently to oral medications. Therefore, the choice of medication and dosage may vary based on factors such as the patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and consultation with a healthcare professional are vital in determining the most effective oral medication regimen.
Insulin therapy becomes necessary when oral medications are no longer effective in controlling blood sugar levels. In some cases, individuals may start with insulin therapy right after diagnosis if their blood sugar levels are very high or if they have other medical conditions that warrant immediate intervention.
Insulin therapy involves injecting insulin into the body to compensate for the lack of insulin or the body’s inability to use insulin effectively. There are different types of insulin available, each with its own onset, peak, and duration of action. The choice of insulin type and dosage will depend on factors such as blood sugar levels, lifestyle, and individual needs.
Insulin therapy can be administered through an insulin pen, insulin pump, or insulin injections using a syringe. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and close coordination with a healthcare professional are essential in achieving optimal blood sugar control and avoiding any complications associated with diabetes mellitus type 2.
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 can be managed through prevention strategies. These include maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and monitoring blood sugar levels. By adopting these practices, individuals can reduce their risk of developing the condition and improve their overall health.
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 is a condition that affects how the body uses glucose. Fortunately, there are proven prevention strategies that can help reduce the risk of developing this chronic disease. By focusing on healthy lifestyle choices, screening, and early detection, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent diabetes Type 2.Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 has a significant impact on the quality of life, affecting daily activities and overall well-being. Managing blood sugar levels, diet, and medications are crucial for individuals with this condition to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 can lead to physical challenges such as fatigue and nerve damage.
Emotionally, it can cause stress and anxiety due to the need for constant management.
Managing diabetes can disrupt social activities and relationships.
Increased medical costs and potential job limitations can lead to economic strain.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Raising Awareness and Future Outlook:
Educational programs are crucial in spreading awareness about diabetes mellitus type 2.
Ongoing research is continuously improving treatment options for diabetes type 2.
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a chronic condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to properly regulate blood sugar levels. It is often caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices like poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity.
Common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds. It is important to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include being overweight or obese, physical inactivity, having a family history of diabetes, high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, and age (being over 45 years old). These factors increase the likelihood of developing the condition, but can often be prevented or managed with lifestyle changes.
To diagnose type 2 diabetes, doctors use blood tests to measure the levels of glucose in the blood. These tests include fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT). A diagnosis is made if the blood sugar levels are consistently high and meet the diagnostic criteria established by medical organizations.
Understanding the meaning of diabetes mellitus type 2 is crucial for managing this condition effectively. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, monitoring blood sugar levels, and following a treatment plan, individuals can reduce the risk of complications. Moreover, seeking regular medical care and staying informed about diabetes can empower individuals to live a fulfilling life despite the challenges posed by this chronic condition.