Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Early detection of breast cancer is crucial, and recommended screening methods include mammography and clinical breast exams. These methods help in detecting breast cancer at its early stages, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
To achieve accurate diagnosis and reduce the risk of false results, it is important for women to have regular mammograms and seek clinical breast exams from healthcare professionals. Additionally, self-exams can also be performed to monitor any changes in the breasts.
These screening methods ensure that any abnormalities or signs of breast cancer are detected early, enabling prompt intervention for improved outcomes. Early detection plays a vital role in saving lives and minimizing the impact of breast cancer.
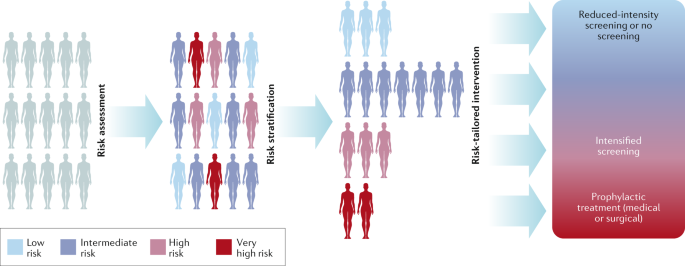
Credit: www.nature.com
Early detection is crucial in identifying breast cancer. Regular screening methods, recommended for early detection, include mammograms, clinical breast exams, and self-exams. Detecting breast cancer early increases the chances of successful treatment and improves survival rates.
Early detection of breast cancer plays a crucial role in improving treatment outcomes and increasing survival rates. Detecting breast cancer at an early stage allows for more effective treatment options and reduces the risk of the disease progressing. Regular screenings can help identify potential signs of breast cancer before any symptoms are noticeable. This section will discuss the age-specific recommendations for breast cancer screening and the many benefits that early detection offers.
The American Cancer Society provides age-specific recommendations for breast cancer screenings, ensuring that women receive appropriate and timely detection measures. These recommendations are as follows:
| Age Range | Screening Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Ages 20-39 | No routine breast cancer screening is required for women within this age group. However, it is crucial to be aware of the normal look and feel of one’s breasts and report any changes to a healthcare professional. |
| Ages 40-44 | Women in this age group should have the option to start annual breast cancer screening with mammograms, based on their personal preferences and risk assessments. |
| Ages 45-54 | Annual mammograms are recommended for women in this age group to detect breast cancer in its early stages, as the risk increases with age. |
| Ages 55 and older | Women aged 55 and older should transition to biennial mammograms or continue with annual screenings, depending on their personal preferences and overall health condition. |
The benefits of early detection of breast cancer are numerous and life-saving. Here’s why it is essential to prioritize regular screenings:
Regular breast cancer screenings provide a crucial first line of defense in the fight against this disease. By following age-specific recommendations and prioritizing early detection, women can take proactive steps towards maintaining their breast health and improving their chances of successfully overcoming breast cancer.

Credit: creeksideobgyn.com
Early detection plays a crucial role in successfully treating breast cancer. One of the most common and effective methods for early detection is mammography screening. Mammography allows healthcare professionals to identify breast abnormalities and potential signs of cancer before they become symptomatic. Let’s dive deeper into the world of mammography screening and discover why it is considered an essential tool in the fight against breast cancer.
Mammography is a specialized medical imaging technique designed to examine breast tissue for any irregularities, such as tumors or abnormal growths. It utilizes low-dose X-ray technology to capture detailed images of the breasts, allowing radiologists to identify any potential signs of cancer.
When it comes to mammography screenings, the frequency will depend on various factors, including age and personal history. In general, it is recommended that women start regular mammogram screenings at the age of 40. However, for those with a higher risk of breast cancer due to family history or genetic factors, screenings may begin earlier and be recommended more frequently.
Here is a recommended frequency guideline for mammography screenings:
| Age Group | Screening Frequency |
|---|---|
| 40-49 | Every 1-2 years |
| 50-74 | Every 1-2 years |
| 75+ | Consult with a healthcare professional |
Mammography screenings have both pros and cons that need to be considered. Understanding these can help individuals make informed decisions regarding their breast health.
Pros:
Cons:
Understanding the pros and cons of mammography screening can help individuals make educated decisions about their breast health and whether to undergo regular screenings.
Detecting breast cancer early is crucial, and clinical breast examination is one of the recommended screening methods. This non-invasive procedure helps identify potential abnormalities in the breast tissue, aiding in early detection and improving treatment outcomes.
A clinical breast examination (CBE) is an essential component of breast cancer screening for women of all ages. Conducted by a healthcare professional, this physical examination aims to detect any potential abnormalities or signs of breast cancer. The CBE focuses on the detection of lumps, changes in breast size or shape, dimpling, nipple discharge, or any other unusual symptoms that could indicate the presence of breast cancer.
The role of a clinical breast examination in early breast cancer detection cannot be overstated. While other screening methods like mammograms are highly effective, the CBE allows for the evaluation of the breast tissue and surrounding structures through touch. It plays a crucial role in detecting early signs of breast cancer that may not be identified through imaging techniques alone. The human touch provides an additional layer of screening, increasing the chances of identifying any potential abnormalities at an early stage.
The procedure for a clinical breast examination involves a systematic approach that ensures no area of the breast is overlooked. The healthcare provider will carefully palpate the breast tissue and surrounding areas, checking for any areas of concern. They will examine both breasts, as well as the armpit and collarbone region, as breast cancer can spread to these areas.
It is recommended that women should have a clinical breast examination at least once every three years between the ages of 20 and 40. After the age of 40, it is advised to have an annual CBE in combination with regular mammograms. Regularity in scheduling these examinations is crucial for detecting any changes or abnormalities and allowing for early intervention.
While a clinical breast examination is an important screening tool, it is important to note that it is not a diagnostic test. If any abnormalities or concerns are identified during the CBE, further diagnostic tests such as mammograms or ultrasounds may be recommended to confirm the presence of breast cancer.
Performing regular clinical breast examinations is a proactive approach to breast health. By being proactive, women can increase their chances of early breast cancer detection, which greatly improves treatment outcomes. Remember, prevention and early detection are key in the fight against breast cancer.
Early detection of breast cancer is crucial, and one recommended screening method is regular breast self-examination. By checking for changes in shape, size, or texture, women can play an active role in their own breast health.
Early detection is crucial in the battle against breast cancer. One effective method for women to monitor their breast health is through regular breast self-examination. By examining your own breasts, you can become familiar with their normal appearance and identify any changes that might indicate the presence of cancer. Below, we will discuss the importance of self-examination, along with instructions on how to perform it correctly and its limitations.
Performing breast self-examination on a monthly basis can significantly increase the chances of detecting breast cancer in its early stages. Being proactive and familiarizing yourself with the normal look and feel of your breasts allows you to quickly identify any changes or abnormalities that may indicate the need for further medical evaluation. Regular self-examinations can help catch breast cancer at an early, treatable stage, potentially saving lives.
To perform a breast self-examination, follow these simple steps:
While breast self-examination is a valuable tool for early detection, it does have its limitations. Some lumps or changes in the breast may not be easily detected through self-examination alone. Additionally, not all lumps found during self-examination are cancerous. It is important to remember that breast self-examination should be used in conjunction with regular clinical breast examinations by a healthcare professional, as well as mammography screenings. These comprehensive approaches increase the chances of detecting breast cancer at its earliest, most treatable stage.
Early detection of breast cancer is crucial. There are several recommended screening methods to detect it, including mammograms, clinical breast exams, and additional screening methods such as MRIs and genetic testing. Regular screenings can help detect breast cancer at its earliest and most treatable stages.
In addition to mammography, there are several other screening methods that can aid in the early detection of breast cancer. These additional methods can be used alone or in combination with mammography, depending on individual risk factors and medical recommendations.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging, commonly known as MRI, is a powerful screening tool that uses strong magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the breast tissue. It is especially useful for women with a high risk of developing breast cancer due to genetic mutations or strong family history.
During an MRI, the patient lies face down on a table that slides into the MRI machine. The machine then generates images, which a radiologist will interpret to identify any abnormalities. Unlike mammography, MRI does not involve radiation exposure.
However, it’s important to note that MRI is not recommended as a routine screening method for all women. It is typically used in combination with mammography for high-risk individuals or those with suspicious findings on a mammogram.
An additional screening method often used alongside mammography is breast ultrasound. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the breast tissue. It can help distinguish between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts, providing additional information for further evaluation.
During a breast ultrasound, a gel is applied to the breast, and a handheld device called a transducer is moved over the area. The transducer emits sound waves that bounce back as echoes, creating a visual representation of the breast tissue on a monitor. Breast ultrasounds are non-invasive and painless.
While ultrasound is useful in evaluating breast abnormalities, it is not a standalone screening method for breast cancer. It is often used as a supplemental tool, especially for women with dense breast tissue or those with a higher risk of developing breast cancer.
Genetic testing is another screening method that can provide valuable information about an individual’s risk of developing breast cancer. This type of testing looks for mutations or changes in specific genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, which are known to increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
If a family history of breast cancer or certain risk factors are present, genetic testing may be recommended. The test involves a simple blood or saliva sample, which is analyzed in a laboratory. The results can help individuals and their healthcare providers make informed decisions about screening, prevention, and treatment options.
| Screening Method | Usage | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | High-risk individuals, suspicious mammogram findings | No radiation exposure, detailed images | Not recommended for routine screening |
| Breast Ultrasound | Supplemental tool, dense breast tissue | Non-invasive, painless | Not a standalone screening method |
| Genetic Testing | Family history, specific risk factors | Provides risk assessment, informs decision-making | Not applicable to all individuals |
It’s important to remember that these additional screening methods are used in conjunction with mammography and may not be suitable for everyone. Discussing your individual risk factors with a healthcare professional can help determine the most appropriate screening plan for you.
Credit: cancerprogressreport.aacr.org
Screening methods for early detection of breast cancer include mammography, which is an X-ray of the breast, and clinical breast exams, where a healthcare professional examines the breasts for lumps or abnormalities. Other methods include breast self-exams and genetic testing for high-risk individuals.
Breast cancer can be detected early through regular mammograms and self-exams. Mammograms are X-ray screenings that can find tumors before they can be felt, while self-exams involve checking for any changes in the breasts. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment and improved outcomes.
Breast cancer screening typically involves mammograms and clinical exams, while diagnosis requires further tests like biopsies and imaging scans. The recommended procedure is early detection through regular screenings, followed by confirmation through diagnostic tests.
To get early breast cancer screening, schedule a mammogram or ultrasound test at a healthcare facility. It’s important to get regular screenings, as early detection can improve treatment outcomes.
To ensure early detection of breast cancer, it is crucial to undergo regular screenings using recommended methods. Mammograms, clinical breast exams, and self-examinations are effective tools in identifying abnormalities and taking prompt action. The importance of early detection cannot be overstated, as it significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and improved outcomes.
By following the recommended screening guidelines, individuals can take control of their health and proactively safeguard against breast cancer. Remember, prevention and early detection are our best weapons against this disease. Don’t delay, take charge of your health today.

