Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Multiple sclerosis and sclerosis are two different medical conditions. Multiple sclerosis is a neurodegenerative disease affecting the central nervous system, while sclerosis refers to the hardening or thickening of body tissues or organs.
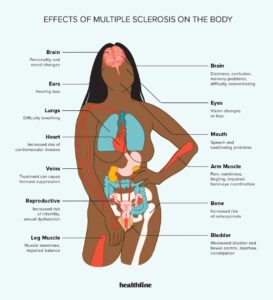
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that damages the protective covering of nerve fibers, leading to communication issues between the brain and the rest of the body. This can result in various symptoms, including fatigue, muscle weakness, cognitive impairment, and difficulties with coordination and balance.
On the other hand, sclerosis refers to the fibrosis and hardening of tissues in the body, often caused by inflammation or the buildup of scar tissue. It can affect different organs, including the skin, liver, and heart, and may cause functional impairments depending on the location and extent of the sclerosis.
Credit: www.healthcentral.com
Welcome to this insightful section of our blog where we delve into the world of sclerosis. In this article, we aim to clarify the confusion surrounding multiple sclerosis and sclerosis by looking at their definitions and causes. Before we dive in, let’s start by understanding the term “sclerosis” itself.
Sclerosis is a medical term that refers to the hardening or thickening of body tissues or organs. It can affect various parts of the body, causing a range of symptoms depending on which area is affected. While the term “sclerosis” may be used in different medical contexts, it is often associated with two specific conditions: multiple sclerosis and atherosclerosis.
Sclerosis can arise from different causes, depending on the specific condition that it is associated with. Here, we explore the causes of both multiple sclerosis and atherosclerosis:
The exact cause of multiple sclerosis is not yet fully understood. However, it is widely believed to be an autoimmune disease, wherein the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers in the central nervous system. This protective covering, known as myelin, becomes damaged, leading to the disruption of nerve signals between the brain and the body.
The primary cause of atherosclerosis is the buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances within the arteries. Over time, these deposits form plaque, which hardens and narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow to vital organs and tissues. Atherosclerosis is often associated with risk factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, obesity, and diabetes.
Understanding the definitions and causes of sclerosis is crucial for distinguishing between multiple sclerosis and sclerosis, as both terms are often used interchangeably. By gaining this knowledge, we can better comprehend these medical conditions and seek appropriate treatment. Stay tuned for the next section, where we will explore the differences between multiple sclerosis and sclerosis in more detail.
When it comes to neurological disorders, it’s important to understand the differences between various conditions. One such condition that often gets confused is multiple sclerosis (MS) and sclerosis. While both conditions share some similarities in terms of symptoms and treatment, they are distinct medical conditions.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, primarily the brain and spinal cord. The immune system mistakenly attacks the protective sheath called myelin, which surrounds the nerve fibers, resulting in disruptions to the transmission of electrical impulses between the brain and the rest of the body.
The exact cause of multiple sclerosis is yet to be discovered, but medical researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors play a role in its development. Genetic predisposition, viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus, and certain environmental factors, like low vitamin D levels and exposure to cigarette smoke, are thought to contribute to the onset of multiple sclerosis.
Although sclerosis and multiple sclerosis share the same root word, they are two distinct conditions with different distinguishing features. While sclerosis refers to the hardening or scarring of tissues or organs, multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. Let’s explore the symptoms of each condition to understand their differences.
Sclerosis involves the abnormal hardening or thickening of tissues, causing a loss in flexibility and function. The symptoms of sclerosis depend on the affected part of the body and may include:
These symptoms can vary in severity and may present differently depending on the underlying cause of the sclerosis.
Multiple sclerosis, on the other hand, affects the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. This autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the protective covering of nerve fibers, called myelin. The symptoms of multiple sclerosis can be diverse and may include:
These symptoms can vary from person to person and may come and go in episodes, known as relapses or flare-ups. It’s important to note that multiple sclerosis is a complex condition with many potential symptoms that can affect various aspects of an individual’s health and quality of life.

Credit: www.mslivingwell.org
Diagnosing and treating sclerosis is crucial for managing the condition effectively. There are distinct differences between multiple sclerosis (MS) and sclerosis. Understanding the diagnostic process and treatment options for sclerosis is essential for those living with this condition. Let’s delve into how sclerosis is diagnosed and explore the available treatment options.
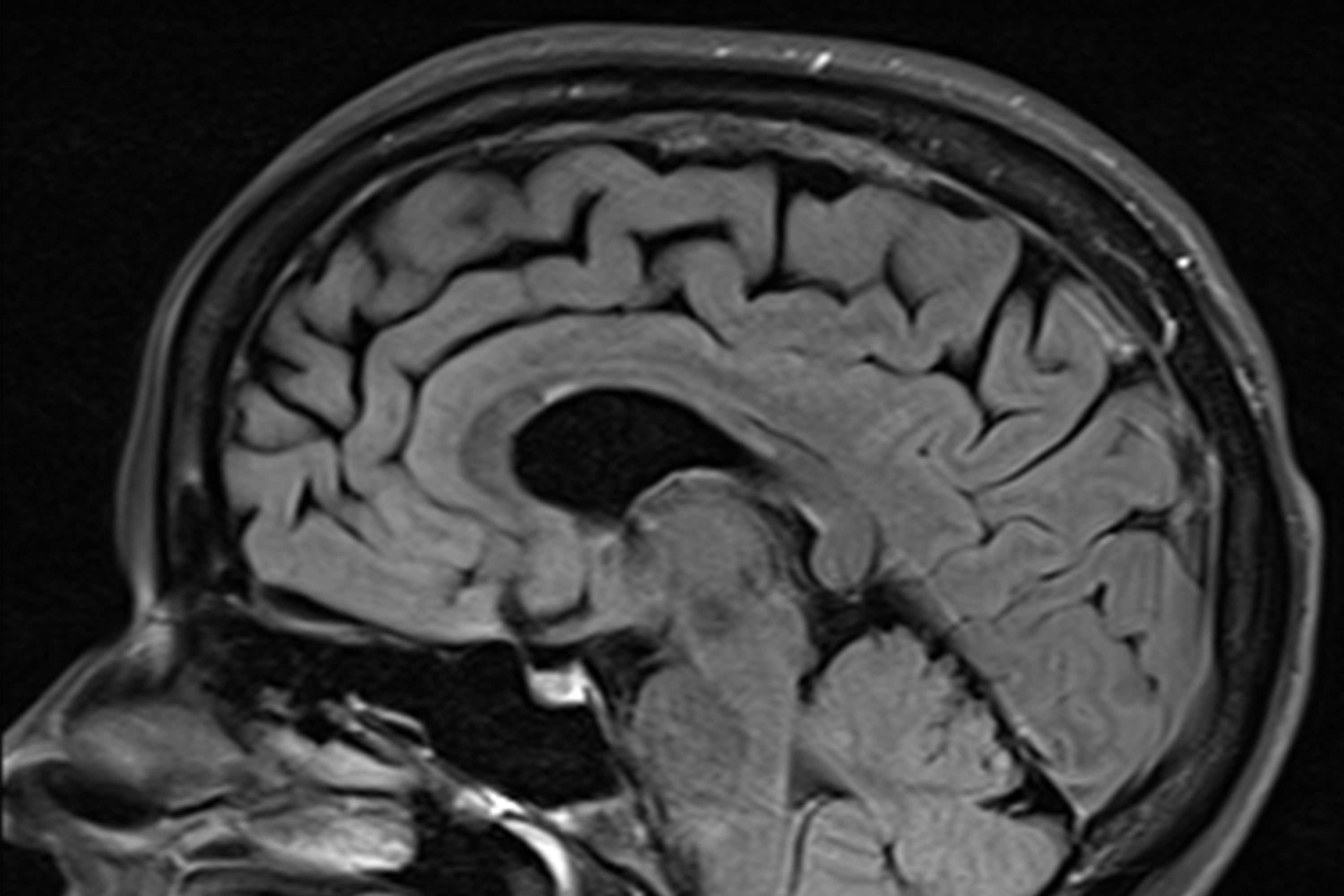
Diagnosing sclerosis involves various medical tests and examinations to assess the patient’s condition. Medical history is crucial in identifying potential risk factors or symptoms that may indicate sclerosis. Neurological examinations, including MRI scans, help to detect any abnormalities in the central nervous system. Blood tests are also conducted to rule out other conditions that may present similar symptoms to sclerosis.
Several treatment options are available for managing sclerosis, focusing on alleviating symptoms and slowing down disease progression. Medication plays a significant role in managing sclerosis, with immunosuppressants and corticosteroids being commonly prescribed. Physical therapy and occupational therapy are vital in improving mobility and enhancing daily living activities for individuals with sclerosis. In some cases, surgery may be recommended to address specific complications related to sclerosis.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and sclerosis are two distinct medical conditions, often confused due to their similar names. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we will focus on the subheading: Diagnosing and Treating Multiple Sclerosis.
Diagnosing MS can be challenging as there is no single test to confirm the condition. Medical professionals rely on a combination of assessments, including medical history, neurological exams, and various diagnostic tests such as MRI, lumbar puncture, and evoked potentials. The presence of characteristic lesions in the central nervous system is key to diagnosing MS.

Credit: www.ajnr.org
Sclerosis and multiple sclerosis are different terms. Sclerosis refers to the hardening of tissue, while multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease affecting the central nervous system.
Sclerosis is a serious condition.
Multiple sclerosis and muscular sclerosis are the same condition. There is no difference between the two terms. Both refer to a chronic disease affecting the central nervous system and its ability to transmit signals between the brain and the body’s muscles.
Multiple sclerosis is triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. These factors can include viral infections, smoking, low levels of Vitamin D, and certain autoimmune disorders.
Understanding the key differences between multiple sclerosis (MS) and sclerosis can help individuals better comprehend these two distinct conditions. While both involve the hardening of tissues, MS is an autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system, while sclerosis refers to the hardening of tissues in general.
Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and management of these conditions.