Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Senile atopic dermatitis is a common skin condition seen in older individuals, characterized by inflammation, itching, and dryness of the skin. In this condition, the skin barrier becomes compromised, leading to increased vulnerability to irritants and allergens.
This can result in recurrent flare-ups and discomfort. Although the exact cause of senile atopic dermatitis is not fully understood, factors like genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers may play a role. Management typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, such as using gentle cleansers, avoiding known triggers, and keeping the skin well moisturized, along with medications to relieve symptoms and control inflammation.
It’s important to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Senile Atopic Dermatitis is a skin condition that predominantly affects older adults. It is characterized by itchy, dry, and inflamed skin, which can be uncomfortable and distressing for those experiencing it. By understanding this condition and its underlying causes, individuals can take the necessary steps to manage and alleviate its symptoms effectively.
Senile Atopic Dermatitis is a type of eczema that occurs in older individuals. Eczema is a chronic skin disorder characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. In the case of Senile Atopic Dermatitis, these symptoms tend to develop later in life, typically after the age of 60. The condition is more common in individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever.
The exact causes of Senile Atopic Dermatitis are not well understood, but experts believe it results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Here are some potential causes and triggers:
Understanding the causes of Senile Atopic Dermatitis is essential in managing the condition effectively. By identifying and avoiding triggers, implementing a proper skincare routine, and seeking medical advice, individuals can keep their symptoms under control, leading to improved quality of life.

Credit: issuu.com
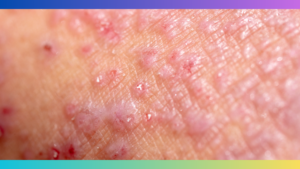
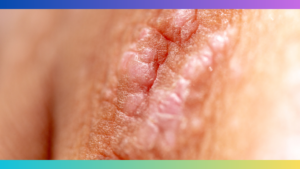
Senile Atopic Dermatitis, also known as elderly eczema, is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects older adults. It is important to be able to recognize the symptoms of Senile Atopic Dermatitis in order to seek appropriate treatment and avoid confusion with other skin conditions.
These symptoms may vary in severity from person to person and can flare up periodically. It is crucial to pay attention to any changes in the skin’s appearance or sensation and consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
While Senile Atopic Dermatitis shares some symptoms with other skin conditions, there are certain factors that can help distinguish it from similar issues:
| Senile Atopic Dermatitis | Contact Dermatitis | Psoriasis |
|---|---|---|
| Age-related onset | Caused by exposure to irritants or allergens | Autoimmune condition |
| Associated with family history of eczema or allergies | Triggered by specific substances or materials | Thick, silvery scales on the skin |
| Affected areas frequently include the arms, legs, and hands | Localized to the exposed areas of contact | Commonly affects elbows, knees, and scalp |
If you suspect you may be experiencing Senile Atopic Dermatitis, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Remember, recognizing the symptoms and seeking early intervention can help manage Senile Atopic Dermatitis effectively, improving your quality of life.
Senile Atopic Dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic condition that commonly affects older individuals. Characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, managing this condition requires a careful approach to skincare and lifestyle choices. In this section, we will explore two key aspects of managing Senile Atopic Dermatitis: an effective skincare regimen and avoiding triggers.
An effective skincare regimen is essential for managing Senile Atopic Dermatitis and providing relief from its symptoms. Here are some tips to create a skincare routine that works:
Creating a consistent skincare routine and sticking to it can help manage Senile Atopic Dermatitis effectively.
To minimize flare-ups and reduce the severity of Senile Atopic Dermatitis symptoms, it is important to identify and avoid triggers. Although triggers can vary from person to person, here are some common triggers to be aware of:
| Common Triggers | Notes |
|---|---|
| Extreme temperature changes | Dress appropriately for the weather and use humidifiers in dry environments. |
| Allergens | Avoid exposure to known allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods. |
| Harsh chemicals | Avoid contact with chemicals found in cleaning products, detergents, and personal care items. |
| Stress | Implement stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or regular exercise. |
Avoiding triggers can significantly improve the management of Senile Atopic Dermatitis, promoting healthier and more comfortable skin.
Senile Atopic Dermatitis can be effectively managed through various treatment options including medications, topical creams and ointments, light therapy, and lifestyle modifications. These approaches help alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve overall skin health for individuals with this condition.
One of the commonly prescribed treatment options for senile atopic dermatitis is the use of topical steroids. These medications work by reducing inflammation and relieving symptoms such as itching and redness. Topical steroids are available in different potencies, ranging from mild to strong, and are usually applied directly to the affected areas of the skin.
When using topical steroids, it is important to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare professional. Apply a thin layer of the medication to the affected area and gently massage it into the skin until fully absorbed. Avoid applying steroids on broken or damaged skin to minimize the risk of side effects such as skin thinning or discoloration.
It is important to note that prolonged or excessive use of topical steroids can lead to adverse effects. Follow the recommended treatment duration and do not exceed the prescribed dosage. If you experience any unusual side effects or your symptoms do not improve, consult your doctor.
In addition to topical steroids, using moisturizers and emollients can help manage senile atopic dermatitis symptoms. These products are designed to hydrate and soothe the skin, reducing dryness and itching.
Look for moisturizers and emollients that are specifically formulated for senile atopic dermatitis. They should be hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and gentle on the skin. Apply a generous amount of the product to the affected areas, gently massaging it in until fully absorbed.
Using moisturizers and emollients regularly can help restore the skin’s natural protective barrier and prevent further moisture loss. It is recommended to apply them at least twice daily or as directed by your healthcare professional. Consider using them immediately after bathing or showering to lock in moisture.
Senile Atopic Dermatitis is a chronic condition that can be managed by adopting certain preventive measures and making positive changes to your lifestyle. By following these tips, you can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups, improve your quality of life, and maintain healthy skin.
In addition to preventive measures, there are certain lifestyle changes you can make to improve your overall quality of life while living with Senile Atopic Dermatitis.
By following these prevention and lifestyle tips, you can effectively manage Senile Atopic Dermatitis and improve your overall well-being. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.

Credit: onlinelibrary.wiley.com

Credit: www.amazon.com
Senile eczema is caused by a combination of factors including dry skin, aging, immune system changes, and genetics. These factors can lead to inflammation and itchiness in older adults, resulting in senile eczema.
Treat dermatitis in the elderly by keeping the skin clean, using gentle cleansers, applying moisturizers, avoiding irritants, and using corticosteroid creams.
The cause of atopic dermatitis is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with atopic dermatitis have a compromised skin barrier, allowing irritants and allergens to penetrate the skin and trigger an immune response.
Eczema and dermatitis are terms used interchangeably to describe a skin condition that causes redness, itching, and inflammation. Both refer to the same condition, but dermatitis is a more general term that encompasses various types of skin inflammation, including eczema.
To effectively manage senile atopic dermatitis, it is crucial to adopt a comprehensive skincare routine and make necessary lifestyle changes. Regular moisturizing, avoidance of triggers, and appropriate medication can help alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for those living with this condition.
Remember, consulting a healthcare professional is always advisable for a personalized treatment plan. By taking proactive steps, individuals can regain control over their skin health and enjoy a better quality of life.