Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

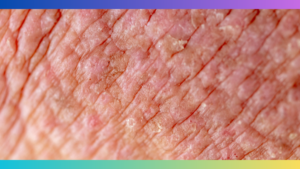
Atopic eczema on the fingers causes red, itchy, and inflamed skin patches. It can be triggered by various factors such as allergens, stress, or contact with irritants.
Individuals may experience intense itching, discomfort, and pain, impacting their daily activities and quality of life. The condition commonly affects both adults and children, and it is crucial to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment. Effective management typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, topical treatments, and self-care practices.
By understanding the causes and implementing appropriate measures, individuals can reduce flare-ups and find relief from atopic eczema on their fingers.
Atopic Eczema Fingers is a common form of eczema that affects the fingers and hands. It is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Atopic Eczema Fingers can be painful and uncomfortable, often leading to cracked skin and open sores. It is important to understand the causes and symptoms of this condition in order to effectively manage and treat it.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of Atopic Eczema Fingers. One of the primary causes is a genetic predisposition to eczema. Individuals with a family history of eczema are more likely to develop this condition on their fingers.
Additionally, environmental factors such as allergens or irritants can trigger or worsen Atopic Eczema Fingers. Common triggers include certain soaps, detergents, fabrics, and metals. Exposure to these substances can lead to an allergic reaction or irritation on the fingers.
Furthermore, dry skin is a key factor in the development of Atopic Eczema Fingers. When the skin lacks moisture, it becomes more vulnerable to inflammation and itching. External factors, such as cold weather or low humidity, can contribute to the drying of the skin on the fingers.
The symptoms of Atopic Eczema Fingers can vary from person to person, but there are some common signs to look out for. The most prominent symptom is intense itching, which can be incessant and difficult to resist the urge to scratch.
Other symptoms may include redness, swelling, and the formation of small blisters or papules. The affected skin may appear dry, scaly, or cracked. In severe cases, the skin may become thickened and develop painful sores.
Atopic Eczema Fingers can also be associated with other forms of eczema, such as atopic dermatitis or contact dermatitis. Therefore, individuals with Atopic Eczema Fingers may experience symptoms in other areas of the body as well.
It is important to note that Atopic Eczema Fingers is a chronic condition and can flare up periodically. These flare-ups can be triggered by certain factors such as stress, allergies, or changes in weather. Understanding the symptoms and triggers can help individuals manage and prevent future flare-ups.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hlt-ezcema-creams-test-pipette-baby-julia-warren-03-7314e13e674448d2a26ac24c8b1b9d53.jpeg)
Credit: www.health.com
Diagnosing atopic eczema fingers involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s medical history and a thorough physical examination. In some cases, additional tests such as patch testing or a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Let’s take a closer look at each diagnostic method:
A detailed medical history is essential in diagnosing atopic eczema fingers. The doctor will ask questions about symptoms, triggers, and any previous treatments. It’s important to provide accurate and specific information to help in determining the cause and severity of the condition. Following the medical history, a physical examination will be conducted to evaluate the affected area. The doctor will inspect the fingers for signs of inflammation, redness, swelling, dryness, and scaling. This assessment helps the doctor eliminate other possible causes and focus on atopic eczema as the underlying condition.
Patch testing is a common diagnostic test used to identify allergies that may be triggering episodes of atopic eczema fingers. During the test, small patches containing potential allergens are applied to the skin on the back. These patches are left in place for 48 hours, after which they are removed, and the skin is examined for any reactions. The results of the patch testing can help determine if contact allergens are aggravating the eczema symptoms. It is important to note that patch testing should only be performed by a qualified dermatologist or allergist.
In some rare cases, a skin biopsy may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis of atopic eczema fingers. This procedure involves the removal of a small sample of affected skin tissue for analysis under a microscope. A biopsy can help differentiate atopic eczema from other skin conditions that may have similar symptoms. The collected tissue is examined for specific cellular changes associated with atopic dermatitis. Biopsies are typically performed under local anesthesia and should only be done by a trained healthcare professional.
When it comes to treating atopic eczema on your fingers, there are several options available to provide relief and improve the condition of your skin. These treatment options can help to reduce itching, inflammation, and the severity of flare-ups, allowing you to better manage your atopic eczema and minimize its impact on your daily life. In this article, we will explore some of the most effective treatment options for atopic eczema fingers, including topical steroids, moisturizers and emollients, antihistamines and oral steroids, and wet wrap therapy.
One of the most commonly prescribed treatments for atopic eczema fingers is the use of topical steroids. These medications are available in various strengths and forms, such as creams, ointments, or lotions, and work by reducing inflammation and relieving itching. Topical steroids should be applied directly to the affected areas of your fingers, following your healthcare provider’s instructions. It’s important to note that these medications are typically prescribed for short-term use and should not be used continuously or for extended periods without medical supervision.
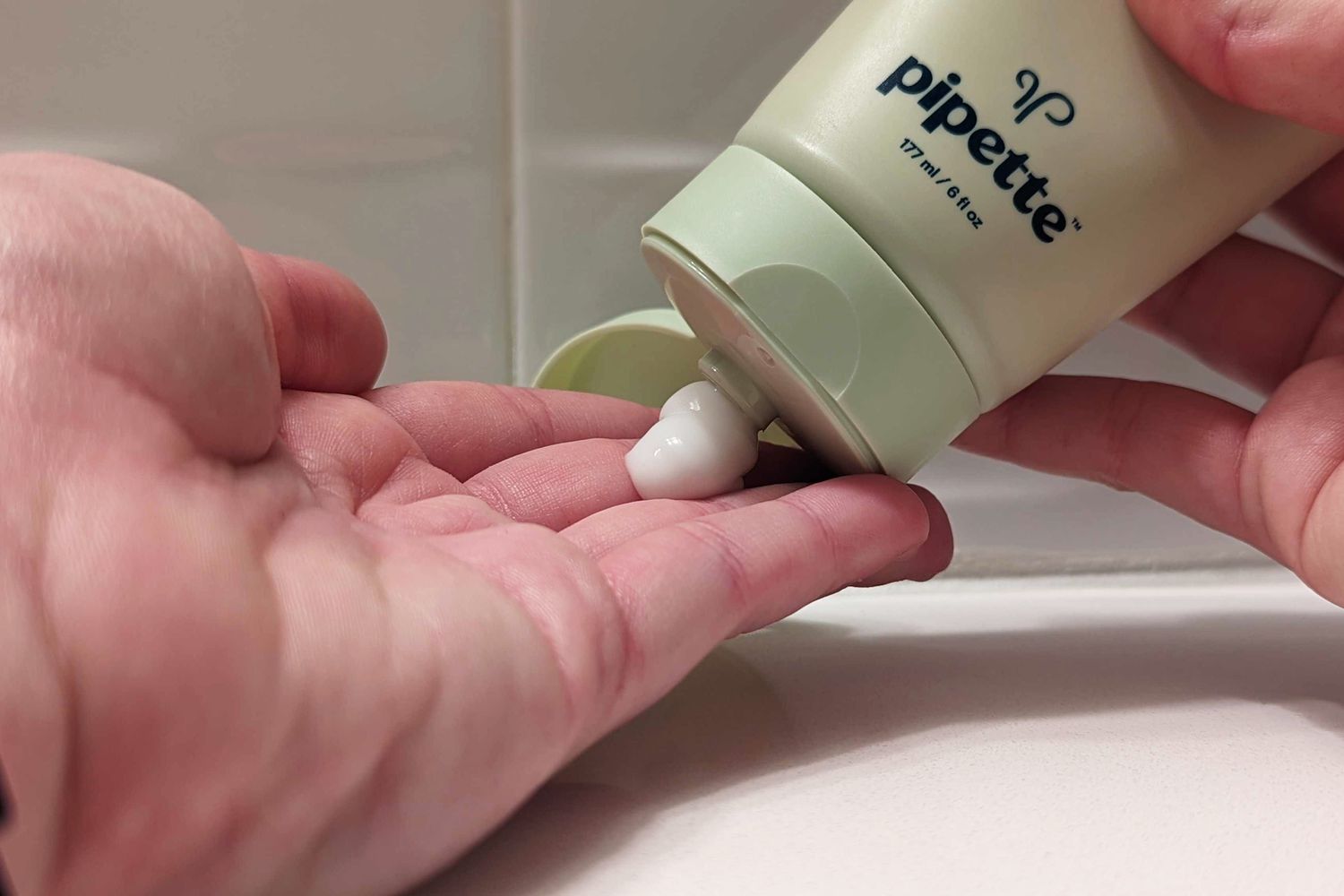
Moisturizers and emollients play a crucial role in managing atopic eczema fingers by keeping the skin hydrated and preventing dryness, which can exacerbate symptoms. These products help to improve the skin’s barrier function and reduce itching. Look for moisturizers and emollients that are fragrance-free and specifically designed for sensitive skin. Apply these products generously and regularly throughout the day, especially after washing your hands or coming into contact with potential irritants. It’s important to note that moisturizers and emollients are not a cure for atopic eczema but can provide significant symptom relief when used consistently.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend antihistamines or oral steroids to manage severe itching and inflammation associated with atopic eczema fingers. Antihistamines can help to reduce itching by blocking the release of histamine, while oral steroids are prescribed for short-term use to rapidly reduce inflammation and improve symptoms. These medications should be used under medical supervision and as directed by your healthcare provider. It’s important to note that long-term use of oral steroids can have potential side effects, so they should not be used without medical supervision.
Wet wrap therapy is a technique that can provide significant relief for atopic eczema fingers by enhancing the effects of moisturizers and topical medications. It involves applying a layer of moisturizer or topical steroid to the affected areas and then wrapping them with damp dressings or bandages. This technique helps to lock in the moisture and medication, allowing your skin to absorb them more effectively. Wet wrap therapy can be particularly beneficial for managing severe flare-ups or persistent symptoms. However, it’s essential to follow proper technique and seek guidance from your healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective implementation.
Avoiding triggers is crucial in preventing atopic eczema flare-ups on your fingers. Certain substances or activities can irritate your skin and make the symptoms worse. It’s important to identify and avoid these triggers as much as possible to keep your fingers healthy and free from eczema.
Regular moisturization is essential in managing atopic eczema on your fingers. Keeping the skin hydrated helps to prevent dryness, itchiness, and cracking, reducing the frequency and severity of eczema flare-ups. Here are some tips for effective moisturization:
Maintaining good hand hygiene is crucial in preventing atopic eczema flare-ups on your fingers. By following some simple practices, you can minimize the risk of infection and keep your hands clean and healthy:
Living with Atopic Eczema Fingers can be challenging. This condition causes dry, itchy and inflamed skin on the fingers, leading to discomfort and irritation. Seeking proper medical treatment and adopting a skincare routine can help manage and alleviate these symptoms effectively.
Living with Atopic Eczema Fingers can be challenging, but there are several coping strategies you can employ to manage the condition and improve your quality of life:
Living with a chronic condition like Atopic Eczema Fingers can be emotionally challenging, but you don’t have to face it alone. Here are some support groups and resources that can provide information, guidance, and a sense of community:
Remember, living with Atopic Eczema Fingers may be challenging, but with the right strategies and support, you can take control of your condition and live a fulfilling life.

Credit: www.healthline.com

Credit: manukabiotic.co.nz
To treat eczema on your fingers, keep them moisturized and avoid irritants. Use gentle, fragrance-free products and wear protective gloves. Apply topical corticosteroids as prescribed by a doctor. Soothe itching with cool compresses and take antihistamines if necessary. Seek medical advice for severe or persistent symptoms.
Certain triggers, such as irritants like chemicals, harsh soaps, detergents, and allergens like nickel or fragrances, can cause eczema on the hands.
Hand eczema can improve or even disappear with proper care and treatment. Following a consistent skincare routine, limiting exposure to irritants, and using moisturizers can help manage and reduce symptoms. Consultation with a dermatologist can provide personalized advice and treatment options for your specific condition.
The sudden onset of dyshidrotic eczema can be caused by factors like allergies, stress, and exposure to irritants. It is important to identify and avoid triggers to manage this condition effectively. Proper skincare, stress management, and medical treatment may be necessary to alleviate symptoms.
Managing atopic eczema on the fingers requires a combination of proper hygiene, moisturizing, and avoiding triggers. By following a routine skincare regimen, incorporating gentle cleansers and emollients, and seeking medical advice for persistent symptoms, individuals can find relief from this uncomfortable skin condition.
Remember, taking care of your fingers’ health is essential for maintaining overall well-being and enjoying a better quality of life.