Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
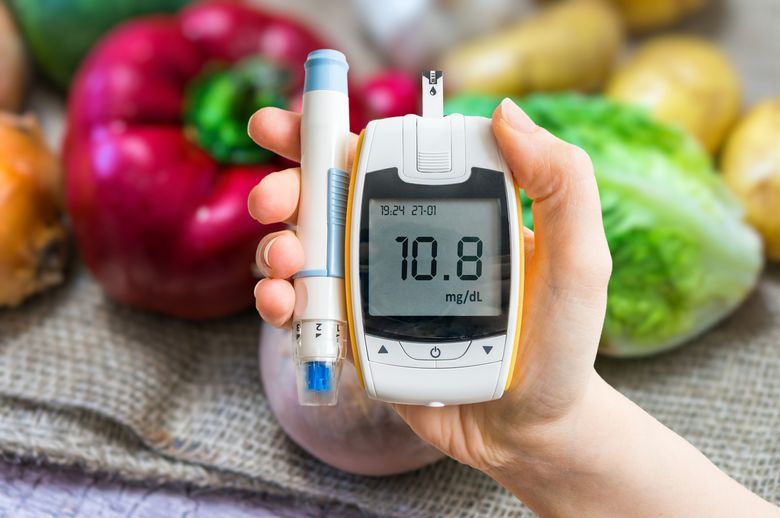
Diabetes is a medical condition, while blood sugar measures glucose levels in the blood. Diabetes affects how the body uses glucose as energy.
When blood sugar levels are consistently high, it can lead to diabetes. Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial to prevent diabetes and other health complications. By understanding the distinction between diabetes and blood sugar, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health effectively.
Let’s explore further the relationship between these two vital aspects of overall well-being.

Understanding Diabetes And Blood Sugar is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Many people often equate diabetes with just high blood sugar, but there are key differences between the two.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body uses blood sugar, also known as glucose. High levels of glucose in the blood can lead to diabetes if not properly managed. Blood sugar, on the other hand, refers to the amount of glucose present in your bloodstream at a given time.
It’s essential to differentiate between diabetes and blood sugar because diabetes is a medical condition, whereas blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day based on various factors such as diet, exercise, and stress. By understanding these distinctions, individuals can take proactive steps to monitor and control their blood sugar levels effectively.
Causes And Symptoms of Diabetes And Blood Sugar
Diabetes is mainly caused by genetic factors and lifestyle choices.
Symptoms of high blood sugar include excessive thirst and frequent urination.
Diagnosis and monitoring are crucial aspects when it comes to effectively managing diabetes and blood sugar levels. Understanding the key differences in the diagnosis and monitoring of the two conditions is essential for maintaining optimal health and well-being.
Diabetes is diagnosed through a series of tests that measure the levels of glucose in the blood. The key tests for diagnosing diabetes include the fasting plasma glucose test, oral glucose tolerance test, and the A1C test. These tests are used to determine if an individual has diabetes and to identify the specific type of diabetes they may have.
Monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for individuals with diabetes. This is typically done using a glucose meter, a small device that measures the amount of glucose in a drop of blood. Regular monitoring helps individuals make appropriate adjustments to their diet, exercise, and medication to keep their blood sugar levels within a healthy range.

Credit: www.diabetes.org.uk
When it comes to managing diabetes or controlling blood sugar levels, it is important to understand the difference between the two. Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body uses glucose, while blood sugar refers to the amount of glucose present in your bloodstream. While both terms are closely related, they refer to different aspects of the same condition. Understanding the difference can help you better manage your health.
Managing diabetes involves a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring. Here are some key methods for managing diabetes:
While managing diabetes is essential for controlling blood sugar levels, there are specific methods focused on directly controlling blood sugar levels. These methods can also be beneficial for individuals without diabetes who want to maintain healthy blood sugar levels:
By incorporating these methods into your daily routine, you can effectively manage diabetes and control blood sugar levels. It is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that suits your needs.
When it comes to understanding diabetes and blood sugar, it’s important to be aware of the complications and risks involved. Both conditions can have significant long-term effects on health and are associated with various health risks.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to produce or use insulin effectively. Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can lead to several long-term complications. These include:
High blood sugar levels, whether caused by diabetes or other factors, can also pose significant health risks. Some common risks associated with elevated blood sugar levels include:
In conclusion, keeping blood sugar levels within a healthy range and effectively managing diabetes is crucial to mitigate the complications and risks associated with these conditions. Long-term effects of diabetes can impact the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. Additionally, high blood sugar levels can increase the risk of infections, delay wound healing, contribute to cardiovascular complications, and affect vision. By understanding and addressing these potential risks, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining overall health and well-being.
Prevention And Lifestyle Changes play a crucial role in managing both diabetes and blood sugar levels. By implementing preventive measures and making healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can effectively lower their risk of developing diabetes and maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
Preventing diabetes involves a combination of maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and consuming a balanced diet. Moreover, individuals should undergo regular medical check-ups to monitor their blood glucose levels and promptly address any abnormalities.
Managing blood sugar levels relies on adopting and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits. This includes consuming a nutrient-dense diet, engaging in regular exercise, and prioritizing adequate sleep. Moreover, individuals should minimize their intake of sugary and processed foods to regulate their blood sugar levels effectively.
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for managing diabetes.
Monitoring and controlling sugar intake is key for individuals
with diabetes to maintain stable blood glucose levels.
To effectively control blood sugar levels, considering nutritional aspects
in the diet is essential. Low-glycemic foods can help stabilize blood sugar
and provide sustained energy.
New therapies and technologies continue to be developed to improve diabetes management.
Personalized medicine approaches aim to tailor treatments to individuals’ specific needs.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems offer real-time insights into blood sugar levels.
Non-invasive monitoring devices are being researched to provide more comfortable options for patients.

Credit: www.seattletimes.com
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes sugar, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Blood sugar, on the other hand, refers to the amount of glucose in your bloodstream at any given time. While diabetes is a medical condition, blood sugar levels can fluctuate in both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals.
Understanding the difference between diabetes and blood sugar is crucial for managing one’s health. Both are interconnected, but they are not the same. By recognizing the distinctions and taking appropriate measures to monitor and control blood sugar levels, individuals can effectively prevent and manage diabetes-related complications.
It is essential to stay informed and proactive in maintaining a healthy lifestyle.

