Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

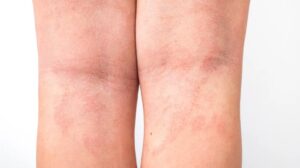
Atopic disease treatment involves managing symptoms through medication, lifestyle changes, and avoiding triggers. Atopic diseases, such as eczema, asthma, and hay fever, are chronic conditions that cause inflammation and allergic reactions in the body.
These conditions can be challenging to treat, as they often require long-term management to minimize symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment approaches typically include the use of topical medications, such as corticosteroids and moisturizers, to reduce inflammation and soothe the skin.
In severe cases, oral medications may be prescribed. Additionally, avoiding triggers such as certain foods, allergens, and irritants can help prevent flare-ups. Finally, incorporating lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and practicing good skin hygiene can also contribute to effective treatment.

Atopic diseases are a group of chronic conditions that often appear during childhood and affect the skin, respiratory system, and digestive system. They are characterized by inflammatory reactions and an overactive immune response. In this section, we’ll explore the common types of atopic diseases, as well as the causes and triggers associated with them.
Atopic diseases encompass several conditions, with the most common types being:
The exact causes of atopic diseases are not fully understood, but several factors contribute to their development and exacerbation. Some of the common causes and triggers include:
The common types of atopic diseases and their causes and triggers, individuals and healthcare providers can take proactive steps in managing and treating these conditions effectively.
When it comes to managing atopic diseases, there are several common treatment approaches that have proven to be effective. These approaches aim to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions. It is important to note that treatment options may vary based on the severity and specific needs of each patient.
Topical medications are widely used for the treatment of atopic diseases, such as eczema and dermatitis. These medications are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin, providing targeted relief. They come in various forms, including creams, ointments, lotions, and gels. Topical corticosteroids, for example, are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. These medications work by suppressing the immune system’s response and soothing the affected skin.
Another type of topical medication often used is emollients or moisturizers. These help to hydrate the skin, improve its barrier function, and prevent moisture loss, which is especially important for individuals with dry and sensitive skin. Additionally, topical calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, may be prescribed for those who do not respond well to corticosteroids.
In some cases, when topical medications alone are insufficient or when the condition is more severe, systemic medications may be recommended. Systemic medications are taken orally or by injection and are designed to treat the body as a whole, rather than just the affected areas of the skin. These medications work by targeting the underlying causes of atopic diseases and modifying the immune system’s response.
One commonly prescribed systemic medication is oral corticosteroids, which are used to control severe inflammation and itching. However, their long-term use may be associated with side effects, so they are often prescribed for short periods. Other systemic medications include oral or injectable immunosuppressants, such as cyclosporine and methotrexate, which help to suppress the immune system and reduce allergic reactions.
Allergen immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots or desensitization therapy, is a long-term treatment approach that aims to modify the immune system’s response to specific allergens. It is particularly beneficial for individuals with allergic asthma or allergic rhinitis. Allergen immunotherapy involves regular injections of small amounts of allergens over a period of time, gradually building up a tolerance and reducing allergic reactions.
This treatment approach is based on the principle of exposing the immune system to small doses of allergens, which helps to train the immune system to become less reactive to those specific triggers. Allergen immunotherapy is typically administered under medical supervision and may involve multiple visits to the healthcare provider over several months or years.
Atopic Disease, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic condition that requires diligent management to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. While medications and therapies play a crucial role, incorporating certain lifestyle changes can greatly enhance the effectiveness of treatment. In this article, we will explore three key lifestyle changes for managing atopic disease effectively.
3.1 Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers is a fundamental step in managing atopic disease. By pinpointing the elements that exacerbate symptoms, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent flare-ups. Here are some triggers to watch out for:
| Allergens | Irritants | Stress |
|---|---|---|
| Pollen | Harsh detergents | Emotional stress |
| Dust mites | Chemical irritants | Fatigue |
| Mold | Fragrances | Anxiety |
| Animal dander | Extreme temperatures | Depression |
By avoiding these triggers to the best of their abilities, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of atopic disease symptoms. It may be helpful to create a trigger diary to track symptoms and identify patterns, aiding in the identification of personal triggers.
A proper skincare routine is vital for individuals with atopic disease. This includes:
Following these skin care practices diligently can help restore and maintain the skin barrier, reducing dryness, itching, and inflammation commonly associated with atopic disease.
Diet modifications can also play a role in managing atopic disease. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, incorporating certain dietary changes may be beneficial:
By working with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian, individuals can personalize their diet plan based on their specific needs and triggers, optimizing the management of atopic diseases.

Credit: www.everydayhealth.com
While traditional medical treatments like medications and topical creams are commonly used for managing atopic diseases, there are alternative therapies that can provide relief as well. These alternative treatments focus on natural remedies, acupuncture, and probiotics. Let’s explore each of these options in more detail:
Natural remedies offer a holistic approach to treating atopic diseases. These remedies involve using ingredients derived from nature to alleviate symptoms and promote skin health. Some common natural remedies for atopic diseases include:
While natural remedies can be beneficial, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying them, especially if you are currently undergoing medical treatment.
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate healing. This therapy aims to balance the body’s energy flow and promote overall well-being. Acupuncture has shown promise in relieving symptoms of atopic diseases, including reducing inflammation and itchiness. Many individuals have reported positive results after undergoing acupuncture sessions.
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial for our health, particularly for the digestive system. However, recent research suggests that probiotics may also play a role in managing atopic diseases. These “good bacteria” can help restore the balance of microorganisms in the gut, which in turn may positively impact the immune system and reduce allergic responses. Probiotics can be consumed through certain foods like yogurt or taken as supplements.
Alternative therapies like natural remedies, acupuncture, and probiotics can be valuable additions to traditional atopic disease treatments. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating these therapies into your treatment plan. They can guide you on the appropriate methods and dosages based on your individual needs. It’s worth exploring these alternative options to find a comprehensive approach to managing atopic diseases and improving your quality of life.
The field of atopic disease treatment is constantly evolving, with researchers and medical professionals exploring new and innovative ways to provide relief to patients. In this section, we will delve into three emerging treatments and technologies that show promising potential in managing and treating atopic diseases.
Biologic therapies have revolutionized the treatment landscape for atopic diseases, offering tailored and targeted approaches to address specific immune mechanisms involved in the condition. These therapies are derived from living organisms, such as human cells, and are designed to target particular molecules or receptors in the body.
One example of biologic therapy for atopic diseases is sarilumab, which acts by inhibiting interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13), two key drivers of allergic inflammation. By blocking the activities of these molecules, dupilumab helps reduce the symptoms of atopic dermatitis, asthma, and other related conditions.
Additionally, biologic therapies such as omalizumab have shown great promise in treating severe or uncontrolled asthma. Omalizumab targets immunoglobulin E (IgE), a protein involved in allergic responses, thereby reducing the severity and frequency of asthma attacks.
Targeted therapies aim to specifically target and modulate certain cells or pathways responsible for the development and progression of atopic diseases. These treatments are designed to deliver more precise and effective results, minimizing potential side effects associated with non-specific treatments.
Crisaborole is an example of a targeted therapy used to treat atopic dermatitis. It works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4), an enzyme involved in the inflammatory response. By targeting PDE4, crisaborole helps alleviate the symptoms of atopic dermatitis, including itching, redness, and inflammation.
Another targeted therapy, JAK inhibitors (Janus kinase inhibitors), are being investigated for their potential to treat atopic diseases. JAK inhibitors interfere with the signaling pathway of certain cytokines involved in allergic responses, providing a novel therapeutic approach for conditions like atopic dermatitis.
Gene therapy holds immense potential to revolutionize the treatment of atopic diseases. This cutting-edge technology involves modifying or replacing faulty genes associated with the condition, thereby addressing the underlying genetic factors contributing to the development of the disease.
In the future, gene therapy could potentially offer targeted and personalized treatments for atopic diseases. By correcting genetic abnormalities, it may be possible to prevent or significantly reduce the symptoms and progression of these conditions.
While gene therapy for atopic diseases is still in its early stages of research and development, it represents a promising avenue for the future of treatment.

Credit: www.medicalnewstoday.com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-atopic-dermatitis-is-treated-5195507_final-cbb0589c087645c3b5841f32936accc5.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
To treat atopic syndrome, several approaches can be used, including topical creams, antihistamines, and corticosteroids for reducing inflammation and itchiness. Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as certain foods or environmental factors, is also vital. It’s best to consult a healthcare professional for personalized treatment options.
Yes, some individuals have found relief from atopic dermatitis, but a complete cure is not yet available.
Common triggers for atopic eczema include allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and pollen. Other triggers can be harsh soaps, detergents, stress, and weather changes. Taking care of your skin, avoiding triggers, and using moisturizers can help manage flare-ups.
Atopic is a serious condition that requires medical attention.
To wrap up, effective treatment for atopic diseases is crucial to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. By following a multidimensional approach that includes lifestyle changes, proper skincare, and medical interventions, individuals can effectively manage their conditions.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action tailored to specific needs. With the right treatment and ongoing care, individuals can find relief and regain control over their lives. Don’t let atopic diseases hold you back – take the necessary steps towards a healthier, symptom-free future.