Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) appears to affect the muscles due to the damage it causes to the nerves that control muscle movement. This damage disrupts the communication between the brain and muscles, leading to muscle weakness, stiffness, and coordination difficulties.
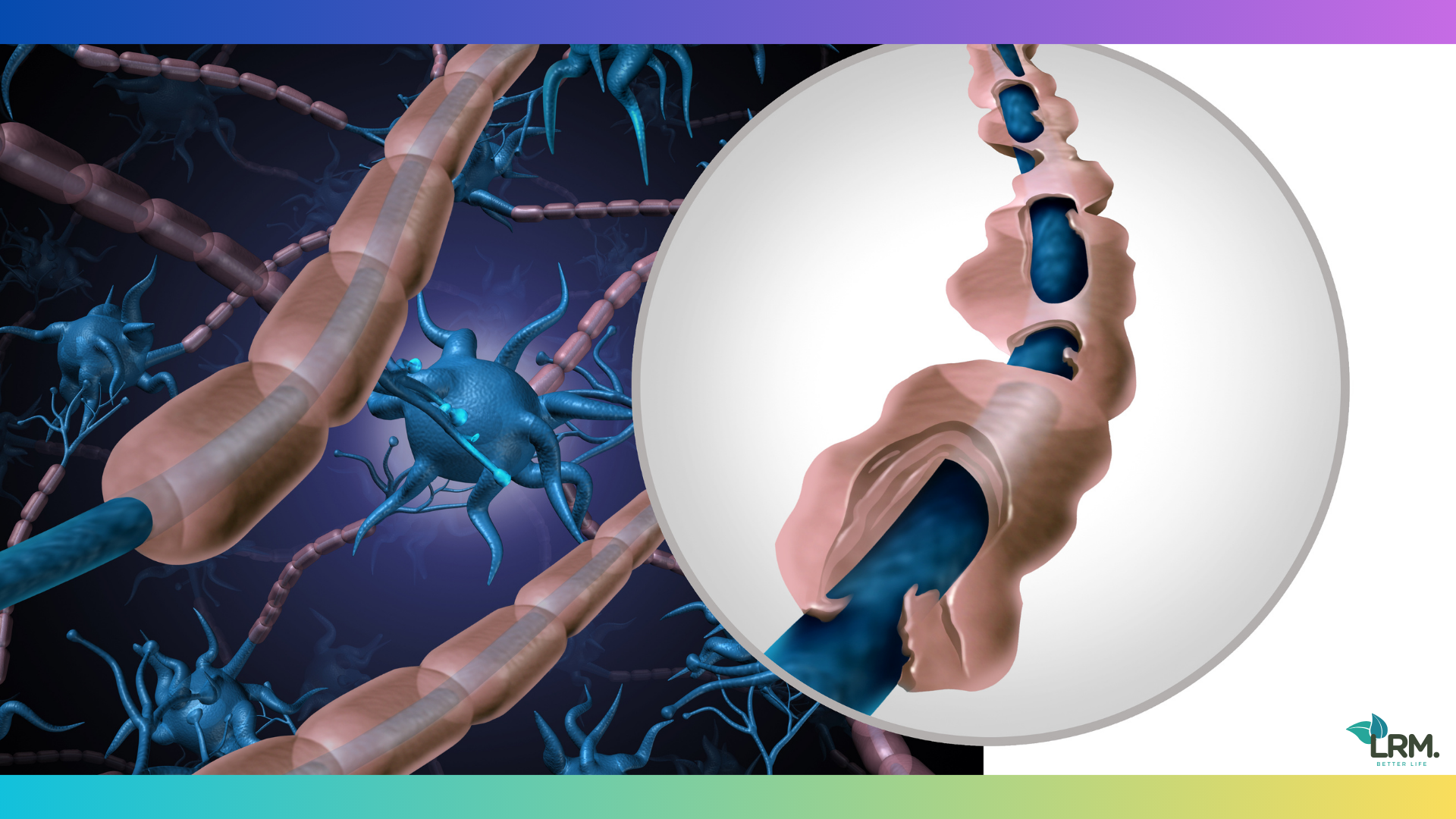
As a chronic autoimmune disease, MS causes the immune system to mistakenly attack the protective covering of nerve fibers, known as myelin, in the central nervous system. The loss of myelin, along with the formation of scar tissue, further impairs the ability of nerves to transmit signals effectively.
Consequently, the muscles do not receive the proper instructions from the brain, resulting in a range of muscular symptoms experienced by individuals with MS.
Multiple Sclerosis affects muscle function due to damage to the nerves that control them. This damage disrupts the communication between the brain and muscles, leading to weakness, stiffness, and spasms. Understanding the impact of Multiple Sclerosis on muscle function is essential for effective management and treatment.
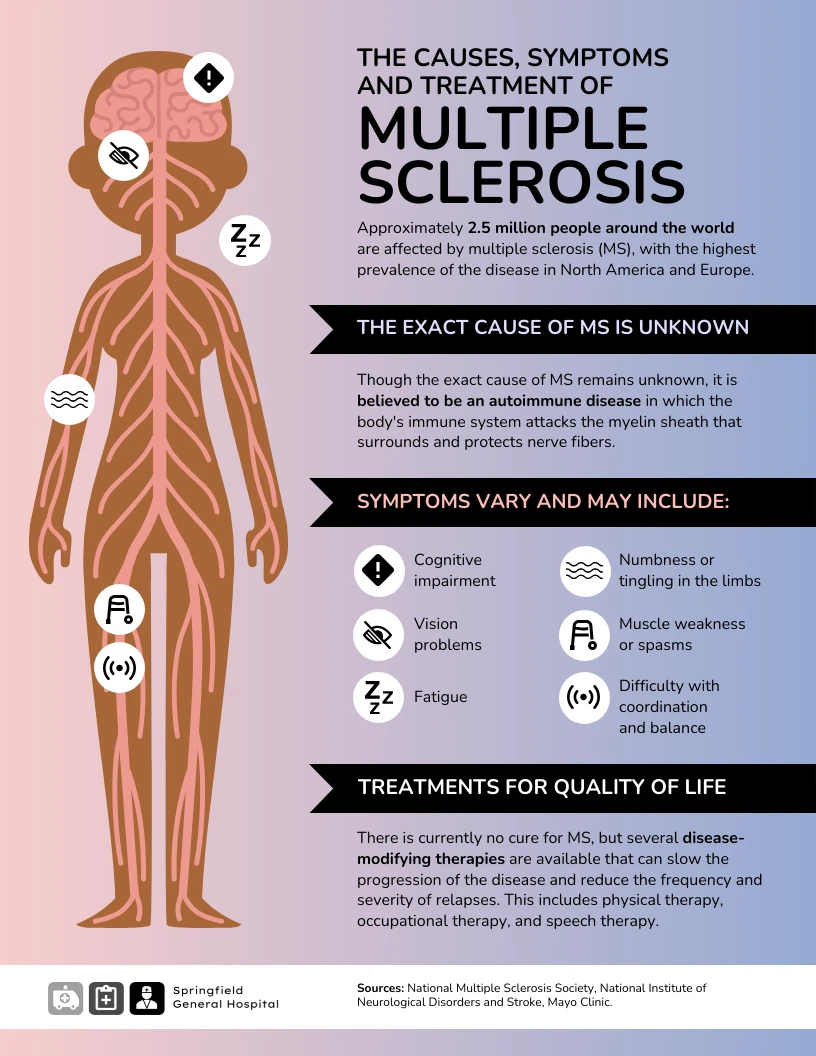
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS), specifically damaging the protective covering of nerve fibers called myelin. This damage disrupts the normal flow of electrical impulses along the nerves, leading to a wide range of symptoms. While MS can affect various parts of the body and cause various symptoms, it often appears to have a significant impact on the muscles, resulting in muscle weakness, spasms, and difficulties with coordination and balance.
MS is characterized by the development of lesions or scars on the nerve fibers of the CNS. These lesions can occur in different areas of the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves, leading to a variety of symptoms that vary widely from person to person. The distribution and severity of these lesions determine the specific symptoms experienced by individuals with MS. Common symptoms associated with MS include fatigue, difficulty walking, numbness or tingling in the limbs, loss of coordination, muscle weakness, problems with vision, bladder and bowel dysfunction, and cognitive changes.
The exact cause of MS is still unknown, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors contribute to its development. Certain genes have been identified as potential risk factors for MS, although these genes alone do not determine whether someone will develop the disease. Environmental factors such as viral infections, low vitamin D levels, and smoking have also been linked to an increased risk of developing MS. It is believed that these factors trigger an abnormal immune response in individuals who are genetically susceptible, leading to the immune system attacking the myelin in the CNS.
In conclusion, multiple sclerosis is a complex disease that affects the central nervous system and is characterized by the development of lesions on the nerve fibers. While the exact cause of MS is still unknown, a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to play a role in its development. This disease can have a profound impact on the muscles, causing weakness, spasms, and coordination difficulties. Understanding the basics of MS is essential for individuals affected by the condition and their loved ones, as it can empower them to seek appropriate management strategies and support.

Credit: www.everydayhealth.com
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) affects muscles due to the damage it causes to the nervous system. This results in disrupted signals from the brain to the muscles, leading to muscle weakness, fatigue, and coordination problems. Understanding this muscle involvement is crucial in managing the symptoms and designing appropriate treatment strategies for individuals with MS.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. While it primarily targets the brain and spinal cord, it also takes a toll on the muscles. Understanding the muscle involvement in MS is crucial in comprehending the physical impact this condition has on individuals. MS can lead to various effects on muscles, which can significantly affect an individual’s daily life.
One of the common effects of MS on muscles is muscle weakness. The communication between the brain and muscles is disrupted, causing muscles to lose their strength. This weakness can manifest differently depending on the muscles affected, ranging from difficulty in lifting objects to problems with balance and coordination.
Another effect is muscle stiffness or spasticity. The disrupted signals from the central nervous system can cause the muscles to become tight, making it challenging to move freely. This stiffness can contribute to muscle cramps, spasms, and even difficulty in maintaining proper posture.
Several factors can contribute to the muscle attack experienced by individuals with MS. The primary factor is the demyelination process that occurs in MS. In this process, the protective covering of nerve fibers, known as myelin, is damaged. Without the proper insulation, nerve impulses are slowed down or interrupted, affecting the communication between the brain and muscles.
Furthermore, inflammation plays a significant role in the muscle attack in MS. The immune system mistakenly recognizes the myelin as a foreign substance and launches an immune response. This inflammation damages the myelin and triggers the muscle attack.
Additionally, the location and extent of the lesions in the central nervous system also play a crucial role in determining the muscle involvement in MS. Lesions in specific areas of the brain and spinal cord can directly affect the muscles controlled by those areas, leading to various muscle problems.
It is important to understand the effects of MS on muscles and the contributing factors as it aids in developing appropriate management strategies. By comprehending the impact MS has on muscles, individuals with the condition, their caregivers, and healthcare professionals can work together to minimize the effects and improve quality of life.
When it comes to diagnosing muscle involvement in multiple sclerosis (MS), it’s essential to pay attention to specific symptoms that may indicate muscle issues. Common symptoms include muscle weakness, stiffness, spasms, and difficulty with coordination and movement.
Doctors may perform various diagnostic tests to evaluate muscle involvement in MS. These may include electromyography (EMG) to assess electrical activity in muscles, nerve conduction studies to measure how well nerves send signals to muscles, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize muscle and nerve damage.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) affects the muscles due to damage to the nerves that control muscle movement. This disruption leads to muscle weakness, spasms, and difficulties with coordination, contributing to the management of muscle involvement in MS.
When it comes to managing muscle involvement in multiple sclerosis (MS), there are various medications and therapies available that can provide relief and support. Properly prescribed medications can help reduce muscle spasms, stiffness, and pain associated with MS. Some common medications used for managing muscle involvement in MS include:
In addition to medications and therapies, implementing certain lifestyle strategies can significantly contribute to managing muscle involvement in MS. Adopting the following practices may help improve muscle function and overall well-being:
By combining medications, therapies, and lifestyle strategies, individuals with MS can effectively manage muscle involvement and enhance their quality of life. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized approach that suits individual needs and goals. So, take charge of your muscle health and explore the various options available to manage muscle involvement in MS.
Researchers are investigating why multiple sclerosis affects muscle function. Understanding the mechanisms behind muscle impairment can lead to improved treatments and therapies. Future developments may provide insight into the underlying causes and help in developing targeted interventions for managing this aspect of the disease.
In the realm of multiple sclerosis (MS) research, innovative treatments hold a promise for improving the management of muscle-related symptoms. Scientists and medical professionals are continuously exploring new avenues to enhance the quality of life for individuals living with MS. One such approach is the use of stem cells, which have the potential to regenerate damaged muscles and nerve tissue. This groundbreaking therapy aims to repair the muscular system, potentially restoring strength and mobility in affected individuals. Stem cell therapy has shown promising results in preliminary studies, igniting hope for an effective treatment option in the future.
Numerous ongoing studies are furthering our understanding of why multiple sclerosis affects the muscles and paving the way for advanced treatment options. These investigations encompass both clinical trials and laboratory research, examining various aspects of MS-related muscle complications. For example, researchers are investigating how the immune system’s misguided attack on myelin influences muscle function and analyzing the mechanisms behind muscle weakness and fatigue. Additionally, studies are focusing on identifying specific genes that may contribute to muscle-related symptoms in MS, shedding light on the underlying molecular pathways involved.
The future holds great promise for individuals with MS, as ongoing research and developments continue to expand our knowledge and improve treatment options. Advanced imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are enabling researchers to observe structural and functional changes in the muscles with greater precision. This invaluable information helps pinpoint areas of muscle damage and better understand the progression and severity of MS-related muscle complications. Furthermore, advancements in genetic studies and gene therapies offer potential avenues for targeted interventions, addressing the specific genetic factors that contribute to muscle-related symptoms in MS.
In conclusion, future research and developments in the field of multiple sclerosis are continuously uncovering new insights into why the disease affects the muscles. These advancements provide hope for innovative treatments, such as stem cell therapy, which may help restore muscle function in those living with MS. Ongoing studies are further deepening our understanding of MS-related muscle complications, paving the way for targeted interventions and personalized treatment strategies. With every scientific breakthrough, the future becomes brighter for individuals grappling with the challenges imposed by muscle involvement in MS.

Credit: www.oprah.com

Credit: www.healthline.com
MS causes muscle spasticity due to damage to the nerves that control muscle movement. When these nerves are affected, they send incorrect signals to the muscles, causing them to become stiff and tight. This happens because MS attacks the protective covering of nerves, disrupting their ability to transmit signals properly.
Yes, multiple sclerosis (MS) can affect joints and muscles. The condition can lead to muscle weakness, stiffness, and spasms. It may also cause joint pain and difficulty with coordination and movement. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage these symptoms effectively.
Multiple sclerosis causes mobility problems by damaging the protective covering of nerve fibers. This disrupts communication between the brain and the body, leading to weakness, balance issues, and coordination difficulties. Inflammation plays a role as well, further impacting mobility. Treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Multiple sclerosis leads to nerve damage due to the immune system mistakenly attacking the protective coating (myelin) around nerve fibers in the central nervous system. This disrupts the transmission of signals and causes nerve damage, leading to various symptoms.
In sum, the impact of multiple sclerosis on muscles is profound. Understanding the mechanisms behind MS-related muscle dysfunction is crucial for treatment. By addressing the issue of muscle involvement in MS, we can enhance the quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Stay informed and stay empowered.

