Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

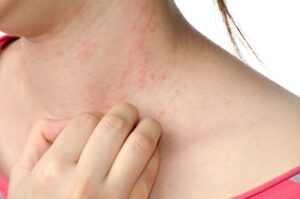
Atopic Eczema of Pregnancy is a skin condition that occurs during pregnancy, causing inflammation and itching. This article will provide an overview of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition, as well as some tips for managing and preventing flare-ups.
Atopic Eczema, also known as dermatitis, is a common condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. When it occurs during pregnancy, it is referred to as Atopic Eczema of Pregnancy. While the exact cause is unknown, hormonal changes and immune system variations are thought to play a role in its development.
Symptoms typically include dry, scaly patches on the skin, intense itching, and in severe cases, blistering and oozing. Treatment options for Atopic Eczema of Pregnancy may include topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, and antihistamines to relieve itching. It is also essential to maintain good skin hygiene, avoid triggers such as harsh soaps and detergents, and keep the skin well moisturized to help manage and prevent flare-ups.
Credit: draxe.com
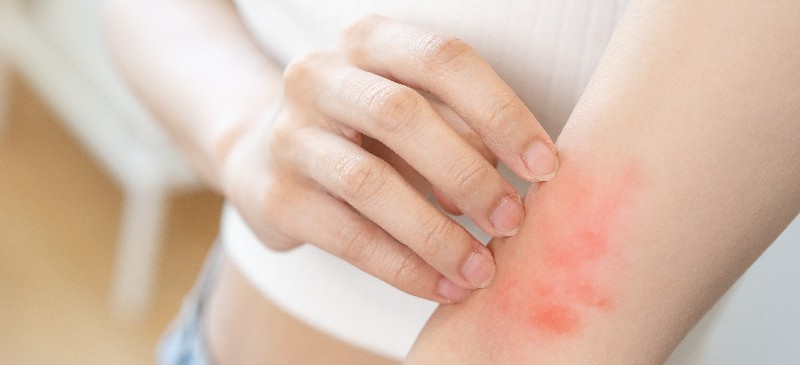
Atopic eczema during pregnancy can be challenging, with symptoms like itchiness and dryness causing discomfort. Take the time to understand this condition to find the best ways to manage and alleviate symptoms for a more comfortable pregnancy experience.
Atopic Eczema, also known as Atopic Dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin that can be both uncomfortable and unsightly. The condition can vary in severity, with some individuals experiencing mild flare-ups and others living with constant symptoms.
During pregnancy, women may experience changes in their skin due to hormonal fluctuations and increased blood flow. For women who already have Atopic Eczema, these changes can have a significant impact on their condition. Some pregnant women may see an improvement in their symptoms, while others may experience a worsening of their Atopic Eczema. It is crucial for expectant mothers with Atopic Eczema to consult with their healthcare provider to effectively manage their condition during pregnancy.
Women who have a history of Atopic Eczema should be aware that hormonal changes during pregnancy can trigger flare-ups or exacerbate existing symptoms. The immune system undergoes a series of changes during pregnancy, which can influence the severity of Atopic Eczema symptoms. Some women may find that their skin becomes more sensitive, dry, and itchy, making it more challenging to manage the condition.
It is important for pregnant women with Atopic Eczema to maintain a consistent skincare routine, keeping their skin moisturized and avoiding triggers that can worsen symptoms. Emollient creams or ointments can help to soothe and hydrate the skin, while avoiding harsh soaps, detergents, and perfumed products can help minimize irritation. Additionally, wearing loose-fitting cotton clothing and using mild, fragrance-free laundry detergents can also be beneficial.
While the exact cause of Atopic Eczema is unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. This means that individuals with a family history of Atopic Eczema are more likely to develop the condition themselves. Pregnancy can be a challenging time, and the added stress and hormonal changes may contribute to the development or worsening of Atopic Eczema symptoms.
If you are pregnant and experiencing symptoms of Atopic Eczema, it is essential to seek medical advice from your healthcare provider. They can offer guidance on suitable skincare products and provide treatment options that are safe for use during pregnancy. With proper management, it is possible to minimize the impact of Atopic Eczema on both the mother and the unborn child.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/amazon-la-roche-posay-toleriane-purifying-foaming-facial-cleanser-cerave-body-wash--alba-botanica-honest-mamas-gotta-glow-face-and-body-wash-d05c647589714d5885fc25df3ecb3554.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellfamily.com
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that can affect women during pregnancy. Understanding the causes and triggers of atopic eczema is essential for managing and preventing flare-ups. In this post, we will explore the various factors that can contribute to the development and worsening of atopic eczema during pregnancy.
Hormonal changes play a significant role in the development of atopic eczema during pregnancy. Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone, can disrupt the skin’s protective barrier, leading to increased dryness and itching. These hormonal changes can also affect the immune system, making the skin more susceptible to inflammation and irritation.
Stress and emotional factors can have a profound impact on the development and severity of atopic eczema during pregnancy. High levels of stress can trigger inflammatory responses in the body, exacerbating eczema symptoms. Additionally, emotional factors such as anxiety and depression can lead to increased scratching and skin irritation, worsening the condition.
The environment can also contribute to the development of atopic eczema during pregnancy. Exposure to extreme weather conditions, such as cold temperatures or excessive heat, can dry out the skin, making it more prone to eczema flare-ups. Indoor environments with low humidity can also contribute to skin dryness, triggering eczema symptoms.
Allergens and irritants present in everyday items can trigger or worsen atopic eczema during pregnancy. Common allergens include dust mites, pet dander, pollen, and certain foods. Irritants like harsh soaps, detergents, and fragrances can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation. It’s important to identify and avoid these triggers to minimize eczema symptoms.
In conclusion, hormonal changes, stress, environmental factors, and allergens/irritants can all contribute to the development and worsening of atopic eczema during pregnancy. By understanding these causes and triggers, expectant mothers can take proactive steps to manage their condition and minimize flare-ups.
Atopic eczema, also known as dermatitis, is a common skin condition that can often affect pregnant women. Its symptoms can range from mild to severe and can greatly impact a woman’s quality of life during this special time. Identifying and managing the symptoms of atopic eczema during pregnancy is crucial to ensure comfort and well-being for both the mother and the baby.
Recognizing the signs of atopic eczema is the first step in managing this condition effectively. Here are some symptoms that pregnant women should be vigilant about:
If you notice these signs on your skin, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Establishing a safe and effective skincare routine is crucial to managing atopic eczema during pregnancy. Here are some tips:
Avoiding triggers and allergens is essential in managing atopic eczema during pregnancy. Here are some precautions to consider:
By following these tips and taking proactive measures, you can effectively manage the symptoms of atopic eczema during pregnancy. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.
Atopic eczema of pregnancy, also known as pruritic folliculitis of pregnancy, can be a challenging condition to manage. While the primary focus is on alleviating symptoms and providing relief, medical treatments and interventions are often necessary. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation, control itching, and promote healing. Here are some common medical interventions used to manage atopic eczema during pregnancy:
Topical medications are typically the first line of treatment for atopic eczema of pregnancy. They are applied directly to the affected areas and are available in various forms such as creams, ointments, and lotions. These medications help to reduce inflammation and itchiness, providing much-needed relief for pregnant women.
Oral medications may be prescribed in cases where topical treatments alone are not providing sufficient relief. These medications are taken by mouth and work to suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation throughout the body. It’s important to note that oral medications should only be used under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional during pregnancy.
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is another option for treating atopic eczema during pregnancy. This treatment involves exposing the affected skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light. UV light can help reduce inflammation and itching, leading to improvements in the skin’s appearance and overall condition.
Other medical interventions may be considered for severe cases of atopic eczema in pregnant women. These interventions could include the use of systemic medications, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, which are administered under strict medical supervision. Additionally, certain procedures like wet wrap therapy or cryotherapy may be utilized to provide relief and promote healing.
In conclusion, medical treatments and interventions play a vital role in managing the symptoms of atopic eczema during pregnancy. Topical medications, oral medications, light therapy, and other interventions offer different approaches to reducing inflammation, controlling itching, and promoting healing. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the severity of the condition and individual needs.
Discover natural remedies and self-care strategies for managing atopic eczema during pregnancy. From soothing herbal creams to gentle skincare routines, these tips can help alleviate symptoms and provide relief without harsh chemicals. Improve your well-being in a safe and holistic way.
If you’re experiencing atopic eczema during pregnancy, you may be searching for natural remedies and self-care strategies to alleviate your discomfort. Luckily, there are several home remedies that can help provide relief from eczema symptoms.
One effective home remedy is moisturizing the skin regularly with natural emollients. Applying a moisturizer rich in ingredients like shea butter, coconut oil, or aloe vera can help soothe dry and itchy skin, reducing the severity of eczema flare-ups.
Your diet and lifestyle choices can also play a significant role in managing atopic eczema during pregnancy. Making certain adjustments can support your overall skin health and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Modify your diet: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, can help reduce inflammation and promote healthy skin. Additionally, avoiding trigger foods known to exacerbate eczema symptoms, such as dairy, gluten, and processed foods, may be beneficial.
During pregnancy, managing stress is vital not only for your overall well-being but also for managing atopic eczema symptoms. Incorporating stress management techniques into your daily routine can help minimize the impact of stress on your skin.

Credit: us.feelunique.com
Pregnancy can trigger eczema due to hormonal changes and increased stress levels. Certain foods, allergens, and skin irritants can also worsen symptoms. It’s best to avoid triggers, maintain a healthy skincare routine, and consult a healthcare provider for proper management during pregnancy.
Treat pregnancy-induced eczema by moisturizing regularly, using mild soaps, avoiding triggers, wearing loose clothes, and consulting a doctor.
Yes, pregnancy eczema typically goes away after giving birth. As hormone levels stabilize, the skin condition tends to improve.
To treat atopic eruption of pregnancy, it is best to consult a healthcare professional for a personalized approach. They may recommend topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, or moisturizers. Avoid potential triggers like harsh soaps, excessive heat, and certain fabrics.
Pregnancy is an incredible journey filled with joy and anticipation, but for some women, it can also bring the challenge of atopic eczema. Understanding the triggers and management techniques is crucial in providing relief and ensuring a smoother experience. By implementing a skincare routine, avoiding irritants, and seeking medical advice, pregnant women can better manage their symptoms and enjoy a more comfortable pregnancy.
Remember, taking care of your well-being is essential for both you and your baby.