Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
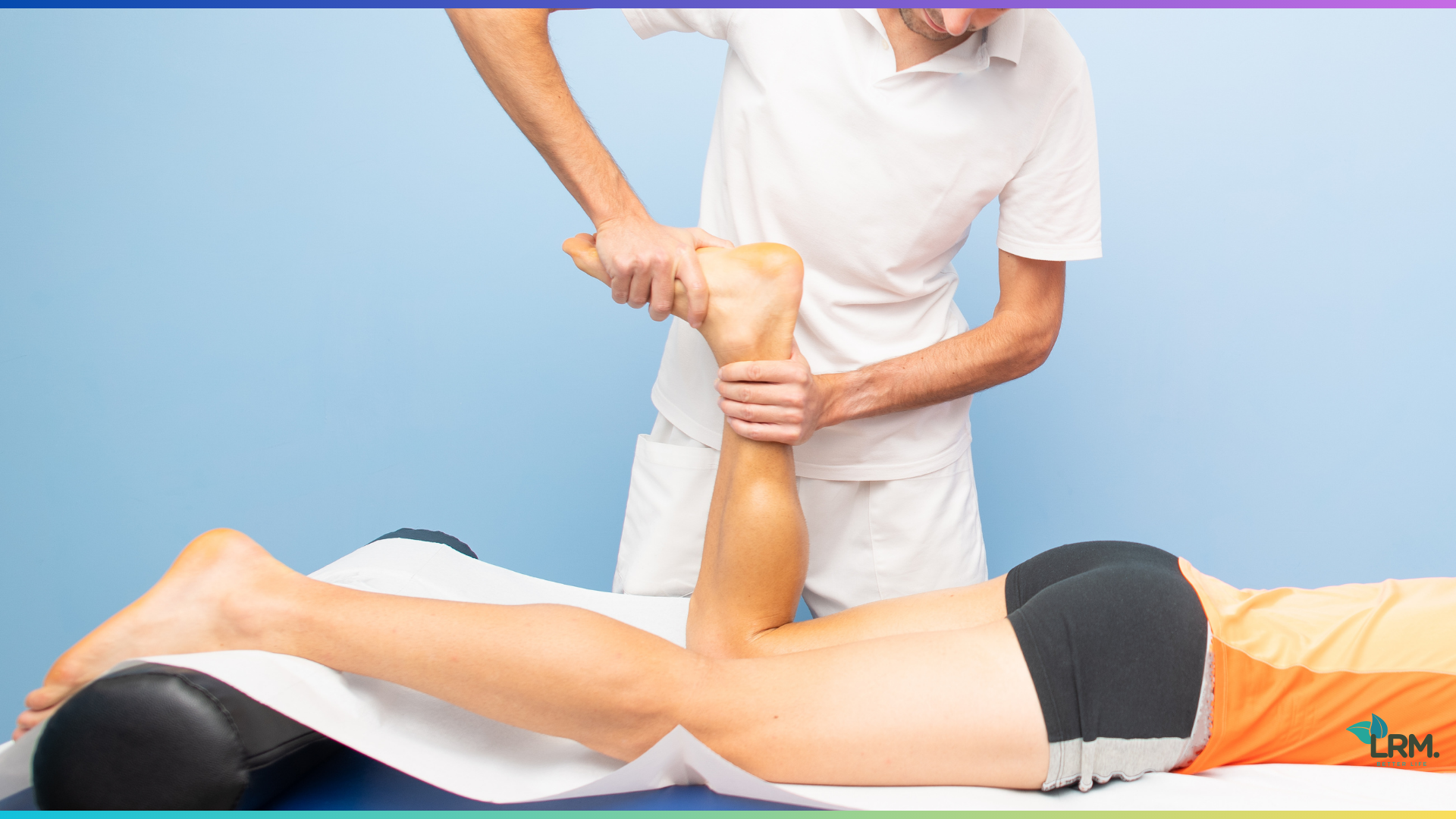
Managing patellar tendonitis in athletes involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to activity. Strengthening exercises and proper biomechanics play key roles in the recovery process.
Patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, is a common overuse injury that can significantly impact an athlete’s performance and long-term health. By following a structured rehabilitation program and identifying and addressing potential risk factors, athletes can effectively manage and prevent the recurrence of patellar tendonitis.
We will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for patellar tendonitis, as well as provide practical tips for athletes looking to recover and return to their sport stronger than before.
Patellar tendonitis is mainly caused by repetitive stress on the patellar tendon.
Athletes prone to overuse injuries are at a higher risk for patellar tendonitis.
Pain just below the kneecap during activities like running or jumping.
Stiffness in the knee, especially after prolonged periods of rest.
Before any intense physical activity, athletes should engage in dynamic warm-up exercises.
Including specific exercises targeting the quadriceps and hamstrings in strength training routines can help prevent patellar tendonitis.
Patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, is a common overuse injury in athletes, particularly those involved in jumping sports. It causes pain and tenderness just below the kneecap, which can impact an athlete’s performance and lead to long-term issues if not managed properly. Fortunately, there are effective treatment options available to help athletes manage and recover from patellar tendonitis.
Rest is crucial in the management of patellar tendonitis. Athletes should refrain from activities that exacerbate the pain and inflammation in the affected area. Ice therapy can help reduce pain and swelling. Applying an ice pack to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can provide relief.
Physical therapy plays a key role in the rehabilitation of patellar tendonitis. Eccentric exercises, where the muscle lengthens while under tension, have been shown to be particularly effective in strengthening the tendon and promoting healing. Quad strengthening exercises can also help alleviate stress on the patellar tendon.
Managing patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, requires a comprehensive approach that includes both rehabilitation and long-term management strategies. By focusing on these aspects, athletes can not only recover from their injury but also reduce the risk of recurrence. In this article, we will explore two critical components of addressing patellar tendonitis in athletes: gradual return to physical activity and long-term management strategies.
After a period of rest and healing, it is important for athletes with patellar tendonitis to gradually return to their desired level of physical activity. Rushing the process can lead to further damage and setbacks. Here are some steps to consider when planning a gradual return:
A gradual return to physical activity allows the body to adapt and heal while minimizing the risk of re-injury. By following these steps, athletes can safely regain their strength and performance while managing their patellar tendonitis effectively.
While a gradual return to physical activity is essential, long-term management strategies play an equally crucial role in the ongoing care of patellar tendonitis. Here are some strategies to consider:
By following these long-term management strategies, athletes can actively manage their patellar tendonitis and minimize the chances of future flare-ups. Prioritizing these strategies as part of an ongoing lifestyle helps ensure optimal performance and overall wellbeing.
To optimize performance and prevent injuries in athletes, it is crucial to manage patellar tendonitis effectively. Utilizing targeted exercises, proper warm-ups, and incorporating rest into training schedules can minimize the risk of this common overuse injury. Additionally, working with a sports medicine professional can provide personalized guidance for recovery and injury prevention.
The patellar tendon plays a critical role in the stability and function of the knee joint, making it particularly susceptible to injury in athletes. To optimize performance and prevent patellar tendonitis, it is essential to build resilience in this important tendon.
Preventing patellar tendonitis and other knee injuries requires implementing effective strategies for injury-free training. Here are some tips to help athletes reduce the risk of developing patellar tendonitis:
By following these strategies and building resilience in the patellar tendon, athletes can optimize their performance and reduce the risk of developing patellar tendonitis and other knee injuries. Remember, prevention is always better than cure!

Credit: www.scribd.com
Patellar tendonitis is the inflammation of the patellar tendon, typically caused by repetitive activities. Athletes involved in sports like running, jumping, and volleyball are at higher risk due to constant strain on the tendon.
Common symptoms of patellar tendonitis include pain and tenderness around the patellar tendon, especially during activities. Swelling, stiffness, and difficulty in moving the knee are also experienced.
Managing patellar tendonitis involves a combination of rest, ice therapy, compression, elevation, and physical therapy exercises. It’s crucial to modify activities, wear proper footwear, and gradually increase intensity to avoid further damage.
Yes, athletes can prevent patellar tendonitis by implementing pre and post-activity stretching, proper warm-up routines, strengthening exercises, using appropriate footwear, and avoiding sudden increases in training intensity.
Managing patellar tendonitis in athletes is crucial for their performance and overall well-being. By implementing a comprehensive treatment plan, including rest, targeted exercises, and proper equipment, athletes can effectively alleviate symptoms and prevent reoccurrence. It’s essential to focus on prevention and seek professional guidance to ensure a successful recovery.

