Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Sleep disturbances in dementia patients often lead to decreased quality of life and increased caregiver stress. These disruptions manifest as difficulty in falling asleep, frequent awakenings, and altered sleep patterns.
Understanding sleep disturbances in dementia patients is essential both for improving patient quality of life and easing the load on caregivers. Dementia often brings about changes in the brain that disrupt the sleep-wake cycle, leading to issues such as insomnia and irregular sleep rhythms.
As patients experience shifts in their sleep patterns, the challenge for healthcare providers and loved ones is to manage these disturbances effectively. This involves addressing contributing factors like the patient’s environment, daily routines, and overall health status. Tailored interventions can include optimizing the sleep environment, establishing consistent routines, and considering medical or therapeutic options. By prioritizing sleep management in dementia care, patients can achieve better rest, potentially slowing cognitive decline and enhancing well-being for both themselves and their caregivers.
Credit: www.aplaceformom.com
Sleep disruptions in dementia patients are not only common but also profoundly affect their well-being. Individuals with dementia may experience a range of sleep-related issues that impact their nighttime rest and daytime functionality. The aim here is to shed light on why these disturbances occur and how they manifest, to ultimately improve the quality of life for those affected and their caregivers.
Many dementia patients face troubles with sleep, but just how many? Studies suggest a significant number do. The fallouts include mood swings, increased confusion, and a higher risk of falls. Understanding these patterns is crucial for better care.
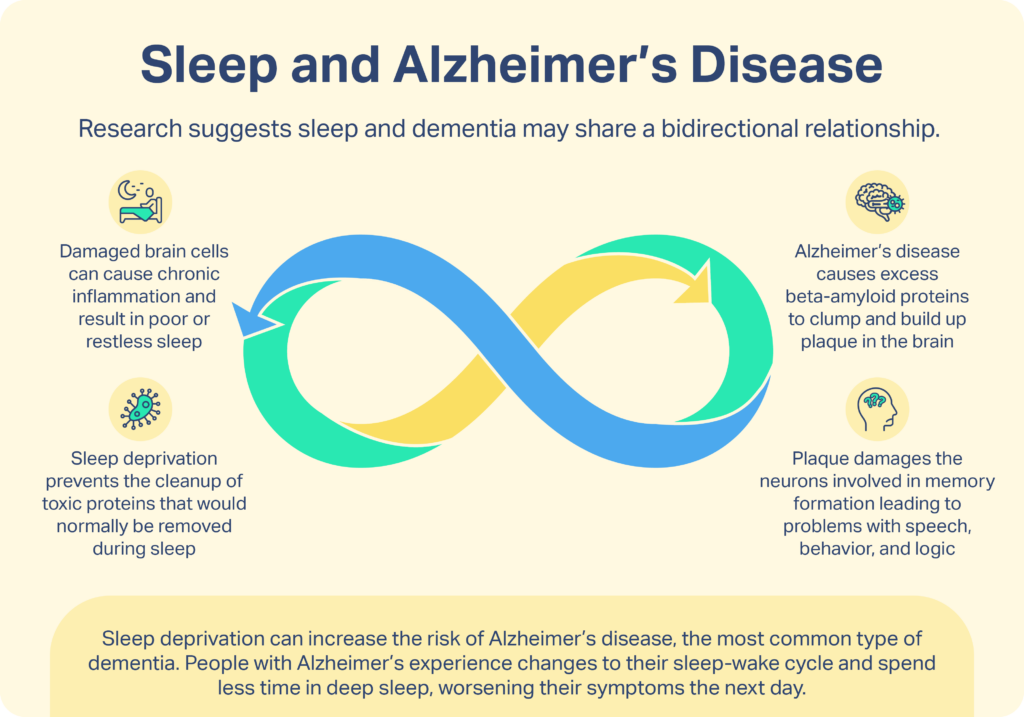
Dementia and disrupted sleep share a complex relationship. Brain changes in dementia can interfere with the sleep-wake cycle. Neurotransmitters that regulate sleep are often harmed, creating ongoing challenges for patients.
| Dementia Impact | Sleep Disruption |
|---|---|
| Brain Cell Damage | Altered Sleep Patterns |
| Neurotransmitter Imbalance | Difficulty Falling Asleep |
Dementia patients often experience a range of sleep issues that can disrupt their health.
Many dementia patients face tricky nights because of sleep disturbances. Their well-being hinges on understanding these challenges. Let’s dive into what stirs these restless nights.
In dementia, the brain undergoes significant changes. Neurons struggle to communicate, disrupting sleep-wake cycles. Dementia messes with the part of the brain that controls sleep. This leads to erratic sleep patterns. Nighttime restlessness often spikes as the brain’s internal clock gets muddled.
Adjusting these elements can boost sleep quality significantly.
Often, other health issues come with dementia. Conditions like sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome worsen sleep trouble. Painful ailments add to discomfort at night. Managing these can mean better sleep for dementia patients.
| Comorbidity | Impact on Sleep |
|---|---|
| Sleep Apnea | Interrupted breathing causes frequent waking. |
| Restless Leg Syndrome | Uncontrollable leg twitching leads to discomfort. |
| Chronic Pain | Continuous aches prevent deep sleep cycles. |
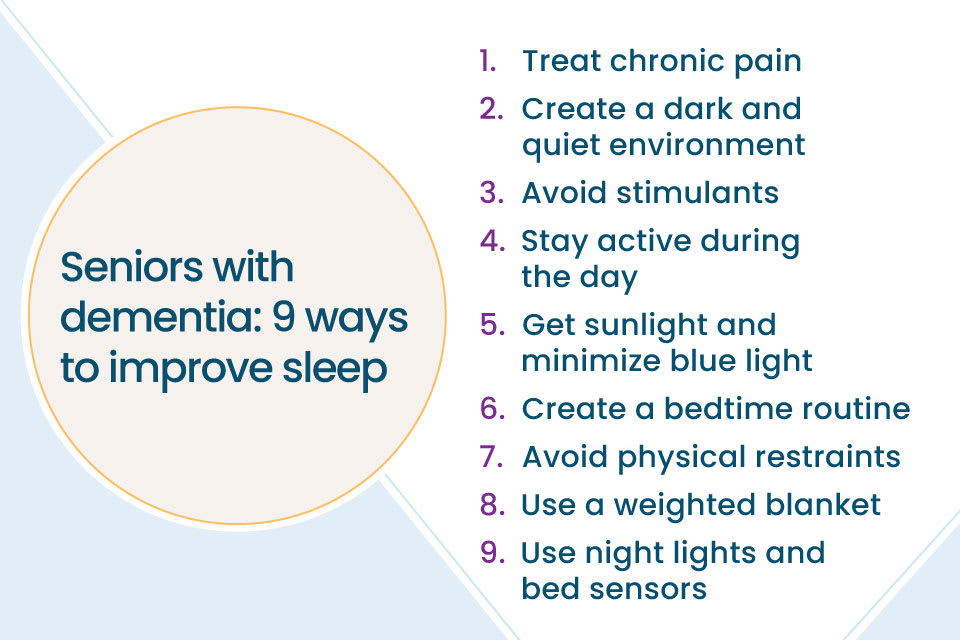
Strategies for Easing Nighttime Difficulties can significantly improve the quality of sleep for dementia patients. Not only does proper sleep benefit the patient, but it also helps caregivers by reducing nighttime stress and fatigue. With thoughtful approaches, both non-pharmacological and pharmacological, caregivers can create a more restful environment. Let’s explore some effective strategies.
| Medication | Use | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep-Aids | Induce sleep | Watch for side effects and dependency |
| Antidepressants | Address sleep disturbance related to depression | Ensure proper evaluation by a healthcare professional |
Credit: www.sleepfoundation.org
Good sleep is vital for health, including for those with dementia. Caregivers and healthcare providers play a key role in managing sleep disturbances in dementia patients. They create routines, environments, and strategies to promote better sleep. This support makes a huge difference in the well-being of patients.
A calming environment can promote better sleep. Caregivers are tasked with adjusting the bedroom to be more sleep-friendly. This might include:
Caregivers need the right tools to manage sleep issues. Training programs provide knowledge and strategies to help patients. Support groups offer emotional support. This training covers:
Sometimes, dementia-related sleep issues need extra help. Professional help is vital if:
This might involve consulting a sleep specialist or a neurologist. They can offer tailored solutions for dementia-related sleep problems.
The future outlook for research and development in the realm of sleep disturbances in dementia patients holds promise. With ongoing scientific inquiry, our understanding of dementia and its impact on sleep is evolving. Enhanced knowledge fosters innovations in care and therapy, paving the way for better management of sleep-related issues encountered by those with dementia.
Today’s scientific landscape is expanding our comprehension of how dementia influences sleep patterns. Studies embrace various dimensions of sleep disruption, from circadian rhythm alterations to the role of brain changes in sleep-wake cycles. Through dedicated research endeavors, insights emerge, guiding healthcare professionals toward more effective interventions.
Unfolding research raises hope for novel therapeutic paths. Experts are exploring medications that target brain chemicals to improve sleep quality. Non-pharmacological strategies, such as light therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy, also show significant potential. These innovations could revolutionize the well-being of dementia patients.
Each person’s experience with dementia is unique. Consequently, personalized care plans are crucial. The integration of personal sleep patterns, medical history, and lifestyle factors into care strategies ensures tailored support. This holistic approach acknowledges individual needs, fostering better sleep and quality of life for patients.
Credit: www.alz.org
Establish a regular bedtime routine and maintain a calm, comfortable sleep environment. Limit caffeine and naps, encourage physical activity during the day, and consider soothing music or white noise machines at night. Seek advice from a healthcare professional for personalized strategies.
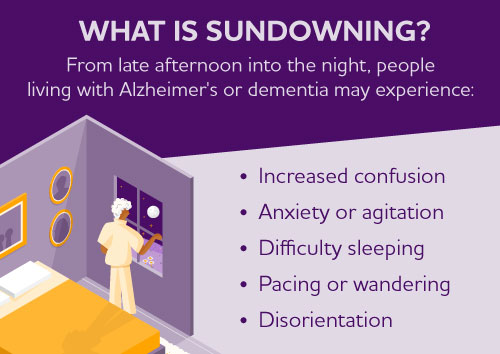
Sleep disturbances can occur in any stage of dementia but are often more prominent in the later stages.
Avoid arguing, don’t correct their reality, and never remind them about their forgetfulness.
Nursing homes use non-restrictive methods such as monitoring, frequent check-ins, and a calming bedtime routine to ensure dementia patients stay safely in bed at night. Comforting room environments and appropriate lighting also promote better sleep.
Navigating sleep issues is crucial for dementia patient well-being. Effective strategies and medical support can enhance rest for these individuals and their caregivers. Remember, proper sleep is not a luxury, but a necessity for health in dementia’s journey. Let’s strive for serene nights and better quality of life for all affected.