Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

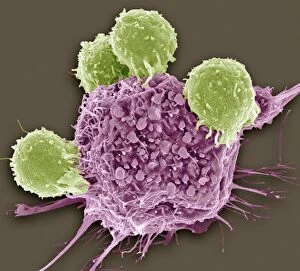
Lymphocytic Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the white blood cells in the body. It is characterized by an overproduction of lymphocytes, which can crowd out healthy blood cells and impair the immune system’s ability to fight infections.
Credit: www.licensestorehouse.com
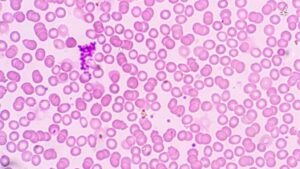
Lymphocytic leukemia is a type of blood cancer that affects the white blood cells known as lymphocytes. These lymphocytes are an important part of our immune system, helping us fight off infections and diseases. When these cells become cancerous and multiply uncontrollably, it leads to lymphocytic leukemia. This condition can affect both children and adults, and understanding its different types, causes, and risk factors is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
There are two main types of lymphocytic leukemia: acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Understanding these distinctions is essential, as they have different characteristics and require different treatment approaches.
The exact causes of lymphocytic leukemia are still unknown, but several factors can increase the risk of developing the disease:
It’s important to note that having one or more risk factors does not guarantee the development of lymphocytic leukemia. Many people with the disease have no known risk factors, and some individuals with multiple risk factors never develop the condition.
If you or your loved ones experience symptoms such as fatigue, unexplained weight loss, painless swelling of the lymph nodes, frequent infections, or easy bruising and bleeding, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. Early detection and prompt treatment can significantly improve the outlook for individuals with lymphocytic leukemia.
Lymphocytic Leukemia is a form of blood cancer that affects the white blood cells in the body. Like other types of leukemia, it can be challenging to detect in its early stages, as the symptoms may be vague and easily mistaken for other common illnesses. However, being aware of the signs and symptoms of lymphocytic leukemia can help in early diagnosis and prompt medical intervention. In this section, we will explore the common symptoms and late-stage symptoms of lymphocytic leukemia.
Lymphocytic leukemia often presents with a range of symptoms that are commonly seen in various other medical conditions. Hence, it is crucial to be vigilant and consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of the following:
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is crucial not to ignore them and to seek medical attention promptly. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes in lymphocytic leukemia.
As the disease progresses, the symptoms of lymphocytic leukemia may escalate, indicating its advancement to the later stages. Late-stage symptoms may include:
It is important to note that the presence of these late-stage symptoms indicates that lymphocytic leukemia has advanced significantly. Timely medical intervention becomes even more crucial at this stage to manage symptoms and explore appropriate treatment options.
Lymphocytic Leukemia Diagnosis and Staging: Accurate diagnosis and staging play a vital role in determining the best treatment approach for lymphocytic leukemia patients. Through various tests and evaluations, healthcare professionals can effectively determine the extent of the disease, enabling personalized and targeted treatment plans.
When it comes to diagnosing lymphocytic leukemia, healthcare professionals rely on a series of diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of this condition. These tests help in accurately identifying the specific type of leukemia and determining the appropriate treatment plan for the patient.
One of the initial steps in diagnosing lymphocytic leukemia is a complete blood count (CBC) test. This test measures the levels of various blood components, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. A high number of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, may indicate the presence of leukemia.
If the blood tests show abnormalities, the next step is usually a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. This procedure involves the extraction of a small sample of bone marrow from the hip bone under local anesthesia. The extracted sample is then examined under a microscope to determine the presence of leukemia cells.
Additionally, imaging tests like CT scans or X-rays may be performed to assess the spread of leukemia to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes or internal organs. These tests help in the staging process, which helps determine the extent and severity of the disease.
Staging is a crucial step in the diagnosis of lymphocytic leukemia, as it helps determine the appropriate treatment plan and prognosis. The staging process categorizes the disease into different stages based on the extent of spread and involvement of various organs.
In stage 0, also known as cancer in situ, the leukemia cells are confined to the bone marrow and have not spread to other areas of the body. At this early stage, the prognosis is usually more favorable, and treatment may focus on close monitoring and preventative measures.
In stage I, the cancer has spread beyond the bone marrow to other lymph nodes and organs. However, the spread is still limited, and the prognosis remains relatively positive. Treatment options at this stage may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapies.
Stage II is characterized by further spread of leukemia cells, involving multiple lymph nodes and organs. The prognosis at this stage becomes more uncertain, and treatment strategies may involve aggressive chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation, or clinical trials.
Stage III signifies a more advanced form of lymphocytic leukemia, with widespread involvement of multiple organs, such as the liver, spleen, or lungs. Treatment options at this stage often focus on palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Stage IV is the most advanced stage of lymphocytic leukemia, indicating the presence of leukemia cells in organs beyond the bone marrow, such as the brain or spinal cord. Treatment options for stage IV leukemia may include palliative care, clinical trials, or experimental therapies.
In conclusion, the diagnosis and staging of lymphocytic leukemia play a crucial role in determining the appropriate treatment plan and predicting the prognosis. Through a series of diagnostic tests and staging evaluations, healthcare professionals can provide personalized care and support for individuals affected by this condition.

Credit: www.fiercebiotech.com
When it comes to lymphocytic leukemia, there are several treatment options available to help manage the disease and improve the patient’s overall health. These treatment options include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and stem cell transplantation. Let’s take a closer look at each of these options:
Chemotherapy is one of the most common treatment options for lymphocytic leukemia. It involves the use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells and prevent their growth. This form of treatment is usually administered in cycles, allowing the body time to recover between treatments. Chemotherapy can be given intravenously or orally, depending on the specific needs of the patient.
During chemotherapy, the patient may experience side effects such as nausea, hair loss, and fatigue. However, these side effects are often manageable and temporary. It is important for patients to communicate with their healthcare team about any concerns they have during the treatment process.
Targeted therapy is another treatment option that specifically targets the cancer cells without harming the healthy cells in the body. This form of treatment works by blocking the specific molecules or proteins that are involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells.
In lymphocytic leukemia, targeted therapy may involve the use of medications that target specific genetic mutations or abnormalities in the cancer cells. These medications can help slow down the progression of the disease and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Stem cell transplantation, also known as a bone marrow transplant, is a treatment option that involves replacing the patient’s diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells. This procedure allows for the production of healthy blood cells and helps to restore the immune system.
In some cases, stem cell transplantation may be recommended for patients with lymphocytic leukemia who have not responded well to other treatments or have a high risk of relapse. It is an intensive treatment option that requires a suitable donor and careful monitoring after the procedure.
Overall, these treatment options provide hope for patients with lymphocytic leukemia. With advancements in medical technology and ongoing research, the outlook for patients continues to improve. It is important for patients to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the best treatment plan for their individual needs.
Living with lymphocytic leukemia can be challenging both physically and emotionally. However, with the right coping strategies and support networks in place, it is possible to navigate through this journey with strength and resilience. In this section, we will explore some coping strategies that can help individuals with lymphocytic leukemia to effectively manage their condition and the crucial role that support networks play in their overall well-being.
When facing lymphocytic leukemia, it is essential to develop coping strategies that can help ease the physical and emotional burden. Here are some effective strategies:
Having a strong support network is crucial for individuals living with lymphocytic leukemia. These networks can provide emotional, practical, and informational support that can significantly impact their well-being. Here are some key reasons why support networks are essential:
By implementing effective coping strategies and building strong support networks, individuals with lymphocytic leukemia can enhance their quality of life and better navigate the challenges they face. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there is support available to help you every step of the way.

Credit: www.licensestorehouse.com
The survival rate for lymphocytic leukemia varies depending on factors such as the patient’s age and overall health. However, advancements in treatments have significantly improved survival rates in recent years. It is best to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate prognosis based on individual circumstances.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is not considered curable, but it can be managed for many years with treatment.
Yes, individuals with chronic lymphocytic leukemia can live a full life with proper medical care and management. Regular treatment and monitoring can help control the disease and its symptoms, allowing patients to maintain a good quality of life.
Lymphocytic leukemia is primarily caused by genetic mutations in white blood cells called lymphocytes. These mutations disrupt the normal growth and function of the cells, leading to their uncontrolled growth and accumulation in the bone marrow and blood.
Lymphocytic leukemia is a complex and serious medical condition that affects the immune system. Understanding the different types and subtypes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare professionals, patients can navigate the challenges of living with this disease.
Remember to prioritize regular check-ups, follow treatment plans, and seek emotional support to manage the physical and emotional aspects of lymphocytic leukemia.