Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Kidney disease is a condition where the kidneys are damaged and cannot filter blood properly, leading to waste buildup in the body. Kidney stones, on the other hand, are hard, solid masses that form in the kidneys due to an accumulation of minerals and salts.
Kidney disease refers to a range of conditions that affect the kidneys’ functioning, such as chronic kidney disease, kidney failure, and kidney infections. It can be caused by various factors, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases. On the contrary, kidney stones are mineral formations that can cause severe pain and may result from dehydration, dietary factors, or genetic predisposition.
Understanding the differences between kidney disease and kidney stones is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. We’ll delve into the distinctions, symptoms, causes, and management of these two kidney-related conditions.

Credit: whynotnatural.com
Kidney disease and kidney stones are two distinct conditions. While kidney stones are solid deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain, kidney disease involves the gradual loss of kidney function. It’s important to differentiate between the two to receive proper treatment and management.
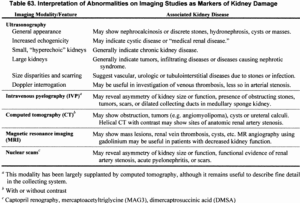
Kidney disease refers to a wide range of conditions that affect the kidneys’ ability to function properly. These conditions can cause serious health problems and, if left untreated, may lead to kidney failure. Causes and Types Kidney disease can be caused by various factors, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and genetic predisposition. There are different types of kidney diseases, such as chronic kidney disease (CKD), polycystic kidney disease (PKD), and glomerulonephritis. Each type affects the kidneys in different ways and may require specific treatments. Symptoms and Diagnosis The symptoms of kidney disease can vary, but commonly include fatigue, swelling, and changes in urination. Diagnosis typically involves blood and urine tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a kidney biopsy to determine the specific type and severity of the disease. Treatment Options Treatment for kidney disease depends on the type and stage of the condition, but may include medications, lifestyle changes, dialysis, or kidney transplant. Early detection and management of kidney disease are crucial for preventing complications and preserving kidney function.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys when the minerals and salts in urine crystallize and stick together. They vary in size and can cause severe pain as they pass through the urinary tract. Understanding the formation, symptoms, and management of kidney stones is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
Kidney stones can develop when substances like calcium, oxalate, and uric acid in the urine become highly concentrated and form crystals. The crystals can combine and grow into larger, hard stones over time, which may obstruct the urinary tract and lead to discomfort.
Common symptoms of kidney stones include intense pain in the back or side, bloody urine, and frequent urination. A medical evaluation involving imaging tests, urine analysis, and blood tests can help diagnose the presence of kidney stones and determine their composition.
When trying to understand the difference between kidney disease and kidney stones, it is important to focus on the distinguishing factors. By examining the nature of the condition, underlying causes, affected population, and treatment approaches, we can gain insights into these two distinct medical issues. Let’s explore these factors in more detail.
Kidney disease involves a gradual loss of kidney function over time, affecting the organs’ ability to filter waste and fluids from the blood properly.
Kidney disease can develop due to various factors such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and genetic predisposition, whereas kidney stones are hardened mineral deposits that form in the kidneys.
Kidney disease primarily affects individuals with underlying health conditions like diabetes and hypertension, whereas kidney stones can occur in individuals of any age, often due to dehydration or certain dietary factors.
Treatment for kidney disease typically involves lifestyle changes, medication, and in severe cases, dialysis or kidney transplantation. On the other hand, kidney stones may be managed through increased fluid intake, pain medication, or procedures to remove the stones.
Complications:
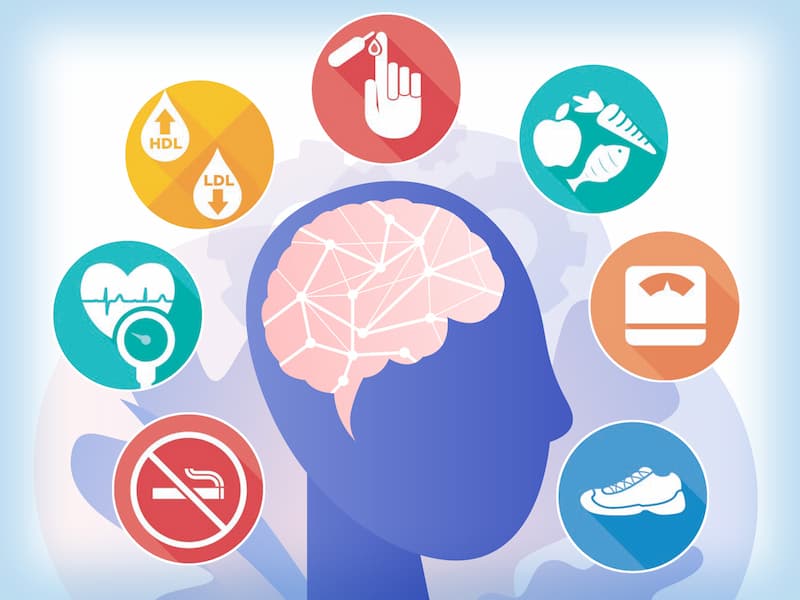
Kidney disease and kidney stones are both serious conditions that can lead to various complications if left untreated. It’s essential to understand the potential risks and serious complications associated with each condition to take appropriate measures for timely treatment. Let’s explore the potential risks of untreated kidney disease and the serious complications of kidney stones:
Kidney disease, also known as renal disease, occurs when the kidneys are damaged and are unable to function properly. If left untreated, kidney disease can lead to various potential risks:
Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause excruciating pain. If left untreated, kidney stones can result in serious complications:
Kidney disease and kidney stones are two distinct conditions. Kidney disease refers to a long-term loss of kidney function. On the other hand, kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys. The prevention methods for these conditions vary, with kidney disease typically requiring lifestyle changes and medications, while kidney stones may be prevented through drinking plenty of water and making dietary adjustments.
Kidney disease can be a serious and life-threatening condition if left untreated. However, there are various strategies that you can adopt to prevent kidney disease altogether and maintain the health of your kidneys. By following these simple yet effective steps, you can reduce the risk of developing kidney disease and ensure that your kidneys function optimally:
Kidney stones can cause extreme pain and discomfort, affecting your daily life. Fortunately, there are several measures you can take to reduce the risk of developing kidney stones and ensure the overall health of your kidneys:

Credit: whynotnatural.com
Kidney disease and kidney stones can significantly affect a person’s well-being.
Kidney disease poses challenges like fatigue, fluid retention, and high blood pressure.
Kidney stones may lead to intense pain and discomfort, impacting daily activities.
| Parameter | Kidney Disease | Kidney Stones |
|---|---|---|
| Pain Level | Chronic dull pain | Intermittent sharp pain |
| Frequency of Symptoms | Continuous | Episodic |
Kidney disease symptoms include fatigue, swelling, frequent urination, and blood in the urine. Kidney stones symptoms include severe pain in the back or side, frequent urination, and pink or red urine.
Kidney disease is a condition where the kidneys cannot function properly, leading to a buildup of toxins in the body. On the other hand, kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys or urinary tract, causing pain and affecting urination.
Yes, kidney disease can increase the risk of developing kidney stones. When the kidneys are not functioning properly, certain substances can build up in the body and contribute to the formation of kidney stones.
Kidney disease can be caused by high blood pressure, diabetes, infections, and certain medications. Kidney stones are often caused by dehydration, a high-sodium diet, certain medical conditions, and genetic factors.
It is crucial to understand the distinction between kidney disease and kidney stones. While kidney disease involves chronic damage to the kidneys, kidney stones are solid deposits that can cause blockages. Being aware of the symptoms and treatment options for each condition is essential for maintaining kidney health.