Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

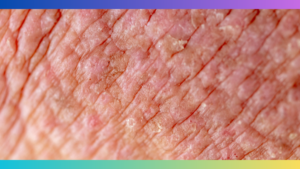
Atopic eczema allergy is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that results in itchy and inflamed patches of skin. Eczema is commonly seen in young children but can also affect adults.
It is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, with triggers including irritants, allergens, and certain foods. Managing eczema involves keeping the skin moisturized, avoiding triggers, and using appropriate skincare products.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(2999x0:3001x2)/the-best-eczema-creams-people-tested-tout-c8c122eabacb4830b1445475aab13250.jpg)
Credit: people.com
Atopic eczema allergy is a common skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed patches. It affects people of all ages and is often associated with allergies and asthma. Treatment options aim to relieve symptoms and manage flare-ups.
Atopic eczema allergy, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, which can cause significant discomfort and affect the quality of life for those who experience it.
The exact cause of atopic eczema allergy is still unknown, but researchers believe it is a combination of genetic and environmental factors. There is often a family history of allergic conditions such as asthma, hay fever, or eczema, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the condition.
The symptoms of atopic eczema allergy can vary from person to person, but common signs include redness, itching, dryness, and the appearance of raised, rough, or cracked skin. In severe cases, blisters and oozing lesions may also be present. The symptoms can come and go in cycles, with flare-ups occurring due to triggers such as dry weather, certain foods, stress, or irritants like chemicals or fabrics.
Atopic eczema allergy can affect individuals of all ages, from infants to adults. It is most commonly diagnosed in early childhood, with about 60% of affected individuals experiencing symptoms in the first year of life. By the age of five, approximately 1 in every 5 children will have atopic eczema allergy. However, the condition can also develop in adulthood, although it is less common.
Table: Prevalence of Atopic Eczema Allergy in Different Age Groups
| Age Group | Prevalence |
|——————|———————————————|
| Infancy | 60% of infants experience symptoms |
| Early childhood | 1 in every 5 children have atopic eczema |
| Adulthood | Less common but can still develop |
Understanding the causes and symptoms of atopic eczema allergy is crucial in managing this chronic condition. By recognizing triggers and employing appropriate treatments, individuals can minimize flare-ups, alleviate discomfort, and improve their overall quality of life.
Atopic Eczema Allergy, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that can cause severe itching, redness, and inflammation. It is important for individuals with this condition to identify the triggers that can worsen their symptoms and take steps to avoid them. By understanding the common allergens and environmental factors that can contribute to flare-ups, individuals can better manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Identifying common allergens is crucial in managing Atopic Eczema Allergy. These substances can irritate the skin and worsen symptoms. The following are some common allergens that individuals with atopic eczema should be aware of:
If you suspect that certain allergens are triggering your eczema flare-ups, it is recommended to visit an allergist for specific allergy testing. This will help you identify the allergens that are causing your symptoms so you can take steps to avoid them.
In addition to allergens, there are various environmental factors that can aggravate Atopic Eczema Allergy. These factors may not directly cause an allergic reaction, but they can still worsen the symptoms. It is important to be mindful of the following environmental factors:
By being aware of these environmental triggers, you can take steps to minimize their impact on your eczema symptoms. For example, using a humidifier in dry environments, opting for gentle and fragrance-free skincare products, and avoiding fabrics that irritate your skin can all help alleviate symptoms.
In conclusion, identifying triggers of Atopic Eczema Allergy is crucial for managing the condition effectively. By understanding common allergens and environmental factors that can worsen symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize flare-ups and improve their overall well-being.
Medical treatments for atopic eczema allergy focus on managing symptoms like itching and inflammation. These include topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, antihistamines, and phototherapy. Additionally, doctors may prescribe immunosuppressants or biologics for severe cases.
Medical Treatments for Atopic Eczema Allergy
Atopic eczema allergy, also known as atopic dermatitis, can cause discomfort and frustration for those affected by it. Thankfully, there are medical treatments available to help manage symptoms and improve the overall quality of life. Two common medical treatments for atopic eczema allergy are topical steroids and immunosuppressants.
Topical steroids are a commonly prescribed treatment for atopic eczema allergy. These medications work by reducing inflammation, itching, and redness associated with the condition. Topical steroids come in various strengths, ranging from mild to potent, and can be applied directly to the affected areas of the skin. They work by suppressing the overactive immune response responsible for causing eczema symptoms.
Using topical steroids correctly is essential to ensure their effectiveness and minimize potential side effects. It’s crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and application instructions provided by your healthcare professional. Applying a thin layer of the steroid cream or ointment to clean, dry skin is typically recommended. Overusing or abruptly discontinuing topical steroids can lead to skin thinning, discoloration, and rebound flares of eczema symptoms.
Immunosuppressants are another class of medical treatments used for atopic eczema allergy. These medications work by suppressing the immune system’s overactive response, thereby reducing inflammation and minimizing eczema symptoms. Immunosuppressant drugs are typically reserved for severe cases of atopic eczema that have not responded well to other treatments.
There are several types of immunosuppressants available, including calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus. These medications are applied topically and can be particularly beneficial for sensitive areas, such as the face and neck, where the use of potent topical steroids may be challenging. Other systemic immunosuppressants, such as cyclosporine and methotrexate, may be prescribed for severe cases that require more widespread immune suppression.
As with any medication, it’s essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of immunosuppressant treatment with your healthcare provider. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are often necessary to ensure safety and effectiveness.
In conclusion, while atopic eczema allergy can be a challenging condition to manage, medical treatments like topical steroids and immunosuppressants can significantly improve symptoms and enhance the quality of life for those affected. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on the severity and individual needs of the patient. Remember, these treatments should always be used under professional guidance, and any concerns or side effects should be promptly reported to your healthcare provider.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-atopic-dermatitis-is-treated-5195507_final-cbb0589c087645c3b5841f32936accc5.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Living with atopic eczema allergy can be challenging, but incorporating natural remedies and making lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms effectively. In this post, we will explore two main areas where making adjustments can make a significant impact: moisturizing and skincare and dietary modifications.
Proper moisturizing and skincare play a crucial role in managing atopic eczema allergies. Here are some essential tips:
Your diet plays a significant role in managing atopic eczema allergies. Making the following dietary modifications can help alleviate symptoms:
By adopting these natural remedies, including proper moisturizing and skincare routines and making dietary modifications, you can take control of your atopic eczema allergy and improve your quality of life.
Living with atopic eczema allergy can be challenging, but there are several strategies you can adopt to help manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. By implementing these tips into your daily routine, you can minimize flare-ups and keep your skin calm and healthy. Let’s explore some effective ways to manage atopic eczema allergy:
Stress is known to trigger flare-ups in individuals with atopic eczema. Therefore, it’s essential to find effective ways to manage your stress levels. Here are some stress-reducing techniques:
One of the key aspects of managing atopic eczema is to steer clear of skin irritants that can trigger a flare-up. Here are some tips to help you avoid common irritants:
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of atopic eczema allergy flare-ups. Remember, everyone’s triggers may vary, so it’s essential to identify what specifically affects your skin and tailor your routine accordingly.

Credit: nationaleczema.org
The triggers for atopic eczema include certain allergens such as dust mites, pet dander, and pollen. Environmental factors like heat and humidity can also exacerbate symptoms. Other triggers may include stress, harsh fabrics, and certain foods or chemicals.
To calm down a flare-up of eczema, try applying a moisturizing cream regularly, avoid scratching the affected area, use gentle, fragrance-free soaps, keep the skin hydrated with lukewarm baths, and wear soft, breathable fabrics.
To stop eczema from spreading, keep skin moisturized with emollients, use mild soap and detergents, avoid triggers like harsh chemicals and irritants, wear loose cotton clothing, and manage stress.
I cured my eczema by following a strict skincare routine and avoiding triggers. I used prescribed medications and natural remedies, such as moisturizers and oatmeal baths. Consistency and patience were key to my success. Seek advice from a dermatologist for personalized treatment options.
To wrap up, managing atopic eczema allergies requires a holistic approach that encompasses understanding triggers, maintaining proper skincare routines, and seeking professional guidance. By identifying and avoiding allergens, practicing good hygiene, and using suitable moisturizers and medications, individuals can experience relief from symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Remember, taking proactive measures can greatly minimize flare-ups and promote overall skin health.