Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

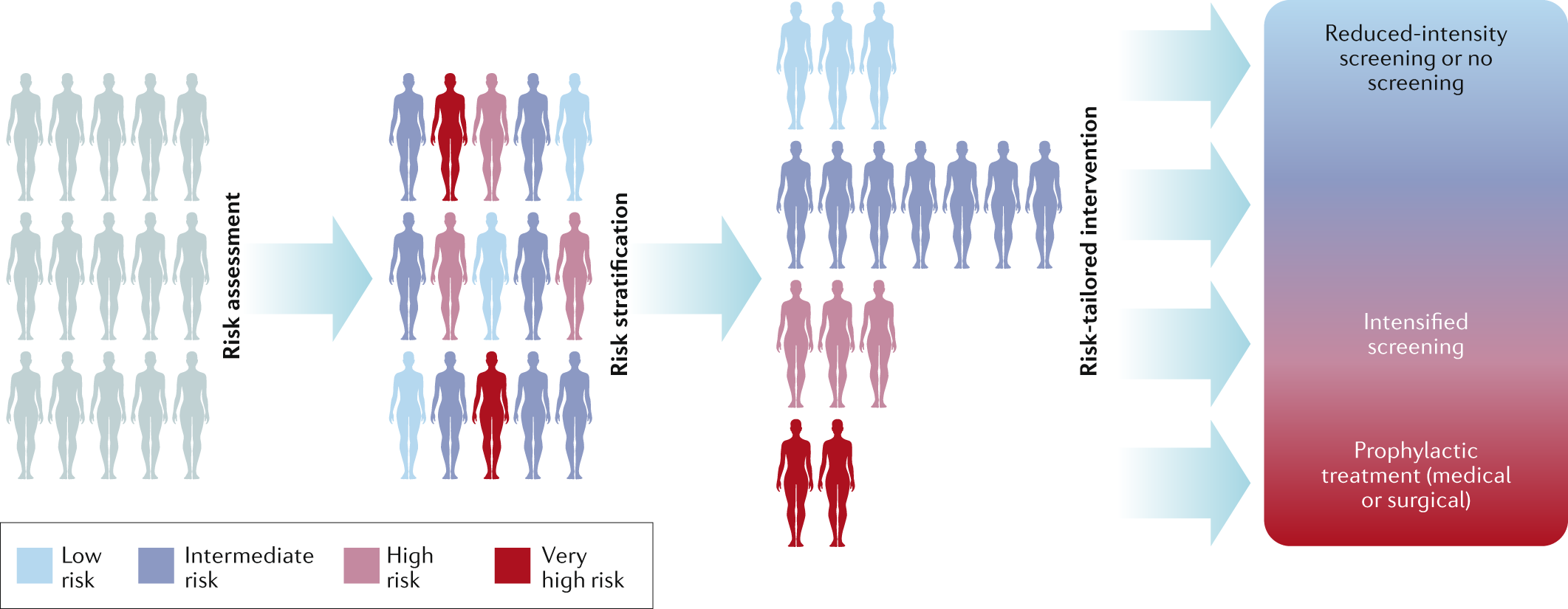
Hereditary or genetic susceptibility to breast cancer is prevalent, and genetic tests play a vital role in assessing one’s risk. Genetic tests are essential tools in identifying individuals who have an increased risk of developing breast cancer due to inherited gene mutations.
Breast cancer affects millions of people worldwide, and while many cases are sporadic, there is a significant proportion influenced by hereditary factors. The presence of certain gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can significantly increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
Genetic tests examine an individual’s DNA to detect these mutations and provide valuable information about their risk of developing the disease. By identifying individuals at higher risk, preventive measures, such as increased surveillance or prophylactic treatments, can be implemented to reduce the chances of developing breast cancer or detect it at an early stage.
Credit: www.nature.com
Breast cancer can have a hereditary or genetic component, and genetic tests are important in assessing an individual’s risk. These tests help identify specific gene mutations linked to breast cancer, aiding in early detection and personalized treatment.
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that develops in the cells of the breast. It can occur in both men and women, although it is much more common in women. There are different types of breast cancer, each with unique characteristics and treatment options.
There are two main types of breast cancer: invasive breast cancer and non-invasive breast cancer. Invasive breast cancer, also known as infiltrating, is the most common type and occurs when cancer cells spread to the surrounding breast tissue. Non-invasive breast cancer, also known as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), remains confined to the milk ducts and does not invade nearby tissue.
Breast cancer is one of the most prevalent forms of cancer worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, it is estimated that 2.3 million new cases of breast cancer were diagnosed in 2020 alone. The impact of breast cancer extends well beyond the physical symptoms and can significantly affect a person’s emotional well-being and quality of life.
Although breast cancer can occur at any age, the risk increases with age. The majority of breast cancer cases are diagnosed in women who are 50 years or older. However, it’s important to note that younger women can also develop breast cancer, and even men can be affected, although it is rare.
Genetic tests can play a crucial role in assessing an individual’s risk of developing breast cancer. Certain gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, are known to increase the risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer. These mutations are usually inherited from a parent and can be identified through genetic testing.
By analyzing a person’s DNA, genetic tests can determine if they carry these gene mutations. This information is valuable as it allows individuals and their healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding their breast cancer risk management strategies. This may include increased surveillance, such as more frequent screening mammograms or other imaging tests, or even considering preventive measures such as prophylactic surgeries.
It’s important to note that not all breast cancer cases are associated with genetic mutations. In fact, the majority of breast cancer cases occur in individuals who do not have a family history of the disease. Therefore, genetic testing is not recommended for everyone. Healthcare providers will consider factors such as personal and family history of breast cancer when determining whether genetic testing is appropriate.
Overall, genetic tests can help individuals understand their risk of developing breast cancer and empower them to take proactive measures to manage their health. By identifying those at a higher risk, healthcare providers can provide personalized care and interventions that may ultimately lead to better outcomes.
Breast cancer susceptibility due to genetics is not uncommon. Genetic tests play a significant role in assessing an individual’s risk and determining hereditary or genetic predisposition to breast cancer.
Breast cancer is a complex disease influenced by various factors, including both environmental and genetic factors. While environmental risk factors such as lifestyle choices and exposure to certain substances can increase the likelihood of developing breast cancer, genetic predisposition also plays a significant role. Genetic tests have become an important tool in assessing an individual’s risk for breast cancer by detecting specific gene mutations associated with the disease. In this section, we will explore the role of genes in breast cancer and the significance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations.
Genes are the blueprints that govern the functioning of our cells and play a crucial role in determining our traits and susceptibility to diseases. In the case of breast cancer, certain genetic mutations can increase an individual’s risk of developing the disease. These mutations can be inherited from one or both parents or occur spontaneously during a person’s lifetime.
Genetic testing can help identify these mutations and provide valuable information about an individual’s risk of developing breast cancer. By analyzing specific genes associated with breast cancer, genetic tests can identify individuals who may benefit from preventive strategies or early detection methods.
Among the various genetic mutations associated with breast cancer, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are among the most well-known and extensively studied. These genes play a crucial role in repairing damaged DNA and preventing the growth of abnormal cells. However, certain mutations in these genes can impair their function, leading to an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
Genetic tests can detect the presence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare. If a person is found to carry these mutations, they can opt for preventive measures such as increased surveillance, prophylactic surgeries, or targeted therapies to reduce their risk of developing breast cancer.
It is important to note that while BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations are strongly associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, they are not the sole determinants of the disease. Other genetic and environmental factors also contribute to the overall risk. Therefore, genetic testing for breast cancer susceptibility should be considered in the broader context of an individual’s medical history and risk factors.
By understanding the genetics of breast cancer and the role of specific gene mutations like BRCA1 and BRCA2, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their risk and make informed decisions about their healthcare. Genetic tests provide valuable insights that can guide personalized preventive strategies and ultimately contribute to improved outcomes in the fight against breast cancer.
One significant factor to consider when assessing the risk of developing breast cancer is an individual’s family history. Family history plays a crucial role in determining the likelihood of inherited or genetic susceptibility to this disease. If close family members, such as a mother, sister, or daughter, have been diagnosed with breast cancer, the risk of developing breast cancer increases.
The risk is even higher if the family members were diagnosed at a young age or if multiple family members have been affected. In such cases, it is important to seek medical advice and take appropriate measures to monitor and manage one’s risk.
Furthermore, it is essential to note that having no family history of breast cancer does not eliminate the possibility of being at risk. In fact, approximately 85% of breast cancer cases occur in individuals without a family history of the disease. Therefore, everyone, regardless of their family history, should be proactive in assessing their breast cancer risk.
Genetic tests play a crucial role in assessing an individual’s risk of breast cancer, particularly when there is a family history of the disease. These tests analyze specific genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, known to be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
By understanding one’s genetic makeup, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their health, including preventive measures and early detection strategies. Genetic tests can determine if an individual carries a genetic mutation that increases their susceptibility to breast cancer, providing valuable information for healthcare professionals to develop tailored preventive approaches.
It is vital to remember that genetic testing is not only relevant for individuals with a family history of breast cancer. In some cases, individuals may choose to undergo genetic testing due to personal risk factors or concerns. These tests help healthcare professionals assess the risk and provide appropriate guidance and care.
In conclusion, assessing breast cancer risk involves considering various factors, including family history and the importance of genetic tests. Understanding how prevalent hereditary or genetic susceptibility to breast cancer is, and utilizing genetic tests can empower individuals in taking proactive steps towards their health and well-being.

Credit: www.cdc.gov
When it comes to breast cancer, understanding one’s risk is crucial for early detection and effective prevention. With advancements in medical science, genetic tests have emerged as a significant tool in assessing an individual’s susceptibility to breast cancer. These tests provide valuable information about genetic mutations that might increase the risk of developing this life-threatening disease. In this blog post, we will delve into the topic of genetic tests for breast cancer, exploring what they are and how they contribute to assessing an individual’s risk.
Genetic tests are diagnostic examinations that analyze an individual’s DNA to identify specific genetic variations or mutations. These variations can impact a person’s likelihood of developing certain diseases, including breast cancer. By examining an individual’s genetic makeup, these tests can help identify inherited mutations that may increase the risk of developing breast cancer. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare and take proactive steps toward prevention and early detection.
Several genetic tests are available to assess an individual’s risk of breast cancer. These tests focus on identifying mutations in particular genes associated with an increased susceptibility to the disease. Three genes that are often tested for breast cancer risk are BRCA1, BRCA2, and TP53.
Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are well-established indicators of a higher risk of developing breast cancer. These mutations can be inherited from one or both parents and can significantly increase the likelihood of developing breast and ovarian cancers. Genetic tests for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations analyze an individual’s DNA to determine if they carry these harmful variations.
The TP53 gene is also associated with an increased risk of breast cancer, albeit in a different way. Mutations in this gene can give rise to Li-Fraumeni syndrome, a rare genetic condition that predisposes individuals to various types of cancer, including breast cancer. Genetic testing can identify TP53 mutations, enabling individuals to take appropriate preventive measures and undergo regular screenings for the earliest signs of cancer.
It is important to note that these genetic tests are not meant for everyone. They are typically recommended for individuals with a family history of breast cancer or other risk factors that suggest a higher likelihood of carrying these mutations. Genetic counseling is often recommended before and after undergoing genetic testing to ensure individuals fully understand the implications of the test results and receive appropriate guidance based on their genetic risk.
As research in genetics and genomics progresses, more advancements are being made in identifying additional genes linked to breast cancer. Genetic tests continue to evolve, aiding in the early detection and prevention of this devastating disease, ultimately increasing the chances of survival and improving overall healthcare outcomes. Understanding one’s genetic susceptibility to breast cancer through these tests provides individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps toward prevention and early intervention.
Genetic tests play a crucial role in determining the hereditary or genetic susceptibility to breast cancer. These tests help assess an individual’s risk and provide valuable insights into their genetic makeup. Understanding the prevalence of such susceptibility is essential for personalized healthcare and targeted interventions.
In the context of genetic testing for breast cancer, understanding genetic mutations is crucial. Genetic mutations are alterations in the DNA sequence that can have significant implications for an individual’s risk of developing breast cancer. These mutations can be inherited from a person’s parents or can be acquired during their lifetime. Identifying specific genetic mutations is an essential part of assessing one’s risk and determining appropriate preventive measures.
Once the results of a genetic test are obtained, interpreting the implications and determining the next steps becomes essential. A positive result indicating the presence of a known genetic mutation associated with breast cancer, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, may suggest a higher risk of developing breast cancer. In such cases, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in genetics or oncology to discuss the implications and explore personalized preventive strategies.
Interpreting genetic test results involves analyzing the information provided by the genetic test and understanding its significance for an individual’s breast cancer risk. It is important to note that genetic test results are not definitive predictors of breast cancer development. Instead, they help assess the likelihood of developing the disease based on identified genetic mutations. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, who can explain the results in detail and provide guidance on the appropriate steps to take.
When interpreting genetic test results, there are several key points to consider:
It is important to approach the interpretation of genetic test results with caution and seek guidance from healthcare professionals specialized in genetics and oncology. Armed with the right knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their breast cancer risk, allowing for proactive measures to reduce the likelihood of developing this disease.
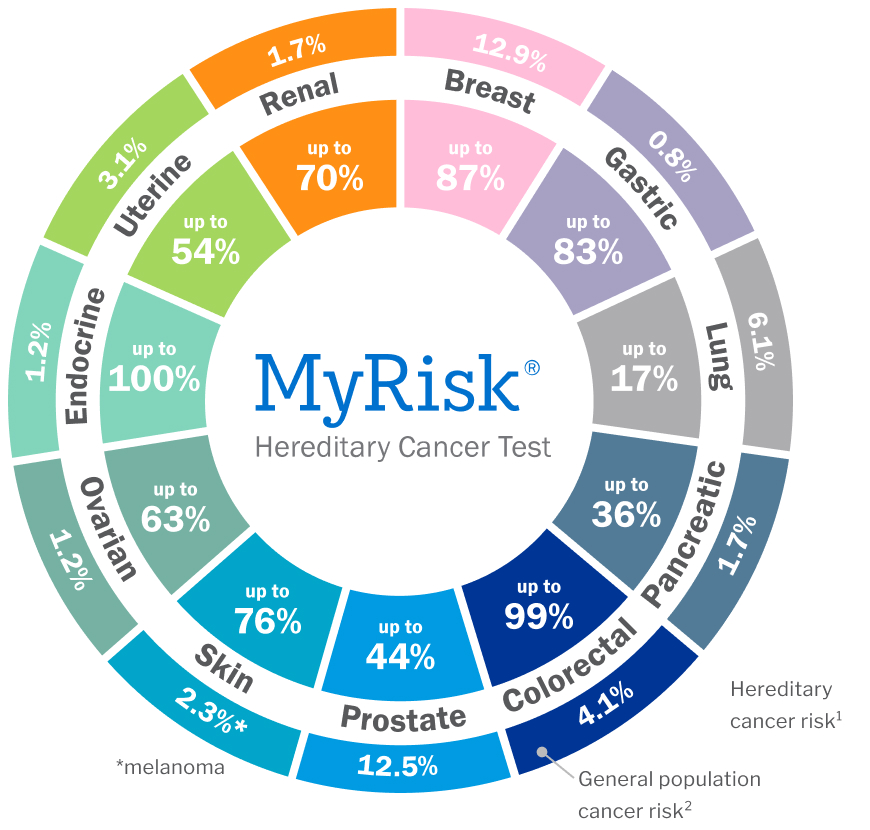
Credit: myriad.com
Genetics plays a significant role in breast cancer. Certain mutations and inherited gene changes, like BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase the risk of developing the disease. These genes help regulate cell growth, and alterations in them can lead to uncontrolled cell division, potentially leading to breast cancer.
Genetic testing helps assess the risk of breast cancer by examining specific genes. It identifies inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, which increase susceptibility to the disease. Results guide medical decisions regarding preventative measures and treatment options. Regular testing is vital for individuals with a family history of breast cancer.
Heredity or genetics plays a role in cancer risk by determining certain gene mutations. These mutations can increase the likelihood of developing certain types of cancer.
Genetic susceptibility refers to certain genes that increase the risk of developing breast cancer. These genes include BRCA1 and BRCA2. Having mutations in these genes greatly increases the likelihood of developing breast cancer compared to those without the mutations.
Understanding the prevalence of hereditary or genetic susceptibility to breast cancer is crucial in assessing one’s risk. Genetic tests play a vital role in identifying specific mutations that increase the likelihood of developing breast cancer. By providing valuable information, these tests enable individuals to make informed decisions about their health and pursue preventive measures.
Stay aware, and proactive, and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.

