Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Nutrition is autotrophic because organisms produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Autotrophic nutrition enables organisms to directly convert inorganic substances into energy-rich organic molecules.
In nature, different organisms have distinct ways of obtaining nutrition. While some depend on the consumption of other organisms (heterotrophs), autotrophs are capable of creating their own sustenance. Autotrophic organisms convert raw materials such as sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy-rich organic compounds through photosynthesis.
This process occurs in their chlorophyll-containing cells, where sunlight is harnessed to produce glucose, a type of sugar. On the other hand, certain bacteria and archaea employ chemosynthesis, using simple inorganic molecules such as hydrogen sulfide or ammonia as energy sources. The ability to generate their own food through autotrophic nutrition allows these organisms to thrive independently, making them integral to the overall balance of ecosystems.
When it comes to the study of nutrition, one of the key concepts to understand is autotrophy. Autotrophic nutrition, or the ability of an organism to create its own food, is fundamental for the sustenance of life. By harnessing energy from the environment, autotrophs are capable of producing the essential nutrients they need to survive.
Photosynthesis, a miraculous process that occurs in green plants, is vital for autotrophic nutrition. Through photosynthesis, these plants convert sunlight energy into chemical energy. This energy is then used to synthesize organic compounds like glucose, which serves as their food source. In this process, carbon dioxide and water are the raw materials, while oxygen is released as a byproduct. Without this efficient source of food production, autotrophs would struggle to meet their nutritional requirements.
Autotrophs possess two main variants: photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs. Photoautotrophs, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, rely on light as their energy source. These organisms carry out photosynthesis to convert light energy into chemical energy. On the other hand, chemoautotrophs derive energy from chemical reactions, allowing them to produce essential nutrients. Examples of chemoautotrophs include certain types of bacteria and archaea.
By better understanding the autotrophic nature of nutrition, we can appreciate the remarkable abilities of organisms to generate their own sustenance. Whether through photosynthesis or chemical reactions, autotrophs play a vital role in the global ecosystem, ensuring the production of nutrients that support life on Earth.
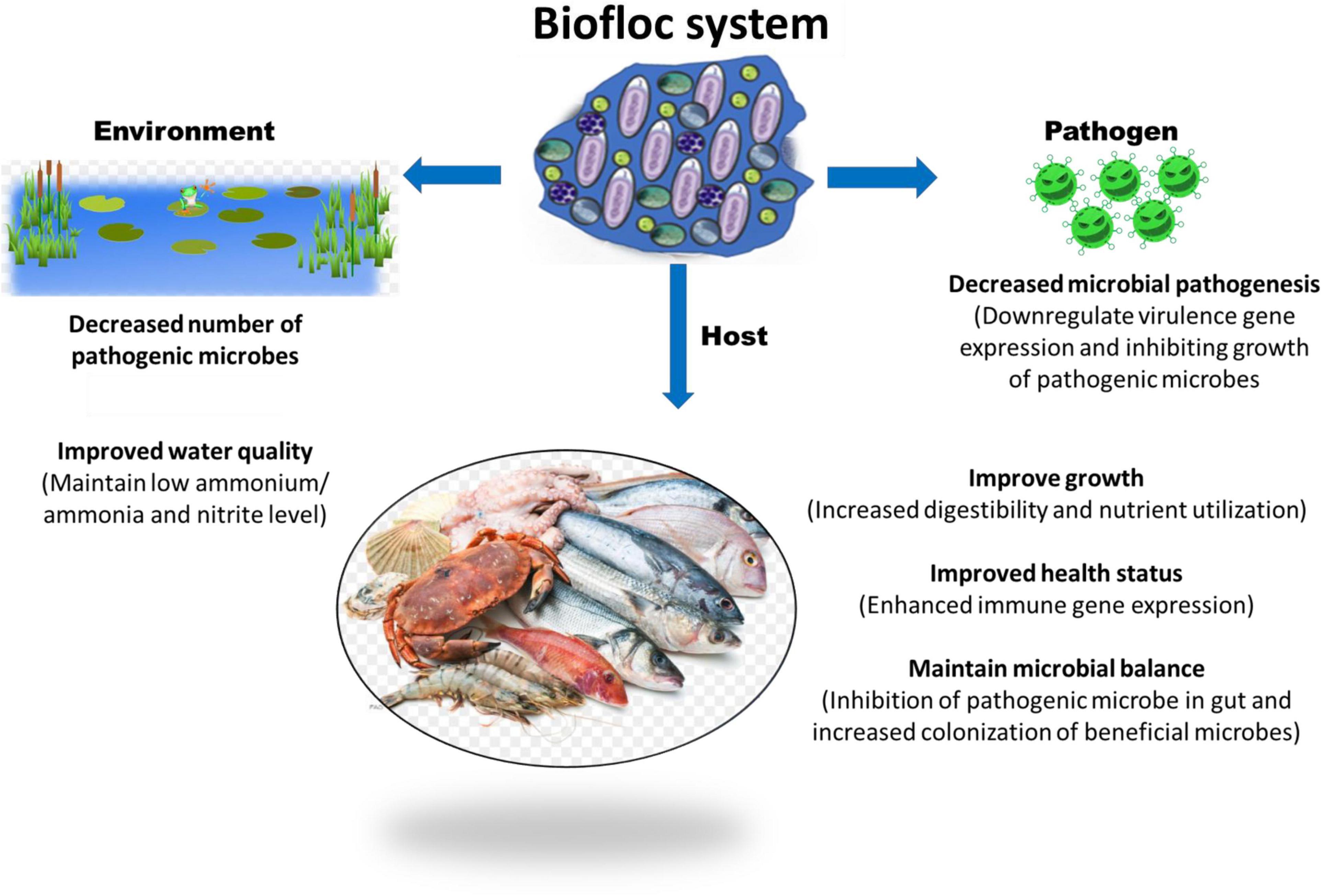
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
When it comes to living a fulfilling life, nothing is more important than maintaining optimal health. Our overall well-being and quality of life depend on our ability to nourish our bodies properly. Nutrition plays a crucial role in achieving and maintaining good health, and understanding why nutrition is autotrophic sheds light on the significance of providing our bodies with the right balance of nutrients.
Nutrition influences every aspect of our well-being, from physical vitality to mental clarity and emotional stability. The food we consume serves as fuel for our bodies, providing the essential building blocks and energy needed for growth, repair, and daily functions. Moreover, an inadequate diet can lead to a variety of health issues such as obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and weakened immune system, while a balanced diet can help prevent and manage these conditions.
Proper nutrition supports the proper functioning of our bodily systems and organs. It strengthens our immune system, enabling us to fight off diseases and infections more effectively. It also promotes healthy brain function, enhancing our cognitive abilities and improving our mood and mental well-being. Additionally, getting the right nutrients allows our bodies to maintain a healthy weight, energy levels, and hormonal balance.
Autotrophy, the ability of organisms to synthesize their own nutrients using simple inorganic substances, is crucial for maintaining optimal health. Autotrophs, such as plants and certain bacteria, harness the energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This process allows them to produce organic compounds, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which serve as nourishment for heterotrophs, including humans.
By consuming autotrophs or organisms that consume autotrophs, we obtain the necessary nutrients for our bodies to function optimally. A balanced diet, rich in plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes, ensures that we receive an array of essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. These nutrients support cell growth, repair, and regeneration, aid in digestion and absorption of food, and provide the necessary energy for daily activities.
Incorporating autotrophic nutrition into our diets is vital for maintaining good health. By prioritizing plant-based foods and reducing our reliance on processed and unhealthy options, we can nourish our bodies with the nutrients they need to thrive. Maintaining a diet rich in autotrophic nutrition not only supports our physical health but also contributes to mental clarity, emotional stability, and a greater sense of well-being.
Nutritional autotrophy in practice involves the consumption of foods that provide essential nutrients through the process of autotrophy. This method of nutrition is essential for sustaining life and maintaining a healthy body. By understanding the practical applications of autotrophic nutrition, individuals can make informed choices about their dietary habits and overall well-being.
An autotrophic diet primarily consists of foods that are derived directly from plants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains. These foods are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, providing numerous health benefits. Incorporating autotrophic foods into one’s diet can lead to improved digestion, increased energy levels, and overall well-being. Additionally, autotrophic diets contribute to weight management and may lower the risk of chronic diseases.
When incorporating autotrophic foods into one’s diet, individuals should prioritize a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This variety ensures a well-rounded intake of essential nutrients, promoting optimal health. Additionally, incorporating leafy greens, citrus fruits, and lean proteins from plants can enhance the nutritional value of meals, supporting overall wellness and vitality.
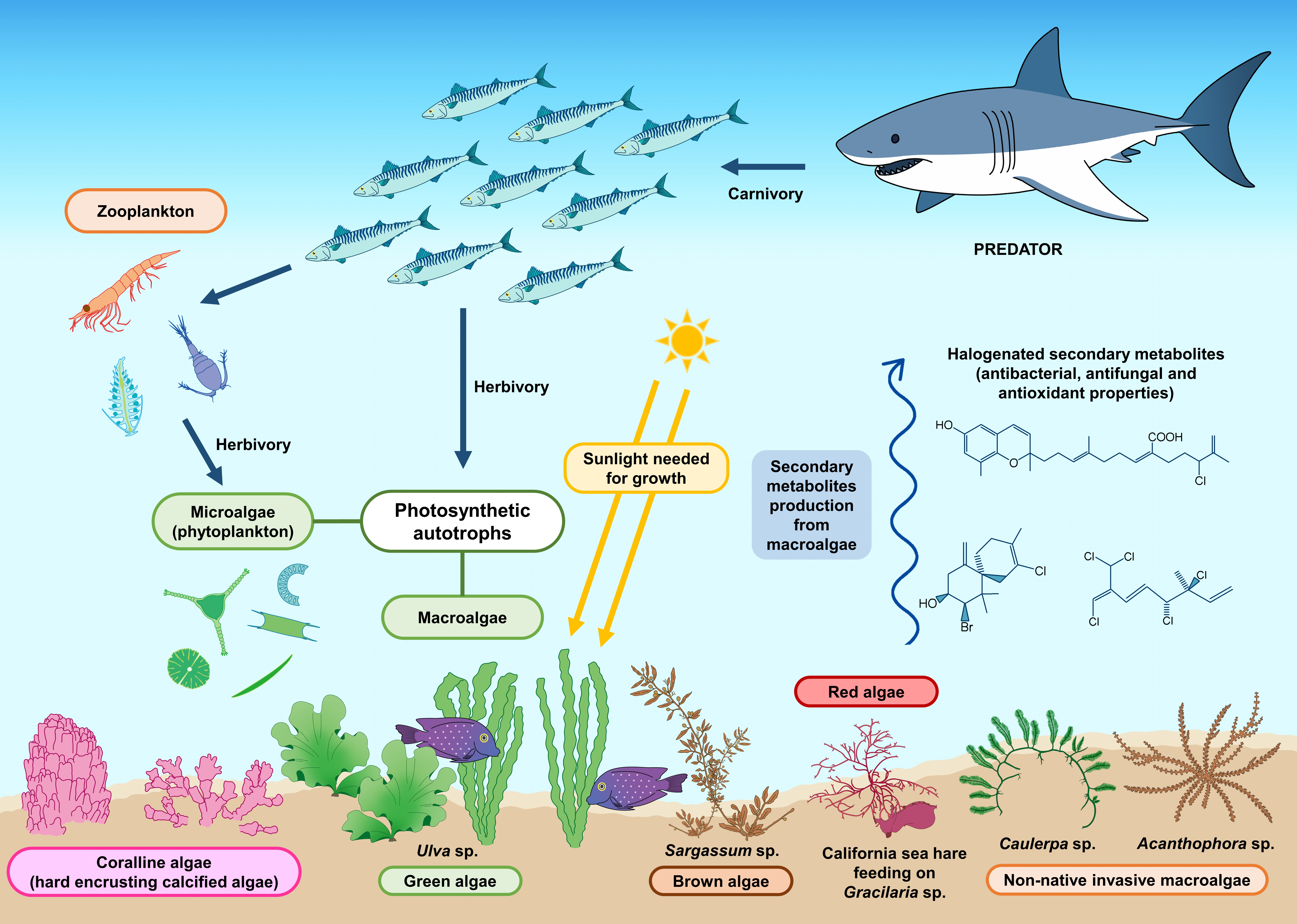
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Nutrition autotrophic presents challenges and misconceptions. Understanding why nutrition is autotrophic helps dispel myths and emphasizes the importance of plants in producing their food. This process plays a vital role in the ecosystem and serves as the foundation of the food chain.
Eating an autotrophic diet offers numerous benefits for our bodies and the environment. However, there are common misconceptions about autotrophic nutrition that need to be debunked in order to fully understand its importance. Additionally, there are certain challenges individuals may face when adopting an autotrophic diet, but rest assured that they can be overcome with the right approach and mindset.
There are several myths surrounding autotrophic nutrition that often lead people to dismiss its significance. Let’s take a closer look at these misconceptions:
Switching to an autotrophic diet can present its own unique set of challenges, but with the right strategies, they can be effectively overcome:
Evolving research and advancements in autotrophic nutrition have opened the doors to a promising future for this innovative field. As society becomes increasingly aware of the ecological impact of traditional farming methods and the benefits of consuming plant-based foods, the attention has now shifted towards autotrophic nutrition as a sustainable and efficient solution. In this article, we will explore the future potential of autotrophic nutrition, focusing on the advancements in autotrophic food products and the potential impacts on global health.
Autotrophic food products have already shown great promise in providing a wide range of nutritious and sustainable options. With ongoing advancements in technology and research, the production of autotrophic food is becoming more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. Here are some key areas of progress:
The future of autotrophic nutrition holds promising implications for global health and wellness. By embracing autotrophic food products, society can benefit in the following ways:
The future of autotrophic nutrition is bright, with advancements in autotrophic food products offering sustainable and nutritious alternatives to traditional sources. With potential impacts on global health and the environment, embracing autotrophic nutrition can pave the way for a more sustainable and thriving future.

Credit: microbiozindia.com
Autotrophs get nutrition through the process of photosynthesis. They use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
An example of autotrophic nutrition is photosynthesis, where plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Autotrophs are important because they produce their own food through photosynthesis. They form the base of the food chain, providing energy for all other organisms. This process also contributes to the production of oxygen, making it vital for the Earth’s ecosystem and balancing atmospheric gases.
Humans are not considered autotrophs. They are heterotrophs, which means they obtain energy from consuming other organisms. Autotrophs, like plants, can produce their own energy through photosynthesis.
Understanding the autotrophic nature of nutrition is crucial for maintaining overall health. By recognizing the importance of producing food through photosynthesis, we can appreciate the interconnectedness of all living organisms. This helps us make informed dietary choices that support sustainable living and well-being.
Embracing autotrophic nutrition is not only beneficial for individual health but also for the health of the planet.