Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Atopic disease in adults is a chronic, inflammatory condition that affects the skin and respiratory system, characterized by symptoms such as itching, redness, and wheezing. This condition can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, causing discomfort and impairing daily activities.
It commonly manifests as atopic dermatitis (eczema), allergic rhinitis (hay fever), or asthma. The exact cause of atopic disease is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While there is no cure for atopic disease, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups.
These may include medications, lifestyle modifications, and avoidance of triggers. Effective management of atopic disease requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals, including dermatologists, allergists, and pulmonologists, to provide comprehensive care and improve the patient’s well-being.
Atopic disease in adults is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including allergens, irritants, stress, and hormonal changes. These triggers can lead to the development and worsening of symptoms such as eczema, asthma, and hay fever. Managing and avoiding these triggers is crucial for maintaining good health and reducing flare-ups.
Atopic disease, also known as atopic dermatitis or eczema, is a chronic condition characterized by itchy and inflamed skin. While the exact cause of atopic disease is still unknown, there are various factors that can contribute to its development and trigger flare-ups. Understanding these causes and triggers is crucial in managing and preventing this condition. In this article, we will explore the environmental factors, genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalance, and stress and emotional factors that play a role in atopic disease.
Environmental factors such as exposure to allergens, irritants, and pollutants can trigger or exacerbate atopic disease. Common allergens include dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold, and certain foods. Irritants like harsh soaps, detergents, and fabrics can also irritate the skin, leading to flare-ups. Additionally, air pollution and changes in temperature and humidity can impact the skin’s barrier function, making it more susceptible to inflammation. It is important to identify and minimize exposure to these environmental triggers to manage atopic disease effectively.
Genetic predisposition is a significant factor in the development of atopic disease. Individuals with a family history of atopic diseases like asthma, hay fever, or eczema are more likely to develop the condition themselves. Specific genes involved in the immune system and skin barrier function have been identified as contributing to the susceptibility to atopic disease. While genetics cannot be changed, understanding your family history can help you take proactive steps in managing the condition.
Hormonal imbalance, particularly during puberty and pregnancy, can influence the occurrence and severity of atopic disease. Fluctuations in hormone levels can disrupt the skin’s natural protective barrier, making it more vulnerable to inflammation and irritants. This may explain why some individuals experience improvement or worsening of symptoms during certain life stages. Taking hormonal changes into account and adjusting skincare routines accordingly can help in managing atopic diseases effectively.
Stress and emotional factors have a direct impact on the immune system and can trigger or worsen atopic disease symptoms. High levels of stress can lead to an overactive immune response, causing increased inflammation in the skin. Moreover, anxiety and emotional distress can trigger scratching and rubbing on the affected areas, further aggravating the condition. Developing effective stress management techniques, such as mindful practices and relaxation exercises, can help reduce the frequency and severity of atopic disease flare-ups.
In conclusion, atopic disease is influenced by various causes and triggers. Environmental factors, genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalance, stress, and emotional factors all play a role in the development and exacerbation of the condition. Identifying and addressing these factors in an individualized manner is essential in managing atopic disease effectively, reducing symptoms, and improving the quality of life for those affected.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(2999x0:3001x2)/the-best-eczema-creams-people-tested-tout-c8c122eabacb4830b1445475aab13250.jpg)
Credit: people.com
Atopic disease in adults is characterized by common symptoms such as skin dryness, redness, itching, and inflammation. Other symptoms may include nasal congestion, sneezing, and respiratory issues. It is crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Atopic disease, also known as atopic dermatitis or eczema, is a chronic condition that affects adults. It is characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. Living with atopic disease can be challenging, as the symptoms can vary in severity and frequency. While the specific symptoms may differ from person to person, there are some common signs to look out for.
One of the most prevalent symptoms of atopic disease in adults is a persistent itch. This itchiness can be debilitating and interfere with daily activities and sleep. The constant urge to scratch can further aggravate the skin, leading to increased redness and inflammation. It is important to resist the urge to scratch and manage the itchiness through proper skincare and medical intervention.
Another common symptom of atopic disease in adults is dry and flaky skin. This occurs due to a decreased ability of the skin to retain moisture. The lack of moisture causes the skin to become dehydrated, resulting in a rough and scaly appearance. Dry skin can worsen the itchiness and lead to further inflammation and discomfort. Proper hydration and regular moisturizing can help alleviate this symptom and improve the overall condition of the skin.
Redness and inflammation are hallmark signs of atopic disease in adults. The affected areas of the skin become swollen, tender, and discolored. The redness can vary in intensity and may be accompanied by a burning sensation. Inflammation is the body’s immune response to the presence of triggers or irritants. By identifying and avoiding these triggers, individuals can reduce redness and inflammation and manage their condition effectively.
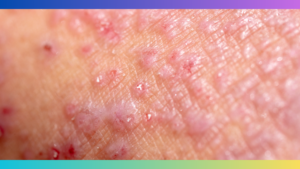
Skin lesions and eczema patches are characteristic symptoms of atopic disease in adults. Eczema refers to the formation of itchy, red, and dry patches on the skin. These patches can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the face, neck, hands, and elbows. Ongoing scratching can lead to the development of skin lesions, which are open sores or crusted areas. It is crucial to seek medical attention to prevent infection and promote the healing of these skin lesions.
In conclusion, atopic disease in adults is associated with various symptoms, including persistent itch, dry and flaky skin, redness and inflammation, and the development of skin lesions and eczema patches. These symptoms can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals with atopic disease. However, with proper skincare, medical intervention, and avoidance of triggers, it is possible to manage the symptoms effectively and improve overall skin health.
Diagnosing atopic disease in adults can be a complex process. Due to the diverse range of symptoms and the potential for coexisting conditions, a comprehensive evaluation is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. This involves a combination of physical examination, patient history, allergy testing, and skin biopsy.
A physical examination plays a critical role in diagnosing atopic disease in adults. During this evaluation, a healthcare professional will carefully assess the patient’s skin, looking for any visible signs of atopic dermatitis, such as redness, swelling, or lesions. Additionally, the examination may involve checking for the presence of other allergic conditions, such as allergic rhinitis or asthma. The physical examination provides valuable insights into the overall manifestation of atopic disease and helps guide the subsequent diagnostic approach.
Obtaining a detailed patient history is essential in diagnosing atopic disease. The healthcare provider will ask the patient about their symptoms when they started, and how they have progressed over time. Additionally, they may inquire about any triggers that worsen or alleviate symptoms. This comprehensive understanding of the patient’s medical history enables the healthcare professional to identify patterns, and potential triggers, and distinguish atopic disease from other similar conditions. Therefore, patients must provide accurate and thorough information during the consultation.
Allergy testing is another valuable tool in the diagnostic process of atopic disease in adults. This type of testing helps identify specific allergens that may be contributing to the symptoms. There are various methods for allergy testing, including skin prick tests, blood tests, and patch tests. Skin prick tests involve exposing the skin to small amounts of common allergens and observing any allergic reactions. Blood tests measure the presence of specific antibodies in the bloodstream, indicating an allergic response. Patch tests are useful for identifying contact allergens that may be causing flare-ups of atopic dermatitis. Allergy testing helps to determine the triggers for atopic disease and provides guidance for effective management and prevention strategies.
In certain cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm an atopic disease diagnosis definitively. During this procedure, a small sample of skin tissue is extracted and examined under a microscope. This allows healthcare professionals to identify specific histopathological features associated with atopic disease, such as increased levels of immune cells or structural abnormalities. Skin biopsies are particularly beneficial when other potential diagnoses need to be ruled out or when the patient’s symptoms are atypical. However, it is worth noting that skin biopsies are not required in all cases and are typically reserved for more complex or uncertain situations.
Treating atopic disease in adults involves a combination of methods to relieve symptoms and manage flare-ups. Here are some popular treatment options:
Topical medications are applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation, itching, and redness associated with atopic disease. Some commonly used topical medications include:
It’s important to use topical medications as directed by your healthcare provider and to avoid excessive or prolonged use, as they may have side effects.
In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to control severe symptoms of atopic disease or to manage related conditions. Some common oral medications used in the treatment of atopic disease include:
Oral medications require close monitoring and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they can have side effects and potential interactions with other medications.
While medications help manage atopic disease symptoms, incorporating certain lifestyle changes can provide additional relief and support overall well-being. Consider the following lifestyle modifications:
Implementing these lifestyle changes alongside medication can help reduce the frequency and severity of atopic disease flare-ups.
In some cases, immunotherapy may be recommended to modulate the immune system’s response and reduce the body’s hypersensitivity to triggers. This treatment option is typically reserved for severe or unresponsive cases of atopic disease. Two common forms of immunotherapy are:
Immunotherapy is a long-term treatment option that requires commitment, and it should be administered and monitored by a qualified healthcare professional.
Atopic disease, also known as atopic dermatitis or eczema, can significantly impact the quality of life for adults.
This chronic condition can cause dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, leading to discomfort and self-consciousness.
Avoiding triggers that can worsen atopic disease is crucial in managing the condition. These triggers can vary from
person to person, but some common triggers include:
Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Keeping a journal
to track symptoms and potential triggers can be beneficial in identifying patterns and making necessary adjustments
to daily routines.
Moisturizing the skin regularly is crucial in managing atopic disease. Dry skin is more prone to irritation and
flare-ups, so maintaining the skin’s moisture barrier is essential. When choosing moisturizers:
In addition to moisturizing, adopting a gentle skincare routine is vital. Avoid harsh soaps, excessive scrubbing,
and hot water, as they can further irritate the skin. Instead, opt for mild cleansers and lukewarm water when
washing.
Managing stress is crucial for adults with atopic disease. Stress can aggravate symptoms and trigger flare-ups.
Some effective stress management techniques include:
Support and education play a vital role in managing atopic disease. Joining support groups or online communities can
provide emotional support and helpful tips from others who understand the challenges of living with the condition.
Additionally, staying informed about the latest research, treatment options, and lifestyle modifications can empower
individuals to make informed decisions about their care.
By adhering to these prevention and management strategies, individuals with atopic disease can experience improved
symptom control and a better overall quality of life.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-Dermnet-250.atopic21-7ece7ff2659246f3bfa8ad8d7649d02b.jpg)
Credit: www.health.com

Credit: www.amazon.com
Atopic dermatitis is mainly caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
An atopic adult is someone who has an ongoing tendency to develop allergic conditions like asthma, eczema, or hay fever. They commonly experience skin irritations, itchy rashes, and respiratory issues. Managing symptoms and avoiding triggers is crucial for their well-being.
Atopic dermatitis appears as itchy, red, dry, and irritated skin. It may have patches or scales, and can sometimes ooze fluid or become crusted.
The most common atopic disorder is eczema, which is characterized by itchy and inflamed skin.
To sum up, atopic disease is a chronic condition that affects adults, causing discomfort and impacting their quality of life. By understanding the triggers, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can effectively manage this condition. From adopting healthy lifestyle choices to seeking medical advice, taking proactive steps can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Stay informed, prioritize self-care, and work with healthcare professionals for optimal management of atopic disease.