Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Multiple sclerosis (MS) impacts the nervous system, causing damage to the protective covering of nerve fibers, leading to communication disruptions between the brain and the rest of the body. This can result in a wide range of symptoms that vary from person to person.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, called the myelin sheath, resulting in inflammation and damage. This damage disrupts the normal flow of electrical impulses along the nerves, impairing the communication between the brain and the body.
As a result, individuals with MS experience a diverse range of symptoms, including fatigue, muscle weakness, balance problems, numbness or tingling, coordination difficulties, visual disturbances, and cognitive impairments. MS is a complex condition with no known cure, making it crucial to understand how it affects the nervous system in order to manage and treat its symptoms effectively.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, particularly the brain and spinal cord. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, known as myelin. Without this protective layer, communication between the brain and the rest of the body becomes compromised. As a result, individuals with MS may experience a wide range of symptoms, including fatigue, pain, coordination and balance issues, muscle weakness, and cognitive dysfunction.
There are different types of Multiple Sclerosis, each with its own unique characteristics and progression patterns. These types include:
Understanding the different types of MS is crucial in diagnosing and managing the disease. The course and progression of the disease can vary greatly from person to person, making it important for individuals with MS to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan.

Credit: www.ohsu.edu
Multiple sclerosis (MS) directly impacts the nervous system, causing a wide range of symptoms. It disrupts the communication between the brain and other parts of the body, leading to issues like muscle weakness, loss of coordination, and impaired sensation. Understanding how MS affects the nervous system is crucial in managing the condition effectively.
The nervous system is a complex network of cells and tissues that carries messages between different parts of the body. It is responsible for controlling and coordinating bodily functions, allowing us to move, think, feel, and respond to our surroundings.
The nervous system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes all the nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
The nervous system uses electrical impulses and chemical signals to transmit messages. These messages travel along nerve fibers called neurons, which are specialized cells that make up the nervous system.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, called myelin, in the CNS. This leads to inflammation, demyelination, and damage to the nerve fibers.
Without the protective myelin, the transmission of electrical signals becomes disrupted. This can cause a wide range of symptoms, depending on which part of the CNS is affected. Some common symptoms of MS include:
The impact of MS on the nervous system can vary from person to person. It can affect mobility, sensory functions, cognition, and even emotional well-being. The unpredictable nature of MS makes it challenging to manage, as symptoms can come and go or worsen over time.
In conclusion, multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the nervous system, particularly the central nervous system. It disrupts the transmission of electrical signals and can lead to a wide range of symptoms. Understanding how MS impacts the nervous system is crucial for managing the condition and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, known as myelin, causing communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body. As a result, MS can lead to a wide range of symptoms that vary in severity and progression. Recognizing the symptoms of multiple sclerosis is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition.
Early signs of multiple sclerosis often appear in a person’s twenties or thirties. These symptoms can be intermittent or continuous, and their severity can fluctuate. It’s important to note that not everyone experiences the same symptoms or in the same order. However, some common early symptoms of multiple sclerosis include:
As multiple sclerosis progresses, more severe symptoms may develop. These progressive symptoms can significantly impact a person’s daily life and independence. Some of the progressive symptoms associated with multiple sclerosis include:
The diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis are vital aspects of managing this chronic condition. Early detection and intervention play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of the disease on the nervous system. Understanding the process of diagnosing multiple sclerosis and the options for managing and treating it can help individuals and their healthcare providers make informed decisions to improve quality of life.
The process of diagnosing multiple sclerosis involves a thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and various diagnostic tests. Neurological examination, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, and cerebrospinal fluid analysis contribute to identifying the characteristic lesions in the central nervous system. McDonald criteria are often used to establish a definitive diagnosis based on the presence of specific symptoms and evidence of disease activity over time. Prompt and accurate diagnosis enables early intervention to manage the disease effectively.
Effectively managing and treating multiple sclerosis involves a multidisciplinary approach focusing on symptom management, disease-modifying therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Physical therapy and assistive devices can help individuals maintain mobility and manage muscle weakness. Disease-modifying therapies aim to reduce the frequency and severity of relapses while slowing the progression of the disease. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary adjustments and stress management, are also integral components of managing multiple sclerosis. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan are essential to address the evolving needs of each individual with the disease.
Dealing with multiple sclerosis (MS) can present many challenges, especially when it comes to managing its impact on the nervous system. MS is a chronic condition that affects the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. As such, it can have a profound impact on a person’s daily life and overall well-being. Understanding how MS affects the nervous system and learning to cope with the challenges it presents is crucial for individuals living with this condition.
When living with multiple sclerosis, having a strong support system is essential. Connecting with other individuals who have MS can provide a sense of community and understanding. Seeking support from family members, friends, and healthcare professionals can also make a significant difference in managing the emotional and physical toll of the condition. Additionally, engaging in therapy or counseling can help individuals develop effective coping strategies and provide emotional support.
Improving the quality of life for those with MS often involves implementing various strategies to manage symptoms and enhance overall well-being. These may include adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate rest. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and meditation can also be beneficial in alleviating symptoms and improving overall quality of life.
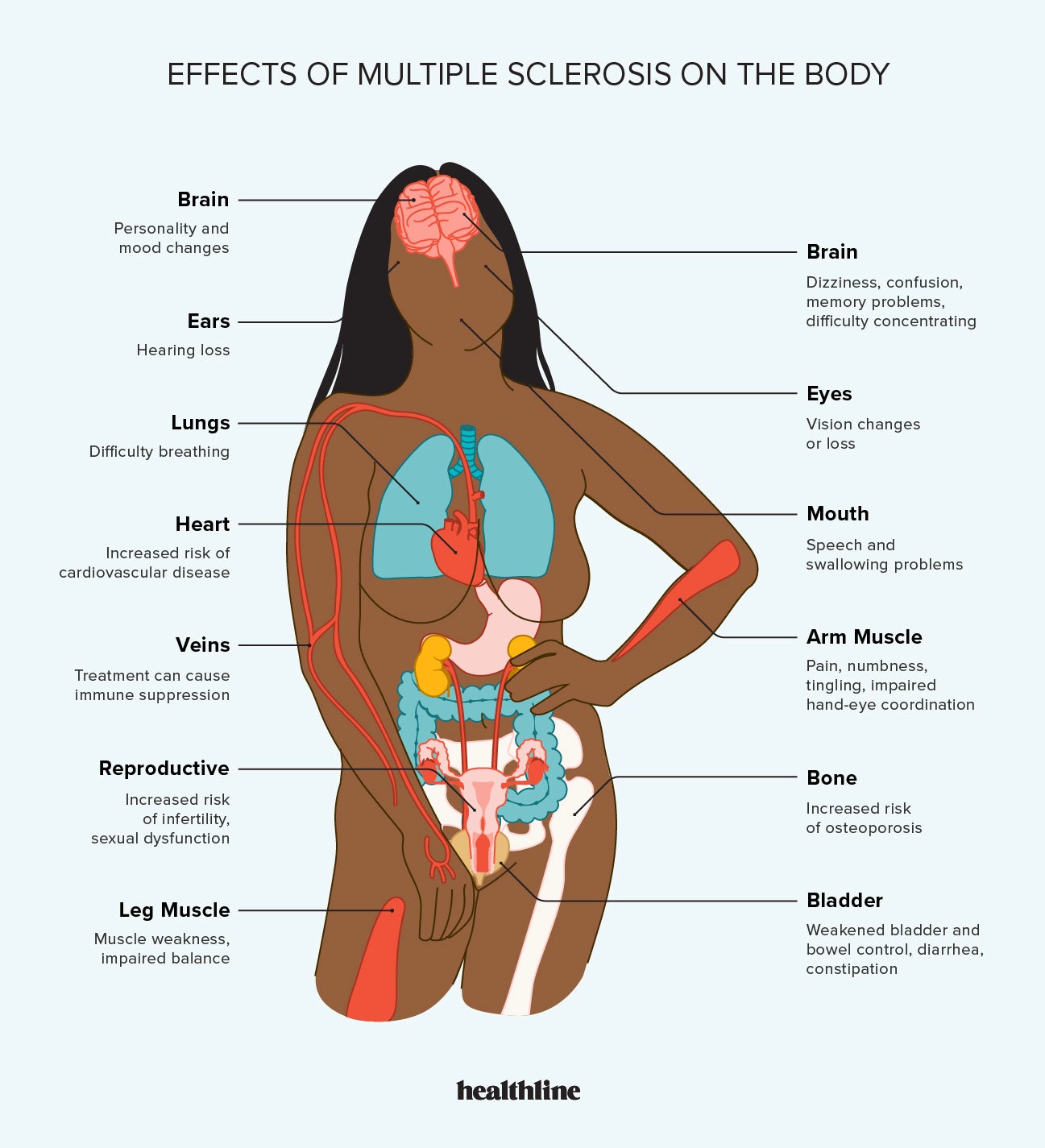
Credit: www.healthline.com

Credit: www.ohsu.edu
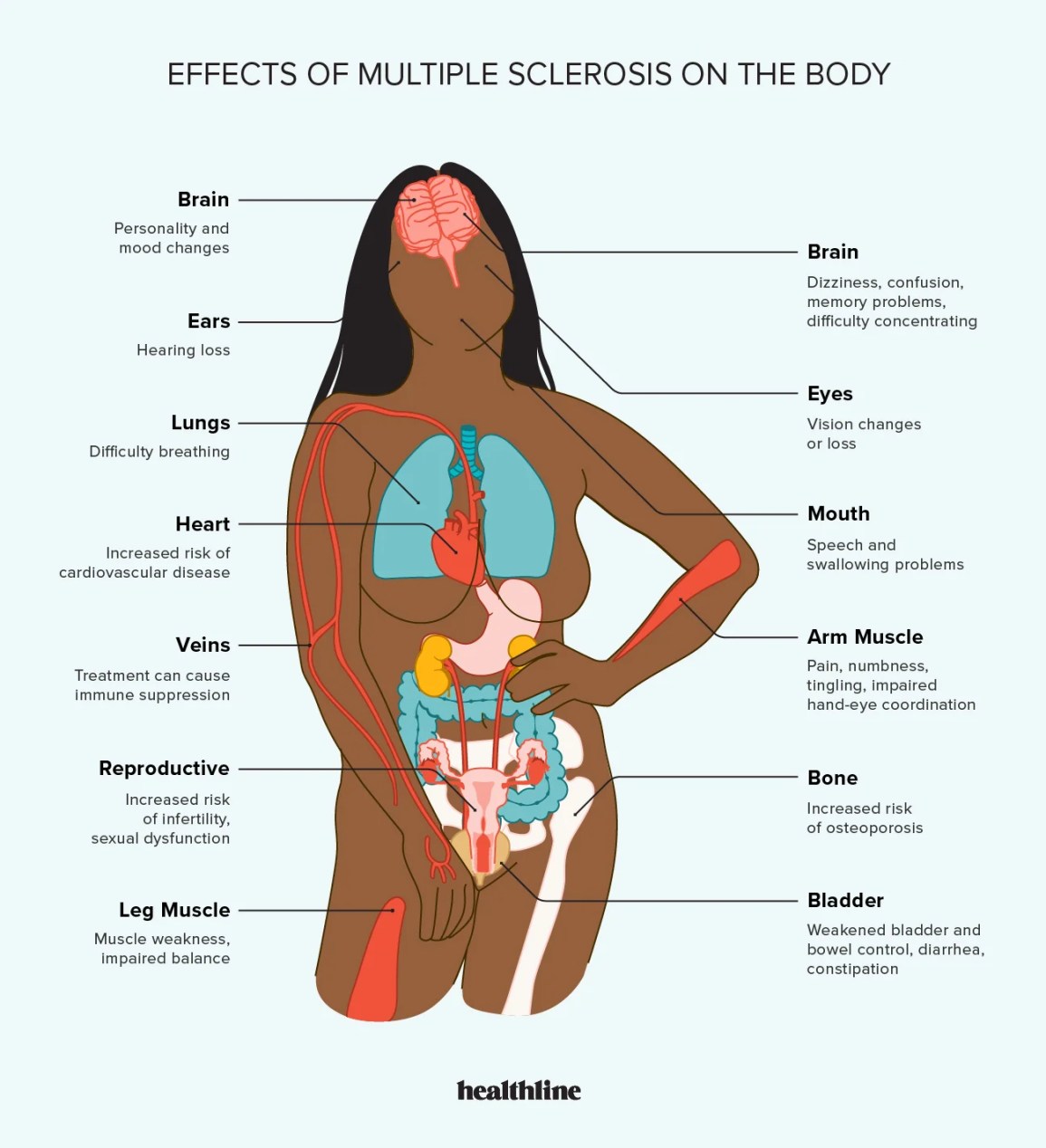
Multiple sclerosis affects the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects the sensory system by disrupting the transmission of nerve signals. This leads to problems with sensation, such as numbness, tingling, or pain. MS can also affect the sense of balance, coordination, and vision. It is a complex disease that varies in its impact on individuals.
MS affects the action potential by disrupting the communication between nerve cells. It damages the protective covering of nerve fibers, slowing down or blocking the transmission of electrical signals. This can cause changes in muscle coordination and weakness.
Multiple sclerosis is characterized by damage to the myelin sheath of neurons, disrupting nerve signals.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease that significantly impacts the nervous system. It can disrupt the communication between the brain and the rest of the body, leading to various symptoms and challenges for those affected. Understanding the effects of MS on the nervous system is crucial for managing the condition and providing appropriate support.
By raising awareness and investing in research, we can strive towards better treatments and improved quality of life for individuals living with MS.