Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
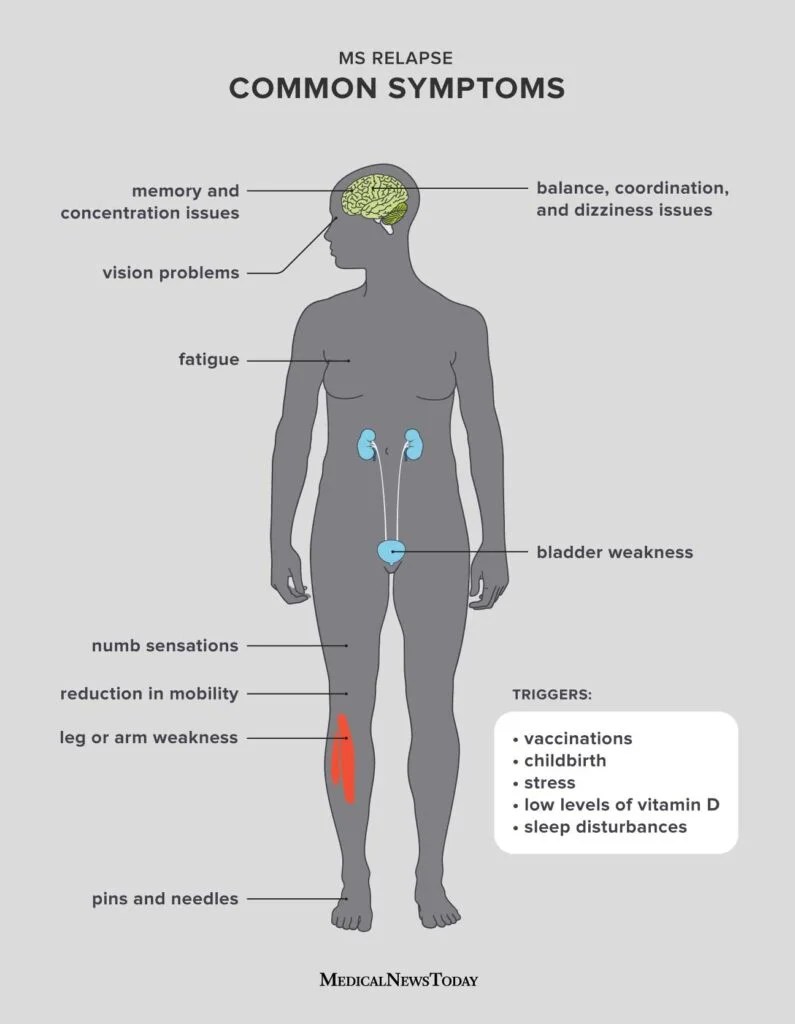
If you experience periods of worsening symptoms followed by periods of remission, you may have relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). RRMS is characterized by the unpredictable flare-up and improvement of symptoms over time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/who-develops-secondary-progressive-multiple-sclerosis-2440700-01-f642320e80384586bc768fe9d3599670.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Being able to recognize the symptoms of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the common indications and neurological manifestations associated with this condition, individuals can take the necessary steps towards managing their health effectively. Let’s take a closer look.
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis often presents with various symptoms that can differ from person to person. Some of the common indications include:
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis primarily affects the central nervous system, resulting in various neurological manifestations. These may include:
Recognizing these neurological manifestations is crucial for understanding the nature of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and seeking appropriate medical support.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-to-know-before-an-ms-attack-5213708_final-01-9ee8016133c44b6587fc19feeeab1fd4.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Diagnosing relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) can be a complex and challenging process. Healthcare professionals follow a systematic approach to determine if an individual has this form of multiple sclerosis. The diagnostic process involves specialized tests and a thorough medical examination.
In order to confirm a diagnosis of RRMS, doctors may order a series of specialized tests. These tests are designed to assess the function and structure of the central nervous system, as well as rule out other conditions with similar symptoms. Some of the commonly used specialized tests for RRMS include:
In addition to specialized tests, a thorough medical examination is an essential part of the diagnostic process for RRMS. During this examination, healthcare professionals will evaluate the patient’s medical history, including any symptoms experienced, their duration, and the frequency of relapses. They will also conduct a comprehensive neurological exam to assess the functioning of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
The neurological exam may involve:
It is worth noting that the diagnosis of RRMS often requires multiple visits and assessments over a period of time. This is because the symptoms of RRMS can be intermittent and may vary from person to person. By considering the results of specialized tests and incorporating the findings from the medical examination, healthcare professionals can make an accurate diagnosis of RRMS.
Distinguishing RRMS:
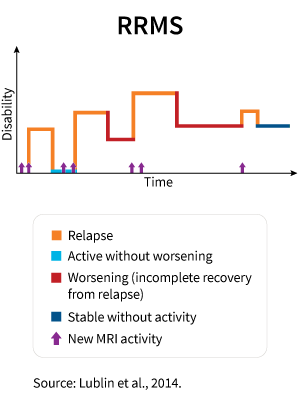
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) is one of the most common forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). It is characterized by distinct periods of relapses, when new symptoms appear or existing symptoms worsen, followed by periods of remission, during which the symptoms partially or completely fade away. Identifying if you have RRMS is essential for understanding the disease and determining the most suitable treatment plan.
Multiple sclerosis can have various subtypes, each with its own distinct clinical course. By comparing RRMS with other types, healthcare providers can better differentiate and classify the specific type of multiple sclerosis that an individual may have.
In RRMS, there are characteristic patterns of symptom occurrence that help distinguish it from other types of multiple sclerosis. The clinical course of RRMS can be summarized as follows:
| Period | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Relapse | Appearance of new symptoms or worsening of existing symptoms |
| Remission | Partial or complete resolution of symptoms |
| Subsequent Relapse | Another occurrence of relapse after a period of remission |
This cyclical pattern distinguishes RRMS from other types of MS, where the progression of symptoms may be more gradual or without distinct relapses and remissions. Understanding this characteristic clinical course is crucial for accurately diagnosing RRMS and guiding appropriate treatment decisions.
Identifying the distinguishing features of RRMS is essential to properly diagnose and manage the condition. By recognizing the specific clinical course and comparing it with other forms of multiple sclerosis, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about treatment options and provide personalized care to individuals living with RRMS.
Credit: www.nationalmssociety.org
The treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) is vital for managing the disease and improving the patients’ quality of life. There are various treatment options available, including disease-modifying therapies and symptomatic management, each serving a different purpose in managing the condition.
Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) are a cornerstone of RRMS treatment. These medications aim to decrease the frequency and severity of relapses, slow the progression of disability, and reduce the number of lesions in the brain and spinal cord. DMTs work by modifying or regulating the immune system to prevent it from attacking the central nervous system. Several types of DMTs are available, including injectable medications, oral therapies, and infusions, allowing individuals and their healthcare providers to select the most suitable treatment based on their specific needs.
In addition to disease-modifying therapies, symptomatic management plays a crucial role in addressing the symptoms that someone with RRMS may experience. This form of treatment focuses on managing specific symptoms, such as fatigue, muscle spasms, pain, and bladder dysfunction, to help improve the individual’s overall comfort and well-being. Symptomatic management may involve a combination of medications, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and lifestyle modifications tailored to the patient’s unique symptoms and needs.
If you have been diagnosed with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), incorporating certain lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing your condition. Adopting a holistic approach that includes physical activity, a healthy diet, and overall wellness can significantly impact the progression and symptoms of RRMS. Here are some lifestyle recommendations to consider:
Staying physically active is essential for individuals with RRMS. Regular exercise can help improve strength, balance, and reduce the risk of complications associated with a sedentary lifestyle. Engaging in activities such as yoga, swimming, or low-impact aerobics can be beneficial. It’s important to find an exercise routine that suits your abilities and preferences.
Eating a nutritious diet can support overall health and well-being for those with RRMS. Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your meals. Limiting your intake of processed foods, saturated fats, and sugary snacks can help manage weight and alleviate certain symptoms. Adding omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and nuts, to your diet may also have potential anti-inflammatory benefits.
To diagnose relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), doctors use a combination of medical history, neurological examination, MRI scans, and other tests. These help identify characteristic symptoms and lesions in the central nervous system, ruling out other conditions.
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) is characterized by periods of symptom flare-ups, called relapses, followed by periods of remission. The criteria for diagnosing RRMS include experiencing at least two separate relapses and evidence of new or active MRI-detected lesions.
Relapsing remitting MS can start at any age, but it most commonly begins between the ages of 20 and 40.
An MS relapse starts when the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers in the central nervous system. This disrupts the flow of electrical signals, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and difficulty walking.
To determine if you have relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Symptom evaluation, medical history analysis, and diagnostic tests can help confirm the diagnosis. Early detection and proper management can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with RRMS.
Stay informed about the latest research and treatment options, and don’t hesitate to reach out for support from medical experts and MS communities. Remember, early intervention is key to managing this condition effectively.

