Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Implementing circular economy practices fosters long-term sustainability by reducing waste and preserving resources. These strategies enhance resource efficiency and promote reuse, repair, and recycling initiatives.
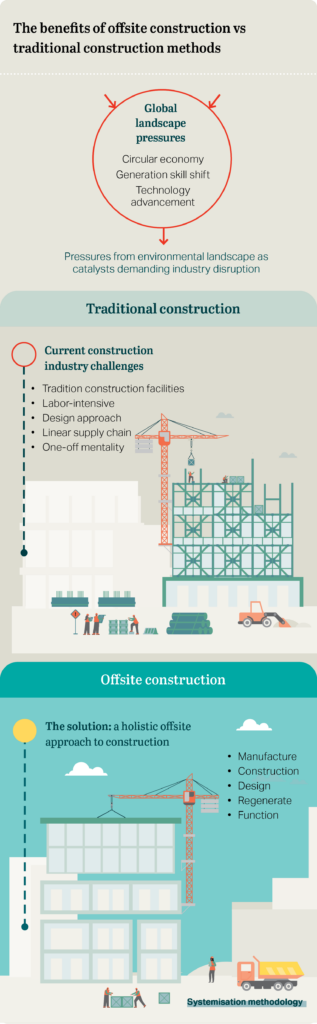
In today’s fast-paced world, businesses and consumers alike are becoming increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their actions. Transitioning from a traditional, linear economy, which follows a ‘take-make-dispose’ pattern, to a circular economy is pivotal for maintaining ecological balance.
The circular economy model emphasizes the importance of keeping products, materials, and resources in use for as long as possible. This shift not only decreases the environmental footprint but also offers economic benefits by creating new job opportunities and stimulating innovation. By prioritizing sustainable design, and maintaining products through repair, reusing materials, and recycling, we can create a more resilient and eco-efficient system. Mindful consumption, together with corporate responsibility, paves the way for a more sustainable future, demonstrating the profound impact that circular economy practices can have on the planet’s well-being and resource security.

The circular economy model is a transformative approach to production and consumption. It involves designing and using products and materials in a way that minimizes waste. This model aims to keep resources in use for as long as possible. It extracts the maximum value from them while in use and recovers and regenerates products and materials at the end of their life cycle.
Our current economic model is ‘linear’. We take resources, make products, use them, and then throw them away. As we throw stuff away, we throw out value. The circular model is different.
By shifting to circular, we use things longer. We reuse them. We make them into new things.
The principles guide this economy. These principles ensure long-term sustainability. They help the planet and people.
These principles shift the focus. They move us from short-term use to long-term value. This is good for our Earth.
Credit: open.sap.com
Circular economy practices help our planet and businesses. They transform how we use and reuse resources. By keeping materials in use, we waste less. Companies gain new opportunities from waste.

Embracing a circular economy offers a pathway to sustainable growth and innovation. Companies across industries recognize the need to transition away from linear ‘take-make-waste’ models. The following key strategies play a vital role in implementing circular economy practices that ensure long-term sustainability.
Products that last longer reduce waste and demand for resources. Designing for longevity involves:
Recycling and upcycling are essential to a circular economy. Pioneering innovations include:
Shifting to circular business models demands:
| Focus Area | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Product-as-a-Service | Leasing products instead of selling |
| Resource Efficiency | Optimizing material use |
| Supply Chain Sustainability | Partnering with green suppliers |
| Collaborative Platforms | Sharing resources among businesses |
Exploring case studies from leading innovators can illuminate a pathway for businesses striving for sustainability. The circular economy model champions reuse, sharing, repair, refurbishment, remanufacturing, and recycling. This model aims to create a closed loop system, minimizing waste and resource consumption. By studying how various companies integrate these practices, businesses can draw valuable insights for their own sustainability efforts.
Companies across sectors embrace the circular economy, redefining traditional business models. They prove that environmental initiatives can also drive profitability and operational efficiency.
| Industry | Company | Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Loop by TerraCycle | Product-as-a-service with reusable packaging |
| Fashion | Patagonia | Recycled materials and repair programs |
| Transportation | Remondis | Waste recycling and urban mining |
Pioneers in the circular economy showcase that innovation and sustainability are inseparable allies. These trailblazers have cultivated best practices that can serve as a roadmap for others.
Key takeaways highlight the importance of community engagement, transparent supply chains, and investment in sustainable materials. By learning from these leaders, companies can forge a more resilient and eco-friendly economy.
Embracing a circular economy opens the road to long-term sustainability. Yet, firms often hit roadblocks. From ingrained linear habits to laws lagging behind, finding a path to circularity needs creativity and resolve. Here’s a look at those hurdles and ways to clear them.
Change is hard. Firms face several blocks on the road to circularity:
Solutions involve:
Regulations and rewards must support circularity. Now, we see:
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Insufficient laws for circular economy practices. | Create regulations that back reuse and recycling. |
| Fiscal structures not favoring sustainable choices. | Introduce tax cuts and grants for circular businesses. |
| Lack of transparency in supply chains. | Adopt digital tools for better supply chain visibility. |
These moves push firms towards circular systems, benefiting all.
Credit: aecom.com
To transition successfully into a circular economy, businesses must track their journey.
Measuring impact and progress is crucial for any sustainable venture.
By evaluating the effectiveness of circular practices, organizations can understand their environmental footprint and economic performance.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) help to assess success in circular economy initiatives.
| Category | Description | Example KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Efficiency | Utilization of materials and energy | Material savings, energy consumption |
| Waste Reduction | Decrease in waste creation | Recycling rates, landfill diversion |
| Lifecycle Extension | Longer product lifespans | Product durability, repair rate |
| Economic Benefits | Financial gains from circular activities | Cost savings, revenue from secondary markets |
| Supplier Engagement | Working with suppliers for circular goals | Supplier sustainability assessments, collaboration level |
Adopting circular economy practices is an ongoing process.
Companies aim for continuous improvement and scaling their efforts.
Organizations take lessons learned and iterate their practices.
This fosters resilience and ensures sustainability benefits all stakeholders.
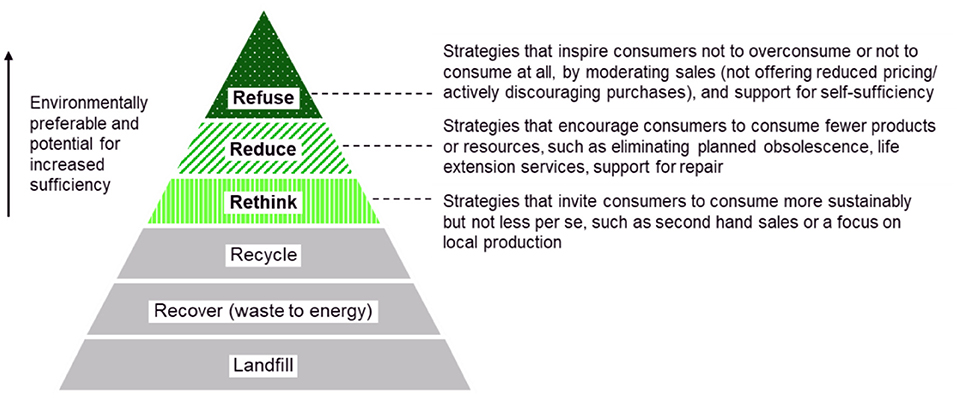
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
A circular economy is an economic system aimed at eliminating waste and the continual use of resources. It emphasizes reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling existing materials and products to create a closed-loop system, minimizing resource input and waste, pollution, and carbon emissions.
By redefining growth and focusing on positive society-wide benefits, a circular economy reduces waste, drives greater resource productivity, and eliminates negative environmental impacts. It helps create a sustainable, low-carbon, resource-efficient and competitive economy.
The key principles of a circular economy are designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. These principles enable businesses and societies to thrive within the planet’s natural boundaries.
Businesses can implement circular economy practices by redesigning products for disassembly and reuse, implementing recycling initiatives, offering services that lease rather than sell products, and investing in renewable energy. These steps contribute to creating a more sustainable business model.
Embracing a circular economy paves the path for sustainable growth. It seeks to redefine growth, with societal benefits integral to business success. This shift ensures resources maintain their value, minimizing waste. For industries, governments, and consumers alike, the journey toward sustainability is not just beneficial—it’s essential.
Let’s commit to circularity for a thriving future.

