Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Multiple sclerosis and systemic sclerosis are two distinct medical conditions. Multiple sclerosis affects the central nervous system, causing damage to the brain and spinal cord.
On the other hand, systemic sclerosis affects the skin, blood vessels, and internal organs, primarily causing excessive collagen production and fibrosis. Multiple sclerosis involves autoimmunity and inflammation, leading to neurological symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and difficulty in coordination.
Systemic sclerosis, in contrast, results in thick and hardened skin, along with complications like Raynaud’s phenomenon and organ damage. Although both conditions may have overlapping symptoms, they differ in their underlying causes, affected systems, and overall prognosis.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
When it comes to understanding the difference between Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and Systemic Sclerosis (SSc), it is crucial to grasp the basics of each condition. In this section, we will delve into the key aspects of Multiple Sclerosis, including its definition, causes, and symptoms. Let’s explore this fascinating neurological disorder in more detail.
Multiple Sclerosis, commonly referred to as MS, is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. With this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, known as myelin. As a result, communication between the brain and the rest of the body becomes disrupted, leading to a range of physical and cognitive symptoms.
The exact cause of MS remains unknown, but experts believe it is likely a combination of genetic and environmental factors that contribute to its development. Some studies suggest that certain genes may increase the risk of developing MS, while environmental triggers, such as viral infections or exposure to certain toxins, may also play a role. However, more research is needed to fully understand the complex causes of this condition.
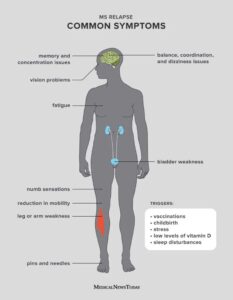
The symptoms and progression of Multiple Sclerosis can vary widely among individuals. Some common symptoms include fatigue, difficulty walking or maintaining balance, muscle weakness or spasms, numbness or tingling, problems with coordination, and cognitive difficulties. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may come and go or worsen over time.
MS typically follows one of four patterns of progression:
Understanding the different patterns of MS progression is important for both patients and healthcare professionals to determine appropriate treatment plans and manage the condition effectively.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Systemic sclerosis is a complex autoimmune disease that primarily affects the skin and other connective tissues in the body. It is often characterized by excessive collagen production, which can lead to thickening, hardening, and tightening of the skin and other organs. Understanding the key aspects of systemic sclerosis can help individuals recognize its symptoms, understand its causes, and get the necessary treatment.
Systemic sclerosis, also known as scleroderma, is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs and systems in the body, including the skin, blood vessels, lungs, kidneys, and digestive tract. It is characterized by the abnormal production of collagen, a protein that forms the structure of connective tissues. This excessive collagen production leads to fibrosis and scarring, causing various complications and impairments.
The exact cause of systemic sclerosis is unknown. It is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Certain genetic variations are associated with an increased risk of developing the condition, but they alone are not sufficient to cause it. Environmental triggers, such as exposure to certain chemicals or infections, may play a role in triggering the autoimmune response. Additionally, abnormalities in the immune system, particularly the overactivation of fibroblasts, contribute to the development and progression of systemic sclerosis.
Systemic sclerosis can manifest in various ways and its symptoms can vary from person to person. Early symptoms often include Raynaud’s phenomenon, which is characterized by color changes in the fingers or toes in response to cold or stress. As the disease progresses, skin thickening and tightening may occur, leading to reduced mobility and joint stiffness. Internal organ involvement can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, heartburn, kidney problems, and lung complications.
There are two main types of systemic sclerosis: limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. In limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis, the skin thickening and tightening mainly affect the hands, face, and lower arms. In contrast, diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis involves more widespread skin involvement, affecting not only the hands and face but also the trunk, thighs, and upper arms.
Systemic sclerosis is a progressive disease that can lead to significant disability and reduced quality of life if left untreated. It is essential to seek medical attention and get a proper diagnosis as early as possible to initiate appropriate treatment and management strategies. While there is no cure for systemic sclerosis, various therapies and medications can help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve overall well-being.
In the world of medical terms, there are often conditions that may appear similar, causing confusion for patients and healthcare professionals alike. This is particularly true for Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and Systemic Sclerosis (SSc), two separate diseases that share certain characteristics but affect different body systems and manifest in distinct ways. Recognizing and understanding the distinguishing features of these two conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and proper management. In this article, we will explore these differences in greater detail, focusing on the affected body systems, symptom manifestations, and diagnostic methods for MS and SSc.
One of the key factors that differentiate Multiple Sclerosis from Systemic Sclerosis is the body systems they primarily affect.
Multiple Sclerosis is a neurological disorder characterized by the immune system attacking the protective covering of nerve fibers in the central nervous system. This can lead to disruptions in communication between the brain and the rest of the body, causing a wide range of symptoms related to movement, sensation, and cognition.
On the other hand, Systemic Sclerosis, also known as scleroderma, primarily affects the connective tissues in various parts of the body. It is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes the overproduction of collagen, resulting in thickening and hardening of the skin and organs such as the lungs, heart, and gastrointestinal tract.
| Multiple Sclerosis | Systemic Sclerosis |
|---|---|
| Attacks the central nervous system | Affects connective tissues and multiple organs |
| Impairs movement, sensation, and cognition | Causes skin and organ fibrosis, and potential organ dysfunction |
Another significant difference between Multiple Sclerosis and Systemic Sclerosis lies in the varied symptom manifestations experienced by individuals with these conditions.
In Multiple Sclerosis, symptoms can vary widely depending on the location and extent of nerve damage. Common manifestations include fatigue, muscle weakness, coordination difficulties, visual disturbances, and problems with balance and gait. Additionally, some individuals may experience cognitive impairment, such as memory loss and difficulty concentrating.
Systemic Sclerosis, on the other hand, primarily presents with skin involvement. It often begins with a thickening and hardening of the skin, commonly affecting the fingers, hands, face, and other areas. This can cause tightness, limited mobility, and cosmetic changes. Systemic Sclerosis can also affect internal organs, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath, gastrointestinal problems, and cardiac abnormalities.
When it comes to diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis and Systemic Sclerosis, healthcare professionals rely on distinct diagnostic methods tailored to each condition.
For Multiple Sclerosis, the diagnosis is typically based on a combination of medical history, neurological examination, and diagnostic tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), cerebrospinal fluid analysis, and evoked potentials. These tests help evaluate the presence of central nervous system damage and rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
In contrast, diagnosing Systemic Sclerosis involves a thorough assessment of the patient’s clinical signs, symptoms, and physical findings. Skin biopsies may be performed to confirm skin involvement and identify specific autoantibodies associated with the disease. Additional tests, including pulmonary function tests, echocardiography, and gastrointestinal studies, may be conducted to assess organ involvement and determine the extent of fibrosis.
Overall, understanding the differences in affected body systems, symptom manifestations, and diagnostic methods is essential for distinguishing Multiple Sclerosis from Systemic Sclerosis accurately. Timely and accurate diagnosis allows for appropriate treatment and management strategies to improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
Treatment Approaches for Multiple Sclerosis and Systemic Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) treatment aims to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. Disease-modifying therapies such as interferon beta, glatiramer acetate, and teriflunomide are commonly prescribed to reduce relapses and prevent disability progression. Corticosteroids may be used to manage acute relapses, while physical therapy helps improve mobility and balance. Additionally, medications such as muscle relaxants and antidepressants may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms. In some cases, plasma exchange may be recommended to treat severe attacks.
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Immunosuppressants like methotrexate and cyclophosphamide may be prescribed to suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and calcium channel blockers are used to manage high blood pressure and improve blood flow. Physical therapy and occupational therapy can help maintain joint flexibility and function. Moreover, medications may be prescribed to address specific symptoms such as acid reflux, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and skin problems.
Managing disease progression involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Patients are encouraged to engage in regular physical activity, maintain a balanced diet, and avoid smoking to help manage symptoms and maintain overall health. Additionally, seeking psychological support and participating in support groups can help manage the emotional impact of both MS and SSc.
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
Systemic sclerosis is a serious condition that can affect the skin, blood vessels, and internal organs. It can cause severe complications, such as pulmonary fibrosis and heart problems. Early diagnosis and management are crucial to prevent long-term damage. Regular medical monitoring and treatment are essential for managing the symptoms and preventing complications.
The three types of systemic sclerosis are limited cutaneous, diffuse cutaneous, and sine scleroderma. These types determine the extent of skin and organ involvement in the disease.
The old name for systemic sclerosis is scleroderma. It is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin and connective tissues, causing hardening and tightening.
The most frequently affected organ in systemic sclerosis is the skin.
It is crucial to understand the key differences between Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. While both conditions affect the body’s immune system, MS primarily affects the central nervous system, while SSc primarily affects the skin and connective tissues.
By recognizing these distinctions, healthcare professionals can provide targeted care and support to patients, improving their overall quality of life. Stay informed and seek medical advice for any concerns or symptoms related to these conditions.