Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

The main difference between multiple sclerosis and myasthenia gravis is that multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system, while myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the muscles, causing weakness and fatigue. Multiple sclerosis (MS) and myasthenia gravis (MG) are both autoimmune disorders that can impact the normal functioning of the body.
MS is characterized by an abnormal immune response that leads to inflammation and damage of the protective covering of nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord. This can result in various neurological symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, coordination problems, and difficulty with balance and walking.
On the other hand, MG is caused by an autoimmune attack on the connection between nerves and muscles, leading to muscle weakness and fatigue, which can particularly affect the muscles that control eye and facial movements. While both conditions involve a faulty immune response, they differ in their specific targets and symptoms.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, called myelin, causing communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body. MS is a complex condition with various causes and symptoms. Understanding the causes and symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis is crucial for early detection and effective management of the disease.
The exact cause of Multiple Sclerosis is still unknown. However, researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors play a role in its development. Genetic predisposition is considered a significant risk factor, as family members of individuals with MS have a higher chance of developing the disease. Environmental factors, such as certain infections or exposure to toxins, may also trigger the immune system to attack the myelin. The specific interplay between genetics and the environment is still being studied.
It is important to note that Multiple Sclerosis is not a contagious or inherited disease in the usual sense. While certain genes may increase the likelihood of developing MS, it does not necessarily mean that the disease will be passed down from one generation to the next.
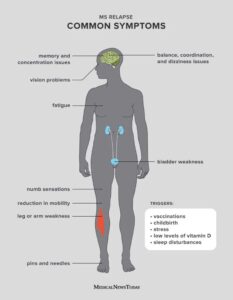
Multiple Sclerosis can cause a wide range of symptoms that vary from person to person. These symptoms depend on the specific areas of the central nervous system that are affected. Some common symptoms of MS include:
MS symptoms can come and go, or they may persist and worsen over time. The severity of the symptoms can also vary, ranging from mild to severe. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any unusual or persistent symptoms to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate medical care.
Diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis involves a thorough neurological examination and various tests to confirm the condition. The key difference between Multiple Sclerosis and Myasthenia Gravis lies in their underlying causes and symptoms. While both affect the nervous system, Multiple Sclerosis is characterized by damage to the protective covering of nerves, whereas Myasthenia Gravis is caused by a breakdown in communication between nerves and muscles.
If you or someone you know is experiencing unexplained symptoms such as fatigue, difficulty with coordination, or numbness, it’s important to understand the process of diagnosing multiple sclerosis (MS). Diagnosing MS can be a complex and challenging task for healthcare professionals due to the similarity of its symptoms to other conditions. In this section, we will explore the medical tests used for diagnosing multiple sclerosis and the challenges that healthcare professionals may encounter during the diagnostic journey.
Medical tests play a vital role in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. These tests are typically conducted to evaluate the patient’s symptoms, assess their medical history, and rule out other conditions that may mimic MS. Here are some common medical tests used in the diagnostic process of multiple sclerosis:
Diagnosing multiple sclerosis can be challenging due to several factors, including the diversity and variability of symptoms, the absence of a definitive diagnostic test, and the potential overlap of symptoms with other conditions. Some of the challenges healthcare professionals may face in the diagnostic process include:
Myasthenia Gravis and Multiple Sclerosis are two distinct neurological conditions. While Multiple Sclerosis affects the central nervous system, causing inflammation and damage to the nerves, Myasthenia Gravis is characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue due to a breakdown in communication between nerves and muscles.
Understanding Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia Gravis is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disorder that causes weakness and rapid fatigue of the voluntary muscles. This condition occurs when communication between nerves and muscles is disrupted due to the body’s immune system attacking its own receptors. It commonly affects the muscles that control eye and eyelid movement, facial expression, chewing, swallowing, and speaking.
The specific cause of Myasthenia Gravis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to an immune system dysfunction. Antibodies are produced by the immune system that block or destroy muscle receptor sites, leading to a breakdown in communication between nerves and muscles.
The hallmark symptom of Myasthenia Gravis is muscle weakness that worsens with activity and improves with rest. Other symptoms may include drooping eyelids, double vision, difficulty speaking, chewing, swallowing, and breathing, as well as weakness in the arms, hands, legs, and neck.
In addition, Myasthenia Gravis can be classified into two main types: ocular and generalized. The ocular form primarily affects the muscles around the eyes, leading to drooping eyelids and double vision, whereas the generalized form affects multiple muscle groups throughout the body.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis is crucial in order to effectively manage and treat the condition. By gaining insight into the intricacies of this disorder, individuals can seek appropriate medical care and support to improve their quality of life.
Credit: impactful.ninja
Diagnosing myasthenia gravis (MG) can be a complex process due to its similarities to other neuromuscular conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS). However, several medical tests are available to accurately diagnose MG and differentiate it from other conditions. It’s important to understand the challenges involved in diagnosing MG to ensure proper evaluation and treatment. Let’s explore the medical tests used for diagnosing myasthenia gravis and the challenges faced in the diagnosis process.
To diagnose myasthenia gravis, doctors employ a combination of clinical examinations, medical history assessment, and specialized tests. These tests help to identify the characteristic muscle weakness and fatigue associated with MG. Some of the commonly used medical tests for diagnosing myasthenia gravis include:
Diagnosing myasthenia gravis can be challenging due to several factors. The symptoms of MG can vary widely from person to person, making it difficult to recognize the condition. Additionally, some symptoms, such as muscle weakness and fatigue, overlap with other neuromuscular disorders. This makes it crucial to differentiate MG from conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS) which have similar manifestations.
Furthermore, the initial symptoms of MG can be subtle and easily mistaken for other health issues. As a result, some individuals may experience delayed diagnoses, leading to delays in receiving appropriate treatment. Moreover, the rarity and complexity of MG can contribute to diagnostic challenges.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional experienced in neuromuscular disorders to properly diagnose myasthenia gravis. By using a combination of clinical examinations and specialized tests, accurate diagnosis can be made, allowing for the development of an appropriate treatment plan tailored to each individual’s needs.
When it comes to managing and treating neurological disorders such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and Myasthenia Gravis (MG), different approaches are taken. Each condition requires a tailored treatment plan to address its specific symptoms and manage its progression. In this section, we will explore the treatment approaches for both MS and MG, shedding light on the methods used to help patients live a better quality of life.
Multiple Sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, causing a wide range of symptoms. While there isn’t a cure for MS, therapeutic strategies aim to slow down its progression, manage symptoms, and enhance the patient’s overall well-being.
The treatment of MS typically involves a combination of medications, rehabilitation therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Here are some commonly used approaches:
Myasthenia Gravis is a neuromuscular disorder that leads to muscle weakness and fatigue. Although there is no cure for MG, treatment options aim to control symptoms, improve muscle strength, and prevent complications.
In the management of Myasthenia Gravis, healthcare professionals may consider the following treatment approaches:
Remember, the choice of treatment and management options for both Multiple Sclerosis and Myasthenia Gravis depends on the severity of the condition, a patient’s specific needs, and the professional advice of a healthcare provider. By implementing a combination of these approaches, individuals with these neurological disorders can achieve improved quality of life and better symptom control.

Credit: www.yumpu.com

Credit: impactful.ninja
Conditions that can be misinterpreted as myasthenia gravis include Lambert-Eaton syndrome, botulism, and some forms of muscular dystrophy.
Myasthenia gravis is associated with other autoimmune diseases such as thyroid disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus.
The key symptom of myasthenia gravis is muscle weakness, which typically worsens with activity and improves with rest.
The two types of myasthenia gravis are generalized myasthenia gravis (affecting multiple muscle groups) and ocular myasthenia gravis (affecting only the muscles that control eye movements).
Understanding the differences between Multiple Sclerosis and Myasthenia Gravis is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. While both are neurological conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatment methods vary significantly. If you or a loved one are experiencing any of the symptoms associated with these conditions, it’s important to seek medical advice for accurate diagnosis and treatment.