Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Urticaria and atopic dermatitis are common skin conditions characterized by itching, redness, and inflammation. These conditions can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergic reactions, stress, and genetic predisposition.
Urticaria, also known as hives, is characterized by itchy, raised welts on the skin that often appear suddenly and disappear within a few hours or days. Atopic dermatitis, on the other hand, is a chronic condition that causes dry, itchy, and red patches of skin.
Both conditions can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes, but it is important to consult with a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Credit: www.usdermatologypartners.com
Do you often experience itchy, red welts on your skin known as Urticaria? Understanding Urticaria is crucial to managing and treating this condition effectively. In this article, we will delve into the causes of Urticaria, providing you with the knowledge you need to take control and alleviate your symptoms. So let’s dive in and explore what exactly Urticaria is and what factors can trigger it.
Urticaria, commonly referred to as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of pruritic, red raised patches on the skin’s surface. These patches, also known as wheals, can vary in size and shape, often appearing and disappearing within hours or a few days. Urticaria is usually caused by a release of histamine, a chemical compound produced by our body’s immune system, leading to an allergic reaction. It can occur anywhere on the body and may be accompanied by itching, burning, or stinging sensations.
The exact causes of Urticaria can vary from person to person. While some individuals may experience hives as a result of specific triggers, others may develop them unexpectedly without an identifiable cause. Here are some common factors that can provoke Urticaria:
If you are experiencing recurrent or severe Urticaria, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Understanding the underlying causes can help you manage and minimize your symptoms effectively.
Credit: www.medicalnewstoday.com
When it comes to the diagnosis of urticaria, it is important to understand the symptoms and undergo medical tests to confirm the condition. Urticaria, often referred to as hives, is a common skin condition characterized by itchy bumps and red welts that can vary in size and shape. Atopic dermatitis, on the other hand, is a chronic skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and irritated patches of skin. In this section, we will focus on diagnosing urticaria and provide information about the symptoms and medical tests associated with this condition.
Urticaria is typically recognized by the appearance of raised, red, and itchy wheals or welts on the skin. These wheels can vary in size and shape, and they may appear and disappear within a few hours or even minutes. Common symptoms of urticaria include:
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. A medical expert will be able to determine whether you have urticaria or another skin condition and recommend appropriate treatment.
The diagnosis of urticaria involves a comprehensive evaluation of your symptoms and medical history. During a consultation with a healthcare provider, you may be asked questions about the duration and frequency of your symptoms, potential triggers, and any other relevant medical conditions you may have. This assessment helps the doctor to understand your specific case better and determine the appropriate medical tests.
In some cases, medical tests may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other possible causes. These tests may include:
These tests provide valuable insights into the underlying causes of urticaria and help guide the appropriate treatment plan. It is important to remember that the diagnosis and treatment of urticaria should always be conducted under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional.
If you are suffering from urticaria, also known as hives, you may be seeking ways to manage and alleviate the uncomfortable symptoms associated with this condition. Urticaria is characterized by red, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body and can be triggered by a variety of factors such as allergies, stress, or certain medications. In this article, we will explore some effective strategies for managing urticaria, including lifestyle changes and medications that can provide relief.
If you are looking to manage urticaria through lifestyle changes, there are several steps you can take to reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks:
If lifestyle changes alone do not provide sufficient relief, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to help manage the symptoms of urticaria:
| Medication | How it works |
|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Antihistamines block the effects of histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction. They can help relieve itching and reduce the severity of urticaria symptoms. |
| Corticosteroids | Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can provide relief for severe cases of urticaria. They are typically used for short periods due to potential side effects. |
| Immunosuppressants | In some cases, immunosuppressants may be prescribed to reduce the body’s immune response, thus alleviating urticaria symptoms. |
It is important to note that medications should be prescribed and supervised by a healthcare professional, as they can have potential side effects or interactions with other medications.
In conclusion, managing urticaria requires a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medications. By making certain modifications to your diet, avoiding triggers, and reducing stress, you can decrease the frequency and intensity of urticaria outbreaks. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for managing your specific condition.
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is crucial in managing its symptoms. This chronic inflammatory skin condition is often accompanied by urticaria, or hives, causing red, itchy patches on the skin. Recognizing triggers and implementing proper skincare routines can help alleviate discomfort and improve overall quality of life.
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin that can appear on different areas of the body. Atopic dermatitis often starts in infancy or early childhood and can continue into adulthood. While the exact cause is unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
Atopic dermatitis can be triggered by various factors, and understanding these triggers is essential for managing and preventing flare-ups. Here are some common triggers to be aware of:
1. Irritants: Substances like soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics can irritate the skin and worsen atopic dermatitis symptoms. It is recommended to opt for gentle, fragrance-free products and avoid scratchy materials.
2. Allergens: Certain allergens like pet dander, pollen, and dust mites can trigger flare-ups in individuals with atopic dermatitis. Identifying and avoiding these allergens can help in managing the condition effectively.
3. Climate: Extreme temperatures and low humidity can lead to dryness and exacerbate symptoms of atopic dermatitis. Maintaining a consistent, comfortable temperature and using a humidifier can help alleviate dry skin.
4. Stress: Emotional stress can aggravate atopic dermatitis symptoms. Finding healthy coping mechanisms, such as exercise, meditation, or therapy, can help manage stress levels and reduce flare-ups.
5. Food Sensitivities: Certain foods, such as dairy products, eggs, nuts, and soy, may trigger atopic dermatitis symptoms in some individuals. Identifying and eliminating these trigger foods from your diet may provide relief.
6. Infections: Skin infections, particularly caused by bacteria or viruses, can lead to flare-ups and worsen atopic dermatitis symptoms. Maintaining good hygiene and promptly treating any infections can help prevent exacerbations.
By understanding the triggers of atopic dermatitis and taking proactive measures to manage them, individuals can better control their symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve their overall quality of life.
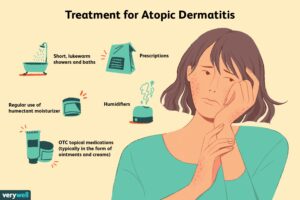
When it comes to managing and treating atopic dermatitis, there are various options to consider. Depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s specific needs, different treatment approaches may be recommended. In this article, we will explore two main categories of treatments for atopic dermatitis: topical treatments and systemic treatments.
Topical treatments are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and restore the skin’s moisture barrier. These treatments are usually the first line of defense for mild to moderate cases of atopic dermatitis. Some commonly prescribed topical medications include:
When topical treatments alone are insufficient or in severe cases, systemic treatments might be necessary. These treatments focus on targeting the underlying causes of atopic dermatitis from within the body. Some commonly prescribed systemic medications include:
It’s important to remember that each individual is unique, and what might work for one person may not work for another. Therefore, finding the right treatment approach often involves a trial-and-error process, closely supervised by a healthcare provider. By working together and considering factors such as the individual’s medical history, severity of symptoms, and personal preferences, an effective treatment plan can be developed to manage atopic dermatitis.
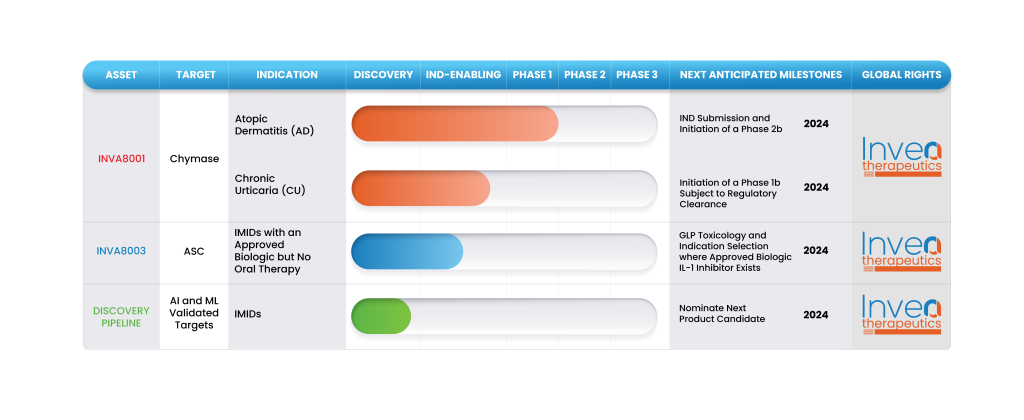
Credit: inveatx.com
Yes, atopic dermatitis can cause urticaria, resulting in itchy, red, and raised skin rashes. These conditions are both allergic reactions, which can be triggered by allergens, stress, or other factors affecting the immune system. Treatment for atopic dermatitis and urticaria may involve medication and avoiding triggers.
Treat urticaria dermatitis by relieving symptoms with antihistamines, applying cool compresses, and avoiding triggers. Consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment, which may include corticosteroids or immunosuppressants.
Urticaria and eczema can be mistaken for each other due to similar symptoms like redness and itching, but they are different skin conditions. Urticaria is characterized by raised hives that come and go quickly, whereas eczema is a chronic skin inflammation with dry, itchy patches.
Contact dermatitis is a skin reaction caused by direct contact with an irritant or allergen, resulting in redness, itching, and blistering. Urticaria, also known as hives, is a raised, itchy rash caused by allergic reactions, stress, or infections.
To sum up, both urticaria and atopic dermatitis are common skin conditions that can cause discomfort and distress. Understanding the triggers and taking appropriate measures can help manage the symptoms effectively. Whether it’s adopting a skincare routine, identifying and avoiding allergens, or seeking medical attention when necessary, proactive steps can greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with these conditions.
Remember, everyone’s experience with urticaria and atopic dermatitis is unique, so consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.