Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Parkinson’s is a neurological disorder characterized by tremors, rigidity, and slow movement. Dyskinesia, on the other hand, refers to involuntary and abnormal movements.
Parkinson’s Disease and dyskinesia are both distinct neurological disorders, but they share a common symptom of movement abnormalities. Parkinson’s Disease is a chronic and progressive condition that primarily affects muscle control, leading to tremors, stiffness, and a slowing down of movements.
It is caused by a loss of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. On the other hand, dyskinesia refers to abnormal involuntary movements that can result from long-term treatment of Parkinson’s Disease with levodopa or other Parkinson’s medications. While Parkinson’s Disease is a specific condition, dyskinesia is a broader term that encompasses various types of abnormal movements. Understanding the differences between these conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that primarily affects movement. It is a chronic and progressive condition that manifests through a variety of motor symptoms. While Parkinson’s is commonly associated with tremors, it encompasses much more than just involuntary shaking. This condition is often confused with dyskinesia, another movement disorder that also involves abnormal movements. In this article, we will explore the differences between Parkinson’s and dyskinesia, starting with an understanding of Parkinson’s symptoms and causes.
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by a range of motor symptoms that gradually worsen over time. These symptoms can include:
Additional non-motor symptoms may also accompany Parkinson’s, such as difficulty with speech and swallowing, cognitive impairment, mood changes, and sleep disturbances. It is important to note that the presence and severity of symptoms can vary from person to person.
The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is yet to be fully understood. However, research suggests a combination of genetic and environmental factors may play a role in its development. Some potential causes and contributors to Parkinson’s include:
While these factors may contribute to the development of Parkinson’s disease, it is important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop the condition.

Credit: www.scirp.org
Dyskinesia is a condition characterized by abnormal, involuntary movements. It often occurs as a side effect of long-term treatment with medications used to manage Parkinson’s disease. While dyskinesia and Parkinson’s may seem similar, they are distinct conditions with different symptoms and causes. In this article, we will delve into the world of dyskinesia, exploring its symptoms and causes, and shedding light on the differences between dyskinesia and Parkinson’s disease.
Dyskinesia presents itself through a variety of symptoms that can greatly impact a person’s daily activities. These symptoms include:
The intensity and frequency of these symptoms can vary among individuals, and they may worsen during periods of stress or emotional excitement. It is important to note that dyskinesia can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and independence.
The primary cause of dyskinesia is prolonged use of levodopa, a medication commonly prescribed to manage the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Levodopa increases the levels of dopamine in the brain, which helps to alleviate the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s. However, with long-term use, dyskinesia can develop as a side effect of this medication.
Other factors that contribute to the development of dyskinesia include the duration of levodopa treatment, the dosage of the medication, and individual variations in medication metabolism.
In addition to levodopa, dyskinesia can also be triggered or exacerbated by other Parkinson’s medications, such as dopamine agonists. These medications directly stimulate the dopamine receptors in the brain, leading to dyskinesia in some individuals.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect you or a loved one may be experiencing symptoms of dyskinesia. Accurately diagnosing dyskinesia and differentiating it from Parkinson’s disease is crucial in order to provide appropriate treatment and improve overall quality of life.
Parkinson’s disease and dyskinesia are both neurological disorders that can affect a person’s movement, but they have distinct differences. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Let’s explore the definitions, distinguishing symptoms, and diagnostic techniques for Parkinson’s and dyskinesia.
Parkinson’s disease is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system. It primarily affects the movement of the body, with symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and impaired balance. The disease progresses slowly, and as it worsens, it can lead to difficulties with speech and swallowing, as well as emotional and cognitive changes.
Dyskinesia, on the other hand, is not a disease itself but rather a symptom of certain conditions, including Parkinson’s disease. Dyskinesia refers to involuntary, abnormal movements that can occur spontaneously or as a side effect of medications used to treat Parkinson’s disease.
To differentiate between Parkinson’s disease and dyskinesia, it is essential to understand their distinguishing symptoms:
Accurate diagnosis is vital in distinguishing between Parkinson’s disease and dyskinesia. Several diagnostic techniques can assist healthcare professionals in differentiating these conditions:
In conclusion, while Parkinson’s disease and dyskinesia share some similarities in terms of their impact on movement, they differ significantly in their underlying causes, symptoms, and diagnostic approaches. It is essential for healthcare professionals to carefully differentiate between these conditions to provide the most appropriate treatment and support for individuals affected by these neurological disorders.
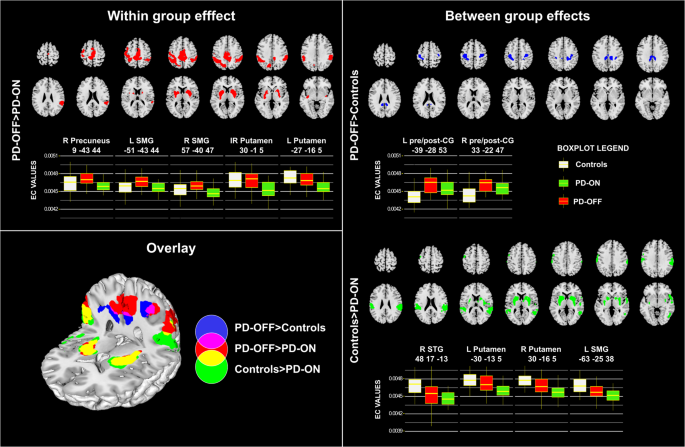
Credit: www.nature.com
In the treatment of Parkinson’s and dyskinesia, various approaches are used to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients. Understanding the differences in treatment strategies for these conditions is crucial in providing effective care. Here, we’ll explore the distinct treatment approaches for Parkinson’s and dyskinesia, including medications and surgical interventions.
Medications for Parkinson’s primarily focus on managing the depletion of dopamine in the brain and addressing motor symptoms, such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. Commonly prescribed medications include:
Treating dyskinesia often involves managing the side effects of Parkinson’s medications, particularly levodopa. Medications such as:
For advanced cases of Parkinson’s and dyskinesia, surgical interventions may be considered when medication management is no longer sufficient. These can include:
Parkinson’s and dyskinesia are both movement disorders, but they differ in their characteristics. Parkinson’s is characterized by tremors, stiffness, and slow movements, while dyskinesia is marked by involuntary jerky movements. Understanding the difference between the two can help individuals better manage their symptoms.
Quality of Life Challenges
Living with Parkinson’s and dyskinesia can pose significant challenges to a person’s quality of life. Both conditions can cause physical and emotional difficulties that may impact daily activities and overall well-being. Parkinson’s disease is characterized by slow movements, stiffness, and tremors, while dyskinesia involves involuntary, erratic movements that can be disruptive and distressing. People dealing with these conditions may struggle with reduced mobility, impaired communication, and increased dependence on others for assistance with daily tasks. The fluctuating nature of dyskinesia can also make it challenging to manage and anticipate the onset of symptoms, which can further contribute to a diminished quality of life.
Coping Strategies and Support
When navigating the complexities of Parkinson’s and dyskinesia, individuals can benefit from implementing effective coping strategies and seeking supportive resources. It’s important to cultivate a strong support system that includes healthcare professionals, family members, and community organizations. Engaging in regular exercise tailored to individual abilities can help manage symptoms and promote overall well-being. Additionally, participating in support groups or seeking counseling can provide emotional support and valuable insights from others facing similar challenges. Finding ways to adapt daily routines and incorporate assistive devices can also empower individuals to maintain a level of independence and enhance their quality of life.
By addressing the unique challenges associated with Parkinson’s and dyskinesia and leveraging available coping strategies and support, individuals can strive to navigate these conditions with resilience and maximize their overall well-being.

Credit: www.neurology.org
Dyskinesia can be triggered by certain medications used to treat Parkinson’s disease. These medications, known as levodopa or dopamine agonists, can lead to abnormal involuntary movements.
Yes, it is possible to have dyskinesia without Parkinson’s. Dyskinesia can occur as a side effect of certain medications, particularly those used to treat Parkinson’s disease. However, it can also result from other conditions or be caused by prolonged use of certain drugs.
Parkinson’s and tardive dyskinesia have similar symptoms, but there are differences. Parkinson’s primarily affects movement and causes tremors, stiffness, and slow movement. Tardive dyskinesia is a side effect of certain medications, causing repetitive, involuntary movements. Consulting a healthcare professional is important for an accurate diagnosis.
Yes, excessive carbidopa levodopa can lead to dyskinesia, a movement disorder. It can cause involuntary muscle movements.
Understanding the difference between Parkinson’s and dyskinesia is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. While both conditions involve movement difficulties, Parkinson’s is a neurodegenerative disease that affects various functions, while dyskinesia refers to abnormal involuntary movements caused by certain medications used to treat Parkinson’s.
Proper identification and differentiation of these conditions can lead to better management and improved quality of life for individuals affected by these disorders.