Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
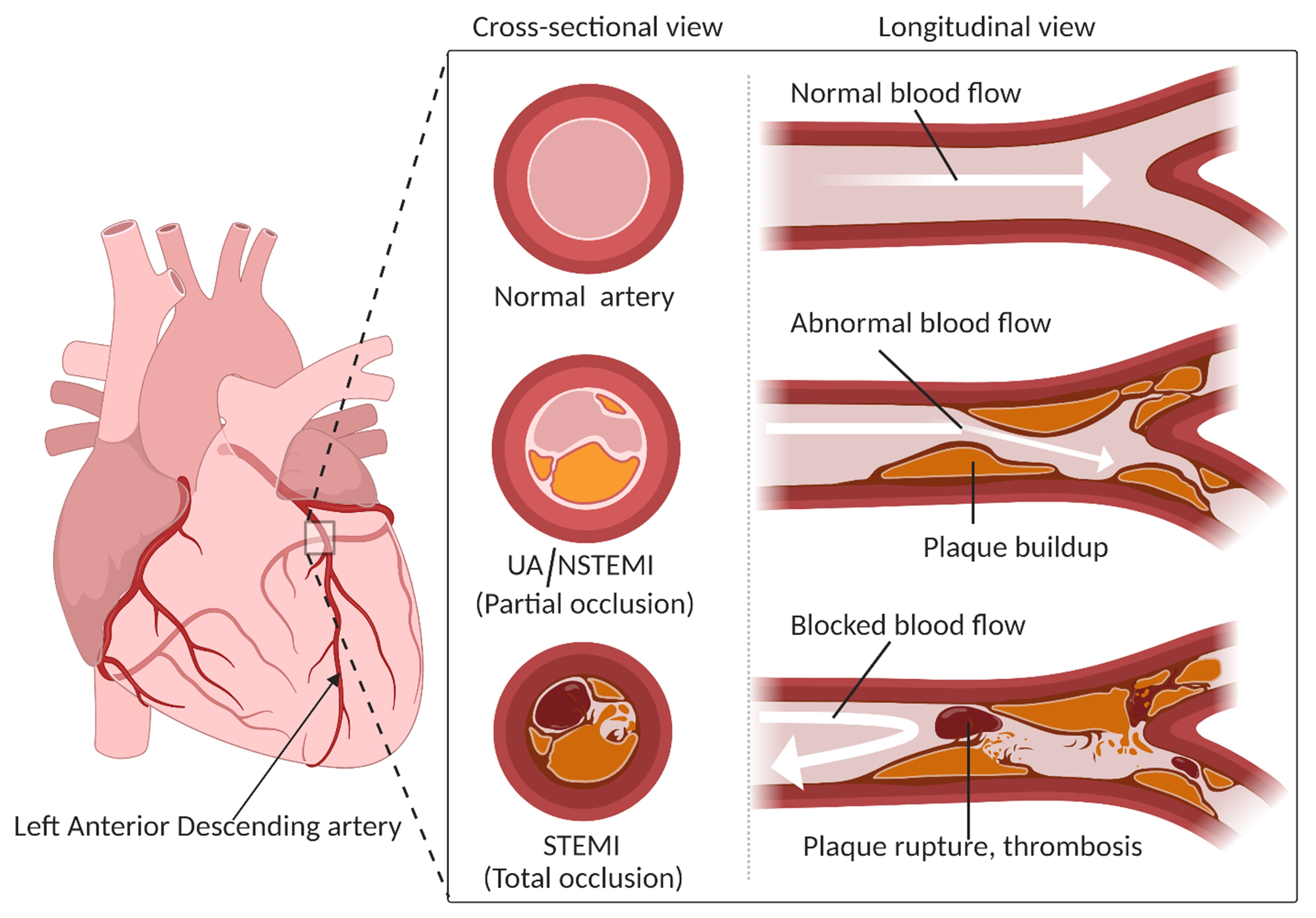
Coronary artery disease affects heart’s arteries, while peripheral artery disease affects arteries outside the heart. Coronary artery disease (CAD) and peripheral artery disease (PAD) are both common cardiovascular conditions, but they affect different parts of the body.
While CAD involves the narrowing or blockage of arteries supplying blood to the heart, PAD occurs when plaque builds up in arteries outside of the heart, usually in the limbs. Despite their unique locations, both conditions share similar risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
Understanding the key differences between CAD and PAD is important for proper diagnosis and treatment, as each condition requires tailored management strategies to reduce the risk of complications and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Caused by plaque buildup in the arteries supplying blood to the heart.
Occurs due to narrowed arteries in the limbs, reducing blood flow.

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Coronary artery disease affects heart arteries, while peripheral artery disease affects blood vessels outside the heart. Both conditions result from plaque buildup, but in different areas of the body. Risk factors like smoking, high cholesterol, and diabetes contribute to the development of these diseases.
| Cause | Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Coronary Artery Disease | Smoking, High cholesterol levels, High blood pressure |
| Peripheral Artery Disease | Diabetes, Physical inactivity, Age over 50 |
Coronary Artery Disease: Smoking, high cholesterol, and blood pressure are key causes and risk factors.
Peripheral Artery Disease: Diabetes, physical inactivity, and age over 50 are main risk factors.
Coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease have distinct symptoms and presentations. Coronary artery disease primarily affects the heart, causing chest pain, while peripheral artery disease mainly affects the limbs, causing leg pain during walking or exercise. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing and evaluating coronary artery disease (CAD) and peripheral artery disease (PAD) involves several tests and assessments to determine the extent and severity of the conditions.
Diagnosing CAD typically involves an initial assessment of the patient’s medical history, followed by a thorough physical examination. The healthcare provider may also recommend a series of tests, including electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, stress test, coronary angiography, and CT angiography to evaluate the severity of the disease and identify potential blockages in the coronary arteries.
For PAD, the diagnosis and evaluation process begins with a comprehensive medical history review and physical examination. In addition to these, further testing such as ankle-brachial index (ABI), ultrasound imaging, CT angiography, and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) may be conducted to assess the blood flow and detect any arterial blockages in the lower extremities.
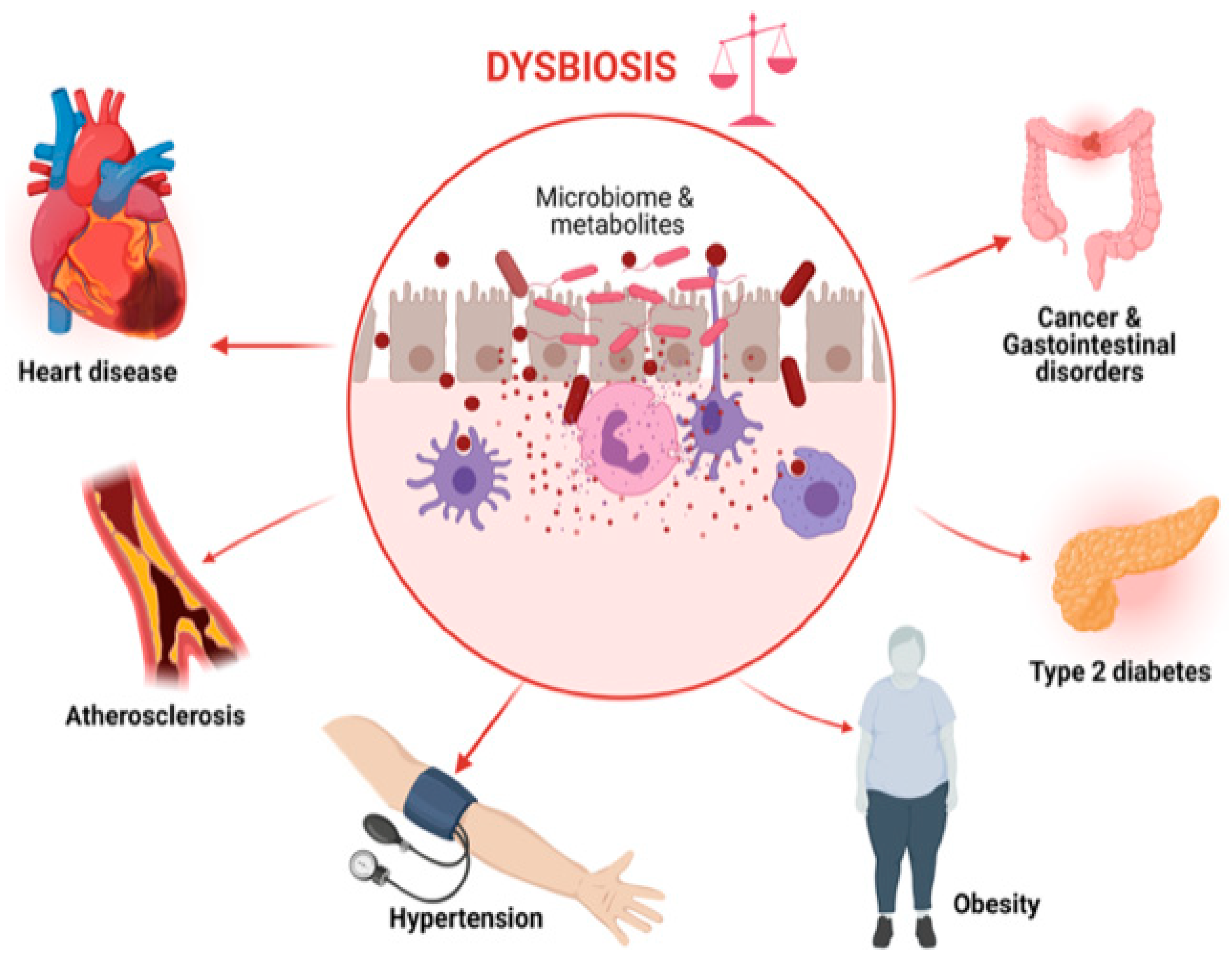
Complications and Consequences: Both Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) and Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) can lead to serious complications and consequences if left untreated. Understanding the differences in these conditions is crucial in order to prevent and manage associated risks.
CAD affects the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. If the blood flow to the heart is reduced or blocked due to plaque buildup, it can lead to:
PAD involves narrowed arteries in the extremities, commonly the legs. Complications of PAD may include:
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Effective treatment approaches are available for both coronary artery disease (CAD) and peripheral artery disease (PAD). However, treatment options may vary depending on the specific condition. In this section, we will explore the treatment approaches for each:
Treatment for coronary artery disease primarily focuses on reducing symptoms, improving overall heart health, and decreasing the risk of complications. The following approaches are commonly employed:
The treatment approaches for peripheral artery disease are aimed at relieving symptoms, improving circulation, and preventing further complications. The following methods are commonly employed:
It is important to note that early diagnosis and consistent management of both CAD and PAD can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Seeking medical attention and adhering to recommended treatment approaches can help individuals effectively manage these conditions and reduce the risk of complications.
Coronary artery disease primarily affects the heart’s blood vessels, while peripheral artery disease affects blood vessels outside the heart. Lifestyle changes and preventive measures such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can help manage and reduce the risk of developing these conditions.
Making these modifications can significantly improve overall cardiovascular health.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a condition where plaque buildup narrows the arteries supplying blood to the heart, leading to chest pain and potential heart attack.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a condition where plaque buildup narrows the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, causing symptoms like leg pain and impaired mobility.
Both CAD and PAD can be diagnosed through physical examination, medical history review, imaging tests (like angiography), and non-invasive tests (like ankle-brachial index) to determine blood flow.
Common risk factors for both CAD and PAD include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease may sound similar, but they are distinct in terms of the blood vessels they affect and the symptoms they cause. Understanding the differences between these two conditions is crucial for early detection and appropriate treatment.
By educating ourselves, we can take proactive steps to maintain heart health and overall well-being. Remember, prevention is always better than cure. So, let’s prioritize our cardiovascular health and lead a healthier and more fulfilling life.