Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
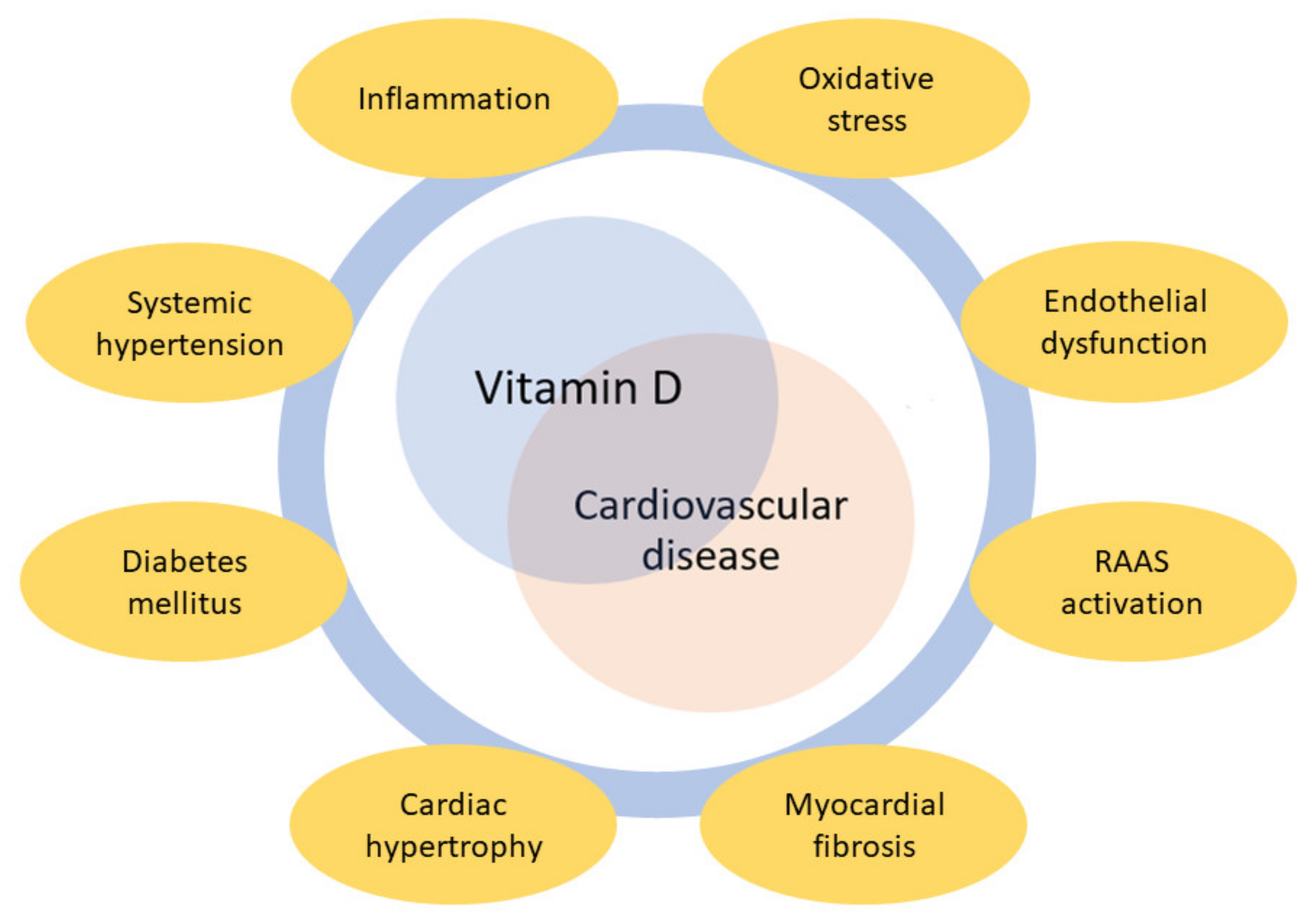
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining brain health and may help prevent dementia. Adequate levels can reduce the risk of cognitive decline and neuronal damage.
Understanding the importance of vitamin D in maintaining cognitive function is essential for preventing age-related diseases such as dementia. While research is ongoing, evidence suggests that vitamin D has neuroprotective properties, supporting brain health through the regulation of neurotrophic factors, neurotransmission, and oxidative stress mechanisms.
As the global population ages, dementia becomes an increasing concern with significant health, social, and economic impacts. Thus, identifying manageable factors like vitamin D supplementation could be key in devising preventive strategies against dementia. Regular exposure to sunlight and the consumption of vitamin D-rich foods or supplements may be simple yet effective measures in preserving mental faculties and enhancing quality of life for seniors.
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
Discover the crucial role Vitamin D plays in staving off dementia, highlighting its potential as a preventive agent. Unveiling the connection between adequate Vitamin D levels and reduced dementia risk offers fresh perspectives on neurological health management.
Vitamin D, often termed the “sunshine vitamin,” is crucial for maintaining strong bones and a healthy immune system. The body creates it when sunlight touches the skin. Yet, many don’t get enough sunshine. Foods like salmon, eggs, and fortified milk can help. Vitamin D aids in calcium absorption and ensures nervous system health. Without enough of it, our bones and overall health could suffer.
Dementia is not a single disease but a term that covers a wide range of specific medical conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease. It describes a set of symptoms affecting memory, social abilities, and daily functioning. The causes can be different for everyone, encompassing genetic factors, brain injury, and lifestyle or environmental factors. Knowing the types and causes helps in understanding the prevention strategies.
| Type of Dementia | Common Causes |
|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Genetic, lifestyle factors |
| Vascular Dementia | Stroke, blood vessel blockage |
| Lewy Body Dementia | Abnormal protein deposits in the brain |
Recent studies hint that Vitamin D plays a part in brain health. With its anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties, it could safeguard the brain. Researchers hypothesize that sufficient Vitamin D levels might reduce the risk of dementia. Elderly individuals with low Vitamin D often show poorer cognitive performance. Thus, maintaining adequate levels of this nutrient could be a key step in dementia prevention.
Did you know Vitamin D is more than just a bone health booster? It’s a key player in brain health too! Powerful studies reveal it might prevent dementia. Let’s dive into this vitamin’s brain-protecting secrets.
Research links low Vitamin D levels to a higher dementia risk. Scientists have looked at thousands of people over many years. They found something interesting:
Vitamin D is like a brain shield. It does several things:
These actions can keep your brain strong and sharp!
Does popping a Vitamin D pill help your brain? Some studies say yes.
| Trial | Results |
|---|---|
| The “D-Health Trial” | Participants with higher Vitamin D levels performed better on brain tests. |
| “VITAL Study” | Some signs of slowed down cognitive decline. |
While more research is necessary, Vitamin D could be a brain health hero.
Vitamin D plays a key role in maintaining brain health. Research suggests a link between vitamin D levels and the risk of developing dementia. Let’s explore how to ensure adequate vitamin D intake to potentially prevent cognitive decline.
Experts recommend different vitamin D amounts based on age, lifestyle, and health. To support cognitive health, adults need approximately 600 to 800 IU daily. Some researchers propose higher doses for those at risk of dementia, but always under medical supervision.
| Age Group | Recommended Intake (IU/day) |
|---|---|
| Adults (18-70) | 600 – 800 |
| Seniors (>70) | 800 – 1000 |
Sunlight is the best natural source of vitamin D. Aim for 10-30 minutes of midday sun several times per week. Diet and exercise also help. Include vitamin D-rich foods and stay active to enhance absorption.
Exercise, particularly outdoors, can increase vitamin D levels naturally. Adequate hydration supports all bodily functions, including nutrient absorption.
Determining the right supplement dose can be challenging. It is essential to test blood levels before starting supplementation. A healthcare provider can recommend the correct dose and form of vitamin D.
Consider potential interactions with other medications and be aware of the signs of vitamin D excess. Ongoing research continues to provide insights into optimal vitamin D levels for dementia prevention.

Credit: www.news-medical.net
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining our health, including potentially warding off dementia. As research unfolds, understanding the public health implications and the paths for future research become more important than ever.
Vitamin D deficiency is not just a personal health issue, it is a widespread public concern. Studies show that insufficient levels of vitamin D are linked to various cognitive declines. This connection emphasizes the need for greater awareness and action at a community level.
Implementing vitamin D enhancement strategies into dementia prevention is essential. Programs that promote sunshine exposure and dietary changes can make a big impact on public health.
The synergy between vitamin D and other factors in dementia prevention is a hot topic for research. Experts suggest that combining vitamin D with other interventions may offer stronger protection against cognitive decline.
| Research Focus | Key Benefits | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D with omega-3s | Enhances cognitive function | May reduce dementia risk |
| Vitamin D and exercise | Improves brain health | Could slow down ageing effects |
| Combination therapies | Targets multiple pathways | Promises a comprehensive approach |
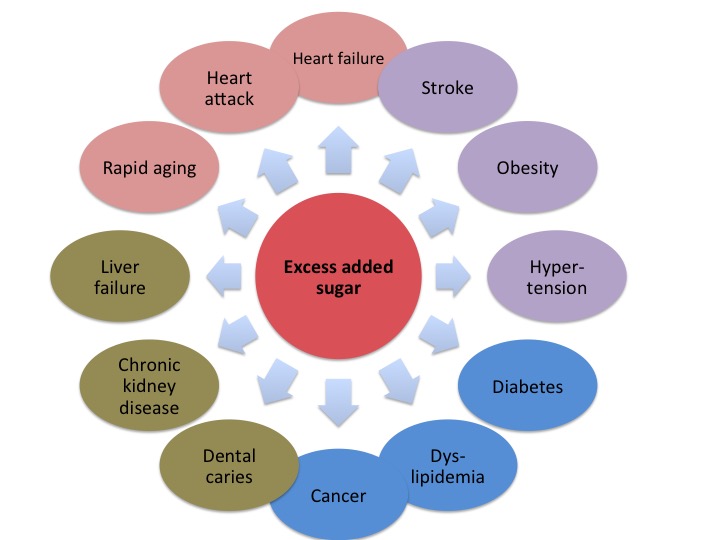
Credit: www.cardiacwellnessinstitute.com
Vitamin B12 plays a critical role in maintaining brain health and may help prevent dementia. Regular intake is essential, especially in older adults.
Vitamin D may help reduce Alzheimer’s risk by regulating brain function and reducing inflammation. Ongoing research examines its potential in Alzheimer’s treatment to improve cognitive health and slow disease progression.
Vitamin D’s role in preventing cognitive decline is still under research. Some studies suggest a correlation, yet conclusive evidence remains elusive. Maintaining adequate levels may support brain health.
Vitamin D3 is typically recommended for Alzheimer’s as it’s better absorbed by the body than vitamin D2. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Understanding vitamin D’s impact on cognitive health is crucial. It’s clear that sufficient levels may shield our brains from dementia-related decline. By maintaining healthy vitamin D levels through diet, supplements, and sunlight, we can potentially fortify our defenses against cognitive impairments.
Prioritizing this nutrient could be a significant step in safeguarding our mental acuity into old age. Remember, prevention is powerful.

