Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
The biology of beauty explains the science behind human attractiveness. Beauty is influenced by various biological factors.
Human attractiveness is a fascinating subject that has intrigued scientists and researchers for decades. It is a complex interplay of various biological factors that contribute to an individual’s attractiveness. The biology of beauty delves into the scientific understanding of what makes a person appealing to others.
From genetic factors that determine facial symmetry and body proportions to the role of hormones in determining attractiveness, there is a wealth of research that sheds light on this intriguing phenomenon. We will explore the different aspects of the biology of beauty and how it impacts human attractiveness. So, let’s embark on a journey to unlock the secrets behind what makes us visually appealing.

When it comes to human attractiveness, there is an intricate dance between genetics and beauty. Our genes play a vital role in determining our physical appearance, influencing everything from our eye color and facial structure to the symmetry of our features. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of genetics and its impact on beauty.
Your genetic makeup is essentially the blueprint that shapes your physical appearance. It determines the color of your eyes, hair, and skin, as well as various facial features such as the shape of your nose, lips, and chin. Genes also influence the development of traits that are commonly associated with attractiveness, such as clear skin, healthy hair, and symmetrical facial proportions.
The complex interplay of genes involved in physical appearance means that each individual possesses a unique combination that contributes to their overall attractiveness. While some people may possess genes that give them naturally symmetrical features and flawless skin, others may have genetic variations that lead to distinctive and interesting characteristics that are equally appealing.
Genetic variations are responsible for the small but significant differences that make each of us unique. These variations can have a profound impact on facial attractiveness. Research has shown that certain genetic variations can influence the symmetry, proportions, and overall harmony of facial features, which are key factors in determining attractiveness.
For example, a study conducted on identical twins showed that even slight differences in the expression of certain genes resulted in noticeable discrepancies in facial features and perceived attractiveness. Additionally, genes involved in collagen and elastin production can influence the quality of the skin, contributing to a youthful and radiant appearance.
It’s important to note that while genetics play a significant role in our physical appearance, environmental factors and lifestyle choices can also influence our attractiveness. Factors such as diet, exercise, skincare routines, and other external influences can either enhance or detract from our natural genetic potential.

Credit: www.technologyreview.com
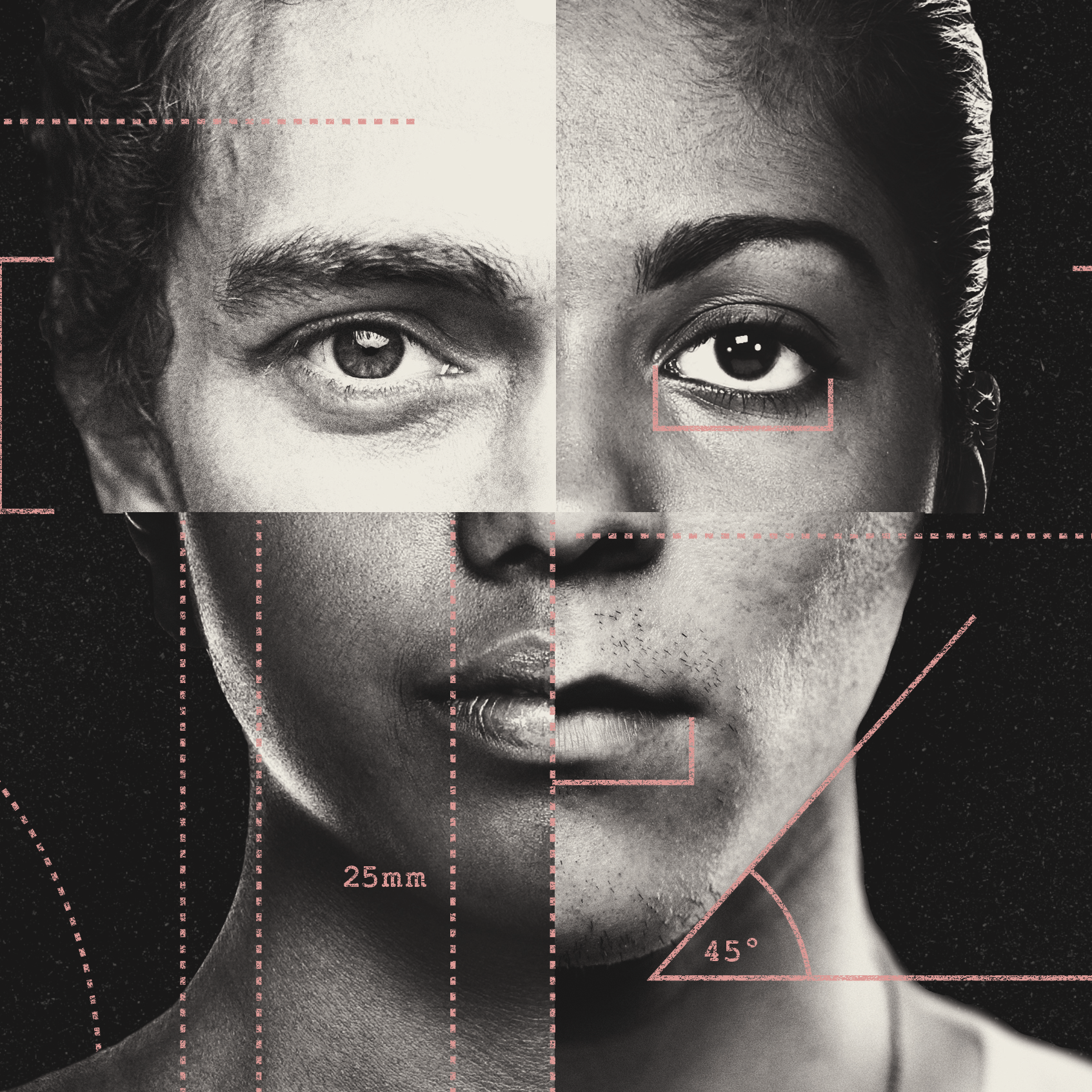
When it comes to facial beauty, one aspect that has been widely studied in the field of biology is symmetry. Scientists have long been intrigued by the significance of facial symmetry in human attractiveness. Evolutionary explanations also offer insights into why we are naturally drawn to symmetrical faces.
Facial symmetry refers to the degree of similarity between the left and right sides of a person’s face. Studies have shown that individuals with more symmetrical faces are generally perceived as more attractive. The reason behind this lies in our subconscious perception of facial symmetry as a sign of genetic fitness and health.
A symmetrical face is believed to indicate that an individual has good developmental stability, meaning they have experienced minimal genetic, environmental, or biological disturbances during their growth and development. Our brains are wired to perceive this as a desirable trait because it suggests that the individual possesses a strong genetic makeup and is more likely to pass down advantageous genes to their offspring.
From an evolutionary perspective, humans have developed a preference for symmetry as a way to ensure the survival and reproductive success of our species. By being attracted to individuals with symmetrical faces, we are unwittingly selecting partners who are more likely to have healthy offspring.
So, why are symmetrical faces considered more attractive? One theory suggests that symmetrical faces are easier for our brains to process and recognize. Our cognitive systems are designed to seek out patterns and symmetry, making it more pleasing and comfortable for us to look at faces that are proportionate and balanced.
Additionally, studies have found that symmetry in the face is related to the overall physical health and genetic quality of an individual. Symmetrical faces are thought to be an indicator of immunity to diseases, such as infections and parasites, that can affect facial development. By choosing partners with symmetrical faces, we may increase the likelihood of producing offspring with a stronger immune system.
In conclusion, the significance of facial symmetry in human attractiveness cannot be overstated. Our innate preference for symmetrical faces stems from our subconscious recognition of symmetry as a sign of genetic fitness, health, and the ability to produce healthy offspring. As we continue to delve deeper into the biology of beauty, understanding the role of facial symmetry provides us with valuable insights into the science behind human attractiveness.
Hormones play a crucial role in human attractiveness, shaping our physical appearance and behavior. The science behind human beauty is rooted in the biology of how hormones affect our development and perception of attractiveness.
Testosterone is a key hormone that plays a vital role in determining male attractiveness. This hormone is responsible for various physical attributes that are considered attractive in men. High levels of testosterone lead to the development of facial hair, a deep voice, and a muscular physique. These masculine features are often associated with strength and dominance, which can make men more attractive to potential partners.

Credit: www.yourtango.com
The psychology of beauty is a fascinating subject that explores the intricacies of how humans perceive attractiveness. Numerous psychological factors influence our perception of beauty, affecting whom we find attractive and why. This article delves into two key psychological factors that contribute to perceived beauty: the Halo Effect and Facial Attractiveness, as well as the impact of personal beliefs and cultural standards on beauty perception.
The Halo Effect is a psychological phenomenon where individuals tend to associate positive qualities with physically attractive people. Research shows that people who possess certain facial features, such as symmetry, clear skin, and proportionate features, are perceived as more attractive. The Halo Effect leads us to perceive attractive individuals as more intelligent, friendly, and successful, regardless of their actual qualities or achievements.
Facial attractiveness is determined by various factors, including facial symmetry, skin complexion, and facial proportions. Evolutionarily speaking, humans are drawn to symmetrical faces as they indicate good health and genetic fitness. Our brains are wired to subconsciously perceive symmetrical features as a sign of genetic quality, making individuals with symmetrical faces seem more attractive.
Furthermore, studies have shown that certain facial proportions, such as the golden ratio, are considered more aesthetically pleasing. The golden ratio refers to specific proportions found in nature that create harmony and balance. Faces that adhere to this ratio are often perceived as more attractive. However, it is important to note that beauty standards can vary across cultures and individual preferences.
Personal beliefs and cultural standards greatly influence our perception of beauty. Beauty ideals are not solely based on universal traits but also shaped by societal norms and cultural values passed down through generations.
For example, in certain cultures, a slender figure may be seen as attractive, while in others, a fuller figure may be prized. Similarly, features such as skin tone, hair color, and facial features can vary in terms of what is considered attractive across different cultures.
Personal experiences, media influence, and upbringing also contribute to personal beliefs about beauty. Messages conveyed through media platforms can significantly impact how individuals perceive attractiveness and internalize beauty standards. These societal influences can shape our preferences and impact our self-esteem.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Yes, there is a science behind attractiveness. Researchers explore various factors like symmetry, facial proportions, and body features to understand what makes a person attractive. Cultural and societal influences also play a role in determining beauty standards.
The biology of beauty is a summary of the scientific understanding behind attractiveness. It explores how genetics, hormone levels, facial symmetry, and physical health influence our perception of beauty.
Physical attractiveness is determined by various factors such as symmetry, facial features, and body proportions. Scientists believe that these characteristics are preferred due to evolutionary reasons.
Yes, there is a scientific basis to beauty. Studies show that certain facial symmetry, clear skin, and healthy hair contribute to attractiveness. Additionally, psychological factors, such as cultural ideals and personal preferences, influence how beauty is perceived. Beauty standards can vary across cultures, but there are scientific elements to beauty.
The biology of beauty delves into the intricate workings of human attractiveness. From facial symmetry to body proportions, our innate preferences for certain features are deeply rooted in evolutionary biology. By understanding the science behind what we find visually appealing, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of human attraction.
So, the next time you find yourself captivated by someone’s allure, remember that there is a fascinating biology at play behind it all.