Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Sustainable agriculture enhances soil health and water quality, benefiting both the environment and human well-being. It reduces pollution and conserves resources, promoting a healthier ecosystem and food supply.
Sustainable agriculture is gaining traction as an invaluable practice for its dual impact on environmental conservation and human health. By employing methods that protect the soil, conserve water and reduce chemical use, this agricultural approach works harmoniously with the earth’s natural systems.
These practices contribute to lessened soil erosion and improved water retention, ensuring that the land remains fertile and productive for future generations. Moreover, the reduction of harmful chemical inputs not only safeguards the health of farmworkers and neighboring communities but also lessens the incidence of pesticide residue on food, making our meals safer to consume. Sustainable farming’s commitment to biodiversity supports a balance in the ecosystem, encouraging natural pest control and pollination processes that are vital for food production. With its favorable impact on both the planet and people, sustainable agriculture is an essential step towards a more resilient and health-oriented food system.
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
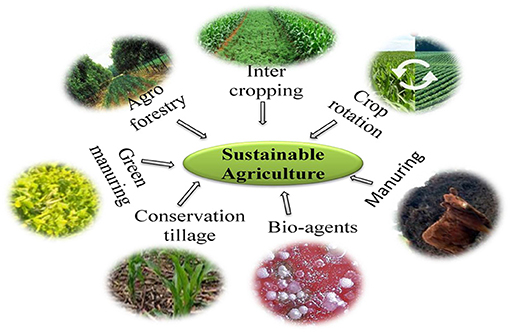
The essentials of sustainable agriculture play a vital role in shaping a greener future. Farming practices that consider the health of the soil, water conservation, and biodiversity are no longer just options, they are necessities. Embracing these methods benefits the planet and leads to healthier food and communities.
Sustainable agriculture practices are methods that maintain the health of the environment and communities. They focus on conserving resources and reducing pollution. This approach balances the need for food production with the preservation of the ecological system.
In sustainable agriculture, three core pillars support its foundation:
| Pillar | Focus | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Health | Resource Conservation | Better soil and water |
| Economic Profitability | Financial Viability | Lasting agricultural businesses |
| Social Equity | Community Well-being | Improved quality of life |
These pillars are essential for long-term sustainability in agriculture. Without one, the system is not balanced and may not stand the test of time.

Credit: www.thelancet.com
Embracing sustainable agriculture brings forth vast improvements in environmental quality and resource conservation. Let’s shed light on how these practices are making positive environmental impacts.
Sustainable farming breathes life into the earth beneath our feet. By using methods like crop rotation, cover cropping, and organic fertilizers, soil retains its vital nutrients and structure. This leads to a surge in soil fertility and health.
Water is precious, and sustainable agriculture is its guardian. Techniques like drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting make sure that every drop counts. These methods help maintain the balance in aquifers and prevent overuse.
| Method | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | Minimizes water waste |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Reduces dependency on external water sources |
| Plant-based Ground Cover | Retains soil moisture |
Protecting natural habitats is a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture. Diverse crop rotations and the inclusion of wildlife-friendly spaces on farms encourage a wide range of species to thrive.
Sustainable agriculture promotes healthier options for both the environment and the people. It helps in producing food in ways that are better for everyone’s health.
Fruits and vegetables from sustainable farms are often more nutritious. They contain higher levels of vitamins and minerals. This happens because the soil on these farms is well-cared-for. Healthy soils grow healthier plants.
Sustainable farming means fewer pesticides and chemicals. This is good because it reduces our contact with substances that can harm our health. Less chemicals mean a healthier body and environment.

Credit: www.sare.org
Economic Advantages for Farmers are significant in the switch to sustainable agriculture. Embracing methods that harmonize with nature not only benefits the environment and human health. It also leads to financial rewards for those who till the land. By maximizing natural resource use and ensuring stable production rates, farmers can experience improved cost savings and income stability.
Sustainable farming practices emphasize the use of on-site, natural resources, which can lead to substantial cost savings. For example, integrating organic fertilizers, such as compost or manure, reduces the need for expensive chemical inputs. Utilizing cover crops and natural predators aids in pest management without relying on costly pesticides.
Stability in production and yield is a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture. By diversifying crops and employing soil conservation techniques, farmers can enhance the resilience of their land. This approach minimizes the risk of complete crop failure due to pests, diseases, or extreme weather events.
| Bio-diversity | Soil Health | Water Conservation |
|---|---|---|
| Promotes resilience against pests | Improves nutrient availability | Ensures consistent water supply |
| Encourages pollinators | Reduces erosion | Reduces runoff |
Adopting sustainable agriculture extends beyond environmental advantages. It nurtures communities and enhances social wellbeing. This initiative strongly supports local economies and fortifies food security. Boldly explore these communal benefits further.
Sustainable agriculture invigorates local markets. When farmers opt for sustainable practices, they often rely on local resources. This encourages money to circulate within the region, bolstering the financial health of the area. Small-scale producers benefit due to increased demand for diverse, locally grown products.
Stable food sources are essential for thriving communities. Sustainable farming practices ensure long-term food production. They minimize dependence on external supplies by enhancing local capacity. This results in a continuous, reliable food supply.
Embracing sustainable agriculture benefits our planet and health. But it’s not easy. Farmers face big challenges. Good news: there are solutions, and we’re finding them every day.
Transitioning to sustainable farming means solving problems. Some crops might not grow well at first. Farms have to change how they work. Money can be tight. Let’s look at these one by one.
Solutions include education programs, government support, and patient trial and error.
Innovation is key. Bright minds are creating smart tools and machines to help. They’re finding better ways to grow food that’s good for you and the Earth.
| Innovation | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Drones | Check crops easily, use less water and chemicals |
| Apps | Give farmers info to make smart choices |
| Seed technology | Grow stronger plants that survive tough weather |
| Composting | Turns waste into rich soil, cuts down trash |
We’re building a better world, one farm at a time. Let’s keep going!
Sustainable agriculture refers to farming practices that protect the environment, public health, and animal welfare. It aims to meet society’s food and textile needs without compromising future generations’ ability to do the same.
Sustainable farming reduces pollution, conserves water, reduces soil erosion, and increases biodiversity. By avoiding synthetic chemicals, it also promotes healthier ecosystems and conserves natural resources.
Yes, sustainable agriculture can improve human health by providing nutrient-rich foods free from harmful chemicals. It also reduces exposure to pesticides and fertilizers that can cause health issues.
Sustainable agriculture can increase profitability through efficient resource use and reduced input costs. It also promotes resilience to climate change and market volatility, supporting long-term economic viability.
Embracing sustainable agriculture reaps tremendous rewards for the planet and our health. This approach conserves resources, nurtures the soil, and minimizes pollution. For humanity, it promises safer, more nutritious food, bolstering overall well-being. As we witness these positive impacts, it’s clear that sustainable farming isn’t just beneficial—it’s essential for our future.

