Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Lewy Body Dementia hallucinations are primarily treated with cholinesterase inhibitors and atypical antipsychotics. Non-pharmacological approaches also play a vital role in management.
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) brings unique challenges, including hallucinations that can be distressing for patients and caregivers alike. Understanding and addressing these visual disturbances is crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected. Treatment options often involve medication, tailored to minimize side effects while alleviating hallucinatory experiences.
Alongside pharmaceutical interventions, supportive strategies such as creating a safe environment, engaging in cognitive activities, and providing reassurance can be beneficial. The goal is to manage symptoms with a careful balance of medication and non-drug therapies, emphasizing person-centered care. With thoughtful treatment planning, managing hallucinations in LBD can lead to better outcomes and enhanced well-being for individuals living with this complex condition.
Credit: medicine.umich.edu
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) stands as a challenging condition, weaving a complex web of symptoms. Among the most impactful are hallucinations. This section illuminates the nature of hallucinations within LBD and explores their profound influence on both patients and caregivers. Grasping these elements paves the way for more compassionate care and tailored treatment strategies.
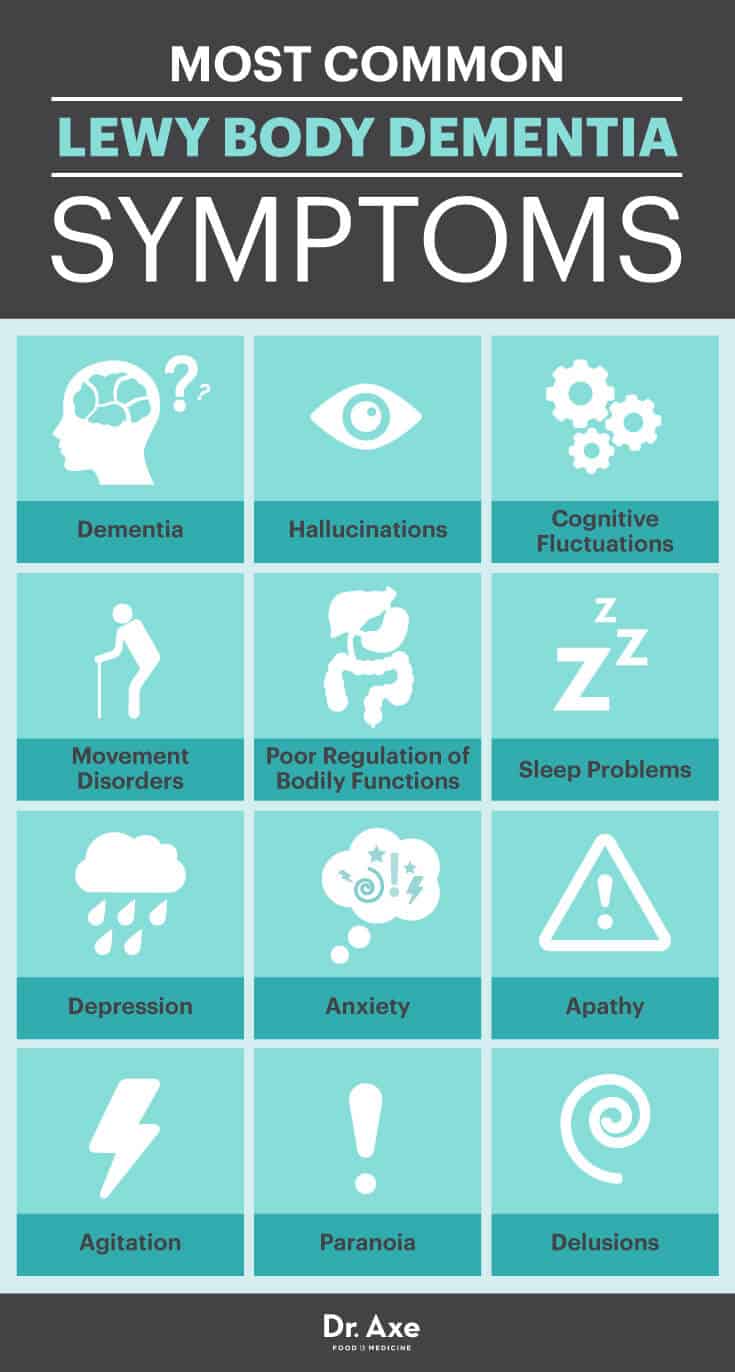
Lewy Body Dementia is a progressive brain disorder. It shares traits with both Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Memory loss and movement issues are common. It’s marked by the presence of Lewy bodies — abnormal protein deposits in the brain.
Hallucinations in LBD can be vivid and frequent. Patients might see people or animals that aren’t there. These visions are not just visual; they can involve sounds, smells, or sensations. Recognizing these as symptoms can help in managing them effectively.
The hallucinations can cause distress for patients. They can lead to sleep problems, anxiety, and sometimes aggression. Caregivers must cope with the challenges of reassurance and safety. Understanding and patience become crucial in this journey. Support networks and medical guidance are key in lessening the load on all involved.
Credit: draxe.com
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) touches lives with a unique set of challenges. Among these, hallucinations stand prominent. They unravel realities, often leaving patients and caregivers in distress. Medical strategies play a pivotal role in limiting these troubling symptoms. Let’s explore how.
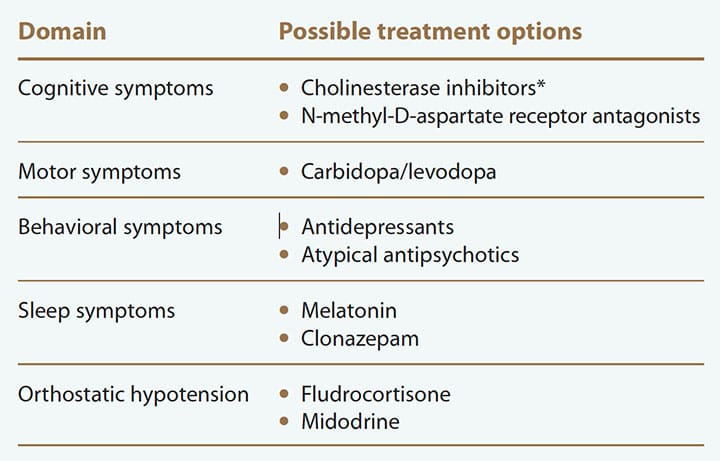
Doctors use medicine to help with LBD hallucinations. These drugs work on brain chemicals to reduce symptoms.
Medicines should match individual needs. A doctor will decide the best course.
Medication carries risks, especially with LBD’s complex nature.
| Medicine Type | Possible Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Cholinesterase Inhibitors | Nausea, appetite loss, increased heart rate |
| Antipsychotics | Sedation, balance problems, severe motor issues |
| Antidepressants | Weight gain, sexual dysfunction, dry mouth |
Monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential to prevent unwanted effects.
Determining success requires observation. Families and doctors should watch for changes in behaviors, the frequency of hallucinations, and overall quality of life.
It’s important to balance benefits with side effects. Frequent check-ups ensure patients are receiving the best possible care.
Remember, treatment success varies. Patience and adjustments are key to management in Lewy Body Dementia.
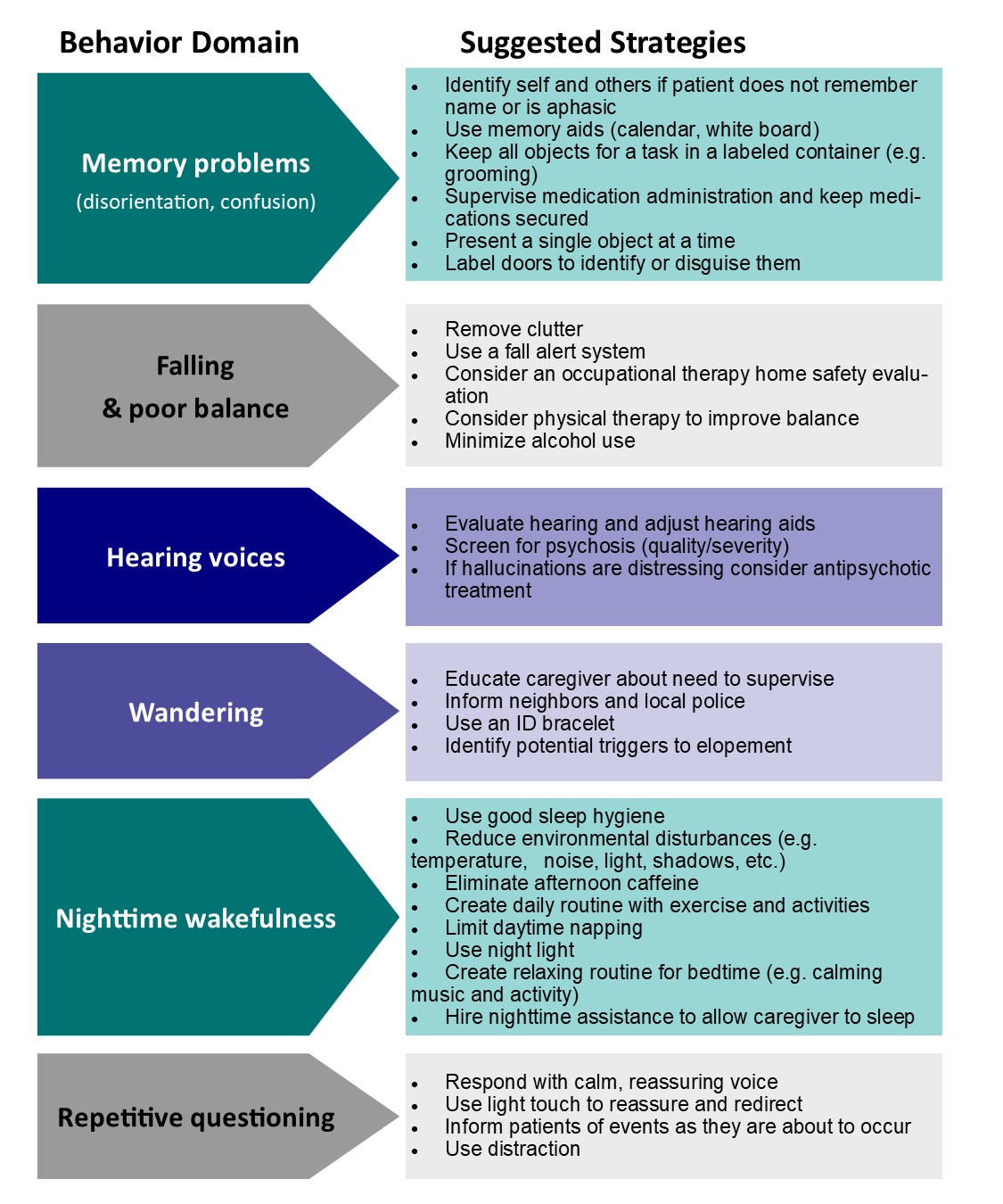
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) often presents unique challenges, including hallucinations which can be distressing for both patients and caregivers. While medication is commonly prescribed, non-pharmacological strategies play a crucial role in managing these symptoms. These tactics foster a sense of comfort and control without the risks associated with drug therapy. Let’s delve into some effective non-medicinal methods to handle LBD-related hallucinations.
Creating a safe and soothing environment is key in minimizing hallucinations. Consider these strategies:
Engage sufferers in activities that promote well-being and distract from hallucinations:
Effective communication is essential for emotional support:
Credit: www.myamericannurse.com
Manage Lewy body dementia hallucinations by providing reassurance, avoiding confrontation, and ensuring a well-lit environment. Consult a doctor about medications or therapies that may help control symptoms. Keep the patient’s surroundings calm and familiar to reduce hallucination triggers.
Cholinesterase inhibitors and antipsychotic medications can help reduce hallucinations in Lewy body dementia. Doctors usually prescribe these carefully due to potential side effects.
People with Lewy body dementia should avoid antipsychotic medications, which can worsen symptoms. They should also limit stress, avoid sleep deprivation, and steer clear of overstimulation. Regular routines and a calm environment are beneficial.
Currently, there is no treatment that can slow the progression of Lewy body dementia, but certain medications may help manage symptoms. Regular exercise and cognitive activities could offer some quality of life benefits.
Treating hallucinations in Lewy body dementia demands patience and sensitivity. Collaboration with healthcare professionals ensures the best therapeutic approach. Medication, lifestyle changes, and supportive care offer hope. Remember, each journey is unique—stay informed, stay supportive. Embrace every good day, and always seek out moments of joy and comfort.