Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) stage 3 is divided into stages 3A and 3B based on the level of kidney function. In 3A, the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is between 45-59 mL/min, while in 3B, the GFR is between 30-44 mL/min.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a condition characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function over time. Stages 3A and 3B signify moderate to moderately severe reduction in kidney function, respectively. Understanding the difference between these stages is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to determine appropriate management and intervention strategies.
By delineating the variances between CKD 3A and 3B, individuals can better comprehend the implications for their health and make informed decisions about their treatment plans. Let’s delve deeper into the nuances of these CKD stages to gain a comprehensive understanding of their impact on kidney health and overall well-being.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a progressive condition that impacts the kidneys’ ability to function properly, leading to an accumulation of waste and fluid in the body. CKD is categorized into five stages, with stages 3A and 3B denoting a moderate decrease in kidney function. Understanding the specific differences between these two stages is crucial for individuals diagnosed with CKD. In this article, we will delve into CKD Stage 3A, focusing on its criteria, symptoms, and progression.
CKD Stage 3 is divided into two substages: 3A and 3B. Stage 3A is characterized by a mild to moderate decrease in kidney function, with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 45-59 ml/min per 1.73 m². This stage signifies a decline in the kidneys’ ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood, potentially leading to the accumulation of toxins in the body.
Individuals with CKD Stage 3A may not manifest noticeable symptoms at the onset. However, as the condition progresses, they may experience symptoms such as fatigue, swelling in the extremities, changes in urination patterns, and complications related to imbalanced electrolytes. In terms of progression, CKD Stage 3A can potentially advance to the more severe 3B stage if left unmanaged, emphasizing the importance of early detection and proactive management.
Looking into the details of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. In this article, we will explore the specifics of CKD stage 3B, including its definition and the differences from stage 3A.
Stage 3B of CKD is characterized by a moderately decreased kidney function with a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 30-44 ml/min. At this stage, the kidneys are not functioning optimally and individuals may start to experience symptoms such as fatigue, fluid retention, and changes in urination patterns. It’s essential for patients in stage 3B to closely monitor their kidney health and work with healthcare professionals to manage their condition.
While both stage 3A and 3B of CKD represent a decrease in kidney function, the key difference lies in the severity. Stage 3A is defined by a GFR of 45-59 ml/min, indicating a milder decrease in kidney function compared to stage 3B. Patients in stage 3A may have fewer symptoms and milder manifestations of kidney disease compared to those in stage 3B. It’s important for individuals to understand the distinctions between these stages as it can impact treatment and lifestyle modifications.
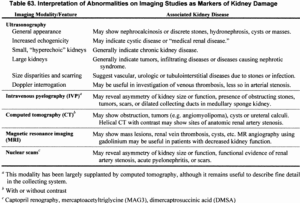
For Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) stages 3A and 3B, different tests are used to diagnose the specific stage of the condition.
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is crucial in determining the stage of CKD, with a GFR of 45-59 ml/min indicating stage 3A and 30-44 ml/min for stage 3B.
Regular monitoring is essential for patients in CKD stages 3A and 3B to track disease progression and manage symptoms effectively.
Monitoring should occur every 3 to 6 months, including blood pressure checks, GFR testing, and proteinuria assessments.

Credit: bmjopen.bmj.com
When it comes to managing chronic kidney disease, there are different treatment approaches that are tailored to each stage of the disease. In stages 3A and 3B, known as moderate CKD, taking proactive steps in terms of lifestyle changes and medical interventions can greatly improve the quality of life for patients.
Implementing lifestyle changes is often the first step in managing chronic kidney disease. Making these changes can help significantly slow down the progression of the disease and minimize symptoms. Below are some key lifestyle changes that play a crucial role in managing CKD:
In addition to lifestyle changes, there are several medical interventions that are commonly used to manage chronic kidney disease stages 3A and 3B. These interventions are aimed at slowing down the progression of the disease, managing symptoms, and preventing complications. Common medical interventions include:
By implementing these lifestyle changes and following medical interventions, individuals with stage 3A or 3B CKD can take an active role in managing their condition and improving their overall health outcomes. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and goals.
Chronic Kidney Disease 3A and 3B have different levels of kidney function, with 3A having a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 45-59 ml/min and 3B having a GFR of 30-44 ml/min. The difference in GFR levels impacts the complications and risk factors associated with each stage.

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Chronic Kidney Disease 3A and 3B differ based on the level of kidney function. 3A has a glomerular filtration rate of 45-59, while 3B is 30-44. Management involves lifestyle adjustments, medication, and monitoring to slow the progression of kidney damage and reduce complications.
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Understanding the prognosis for chronic kidney disease (CKD) stages 3A and 3B is crucial for effective management.
Exploring the different management strategies between CKD stages 3A and 3B can significantly impact patient outcomes.

Credit: link.springer.com
The symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease 3A and 3B include fatigue, swelling in the legs and ankles, changes in urine output, high blood pressure, and anemia. These symptoms may worsen over time and require medical attention.
Chronic Kidney Disease 3A and 3B differ based on the level of kidney function. 3A indicates a moderately decreased kidney function, while 3B signifies a further decline. The stages help healthcare professionals assess the disease progression and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Yes, Chronic Kidney Disease 3A can progress to 3B over time. The progression can be influenced by various factors such as underlying health conditions, lifestyle choices, and adherence to treatment plans. Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare professionals are crucial to manage and slow down the progression.
The treatment options for Chronic Kidney Disease 3A and 3B focus on managing the underlying cause, controlling blood pressure, maintaining a healthy diet, and monitoring kidney function. Medications, lifestyle modifications, and dialysis may be recommended depending on the severity of the disease.
Understanding the nuances between stages 3A and 3B of Chronic Kidney Disease is crucial. These variances in kidney function levels impact treatment and prognosis. Identifying and managing these stages early can significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Stay informed, consult with healthcare professionals for personalized care.