Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

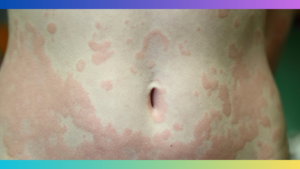
Atopic eczema affects black skin, causing inflammation, itching, and dryness. This condition can be managed through proper skin care and medical treatments.
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that affects people of all ethnicities, including those with black skin. However, it can present unique challenges for individuals with darker complexions. Black skin has a tendency to be drier and more sensitive, making it more susceptible to irritation and inflammation.
This can lead to increased itching, discomfort, and a higher risk of complications. Understanding the specific needs of black skin when it comes to managing atopic eczema is crucial for effective treatment. We will explore the causes, symptoms, and recommended treatments for atopic eczema on black skin. By gaining insights into the condition and learning how to care for black skin, individuals can effectively manage their atopic eczema and improve their quality of life.
Understanding Atopic Eczema in Black Skin delves into the unique challenges faced by individuals with black skin in managing this common skin condition. This comprehensive guide provides insights, tips, and recommended treatments tailored specifically for black skin, empowering those affected to take control and find relief.
Atopic Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects people of all ages, races, and ethnicities. It is a type of eczema that manifests as patches of dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. These patches can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the face, neck, hands, and legs. Atopic eczema is not contagious and can vary in severity, with some experiencing mild symptoms while others may have recurring or widespread flare-ups.
Understanding atopic eczema in black skin requires recognizing the unique aspects of its presentation. While the symptoms and causes of eczema are similar across different skin tones, black individuals may have specific concerns due to their skin type and its related characteristics:
It is important to note that despite these differences, the underlying causes and treatment options for atopic eczema are similar for all individuals, regardless of their skin color. It is essential to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of black skin.
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects people of all ages and ethnicities. However, when it comes to atopic eczema in black skin, there are specific causes and triggers that are unique to this population. Understanding these factors is crucial in managing and treating this condition effectively. In this section, we will explore the causes and triggers of atopic eczema in black skin, including genetic factors, environmental factors, skin barrier dysfunction, and allergens and irritants.
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of atopic eczema in black skin. Studies have shown that certain genetic variations can increase the risk of developing this condition. These variations affect the skin’s ability to retain moisture and maintain a healthy barrier function, making it more susceptible to inflammation and irritation. Although genetics alone cannot fully explain the onset of atopic eczema, they do contribute to an individual’s vulnerability to the condition.
Environmental factors, such as climate and pollution, can also trigger atopic eczema in black skin. The dry and cold weather can cause the skin to become dehydrated, leading to increased itching and flare-ups. Furthermore, exposure to certain allergens and irritants present in the environment, such as pollen, dust mites, and air pollutants, can worsen the symptoms of atopic eczema. It is important for individuals with black skin to be mindful of their surroundings and take necessary precautions to minimize exposure to these triggers.
Skin barrier dysfunction is a common characteristic of atopic eczema in black skin. The skin’s barrier serves as a protective barrier against external elements, but in those with atopic eczema, this barrier is compromised. The reduced production of ceramides, natural lipids that help retain moisture, and an imbalance in the skin’s pH levels contribute to a weakened barrier. As a result, the skin becomes more susceptible to allergens, irritants, and bacterial infections, leading to inflammation and flare-ups of atopic eczema.
Allergens and irritants can trigger and exacerbate atopic eczema in black skin. Common allergens include certain foods, such as dairy products, eggs, and nuts, as well as certain fabrics, such as wool and synthetic materials. Additionally, irritants such as harsh soaps, detergents, and fragrances can also cause flare-ups. It is important for individuals with atopic eczema to identify and avoid these triggers in order to manage their condition effectively.
Overall, understanding the causes and triggers of atopic eczema in black skin is essential for effectively managing and treating this condition. By addressing genetic factors, environmental factors, skin barrier dysfunction, and allergens and irritants, individuals with black skin can take proactive measures to minimize flare-ups and improve their skin health.
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition characterized by inflamed, itchy, and dry skin. While it can affect people of all skin types, managing this condition in black skin requires some specific considerations. The unique structure and characteristics of black skin make it more prone to certain skin issues and can require a tailored approach to treatment and care. In this blog post, we will explore some effective strategies for managing atopic eczema in black skin.
A consistent skincare routine is essential for managing atopic eczema in black skin. Creating a routine involves gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and protecting the skin. Here are some key steps to include:
When it comes to managing atopic eczema in black skin, selecting the right products is crucial. Look for products formulated specifically for sensitive skin and those free of common irritants such as fragrances and dyes. It’s also important to consider the unique needs of black skin, such as its tendency to be more prone to dryness and hyperpigmentation. Consider products that address these issues and provide targeted hydration and even skin tone.
Topical medications play an important role in managing atopic eczema in black skin. Your dermatologist may prescribe corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory creams to reduce redness and itching. It’s essential to follow their instructions carefully and use these medications as directed. Remember to moisturize regularly as these medications can sometimes cause dryness.
In addition to external care, making certain nutrition and lifestyle changes can also have a positive impact on managing atopic eczema in black skin. While there is no specific diet for eczema, consuming a balanced diet and incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and flaxseed, may help reduce inflammation. Avoiding triggers such as harsh detergents, extreme temperatures, and certain fabrics can also minimize flare-ups. Additionally, reducing stress levels through practices like meditation or exercise can help improve overall skin health.
Managing atopic eczema in black skin requires a comprehensive approach that includes a consistent skincare routine, choosing the right products, utilizing topical medications as prescribed, and making nutrition and lifestyle changes. By following these strategies, individuals with black skin can effectively manage their atopic eczema and achieve healthier, more comfortable skin.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-best-lotions-for-eczema-tested-and-reviewed-tout-with-badge-62ad962a69324d43b6a3c2f97f5939dc.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects people of all ages and ethnicities. However, when it comes to treating atopic eczema in black skin, it is essential to take into account the unique challenges and characteristics of this skin type. Holistic approaches that address the underlying causes and triggers of eczema can be effective in managing and reducing symptoms. In this article, we will explore alternative therapies, stress management techniques, and allergy testing and immunotherapy as holistic approaches for treating atopic eczema in black skin.
Alternative therapies offer natural and non-invasive methods for managing atopic eczema in black skin. These approaches focus on restoring balance to the body and strengthening the immune system. Some alternative therapies that have shown promise in easing eczema symptoms include:
Stress is known to be a trigger for eczema flare-ups. Implementing stress management techniques can help reduce the frequency and severity of these episodes in black skin. Here are some effective stress management techniques:
Allergy testing and immunotherapy can play a crucial role in managing atopic eczema in black skin. Identifying and avoiding allergens that trigger eczema flare-ups is essential for long-term symptom management. Allergy testing can help pinpoint specific allergens, such as certain foods, pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, that may be contributing to skin inflammation. Additionally, immunotherapy, such as allergy shots or sublingual tablets, can gradually desensitize the immune system to specific allergens, reducing eczema symptoms over time.
If you are an individual struggling with atopic eczema in black skin, it’s important to know that you are not alone. There are various patient support groups, online communities, and educational materials available to provide the necessary support and resources you need to manage and cope with this skin condition. These valuable sources can offer insights, tips, and emotional support from individuals who understand the unique challenges faced by those with atopic eczema in black skin. Let’s explore some of these resources:
Joining a patient support group can provide a sense of community and solidarity. These groups consist of individuals who are going through similar experiences and can offer valuable advice and encouragement. Check if there are any local support groups in your area that specifically focus on atopic eczema in black skin. Participating in these groups can help you gain insights from others who have tried different treatments or strategies, and provide emotional support during challenging times.
In today’s digital age, online communities have become powerful platforms where individuals can connect, share experiences, and seek support. There are various forums, discussion boards, and social media groups dedicated to atopic eczema in black skin. These online communities allow you to interact with individuals from around the world who are dealing with the same challenges. Here, you can exchange advice, learn about new treatment options, and find comfort in knowing that you are not alone on your journey.
Educating yourself about atopic eczema in black skin is crucial in managing the condition effectively. Look for educational materials such as brochures, books, and online resources that provide in-depth information about this specific type of eczema. These resources can help you better understand the triggers, symptoms, and treatment options available. Additionally, educational materials may offer guidance on skin care routines, self-care techniques, and lifestyle modifications that can help minimize flare-ups and improve your overall well-being.
In conclusion, finding support and resources is essential for individuals dealing with atopic eczema in black skin. Patient support groups, online communities, and educational materials can provide invaluable guidance and emotional support, ensuring that you are equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to manage this condition effectively. Remember, you are not alone, and there is hope for a better quality of life!

Credit: www.semanticscholar.org
To relieve eczema on Black skin, you can try these remedies: moisturize daily, avoid harsh soaps, use mild cleansers, wear breathable clothing, and identify trigger factors.
Dark-skinned people with eczema experience similar symptoms as those with lighter skin, including dry, itchy, and inflamed skin patches. However, eczema can be more challenging to diagnose due to differences in appearance. Treatment options, such as moisturizers and topical steroids, are effective in managing eczema for all skin types.
No, atopic eczema is not a fungal infection. It is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation and itching. It is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, not by fungal infection.
Atopic dermatitis is common in African Americans.
Managing atopic eczema in black skin requires a comprehensive approach that addresses underlying factors and provides targeted treatment. By understanding the unique challenges and sensitivities faced by individuals with atopic eczema in black skin, we can implement effective strategies for prevention, symptom management, and overall skin health.
Through consistent care, adequate moisturization, and avoiding triggers, individuals can find relief and reduce the impact of atopic eczema on their daily lives. Remember, self-care and awareness are key to maintaining healthy, radiant skin.